6b How to ID an Unk organism
... The small “i” does not stand for anything; it just makes pronunciation easier. The IMViC tests were developed as a means of separating members of the Enterobacteriaceae, particularly the coliforms, to determine if drinking water is contaminated with sewage. A coliform is a gram negative, aerobic or ...
... The small “i” does not stand for anything; it just makes pronunciation easier. The IMViC tests were developed as a means of separating members of the Enterobacteriaceae, particularly the coliforms, to determine if drinking water is contaminated with sewage. A coliform is a gram negative, aerobic or ...
Studies Into the Allosteric Regulation of ADP
... Espada, at the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina.6 The enzyme requires a divalent metal ion, such as Mg2+ or Mn2+. Although the enzyme catalyzes both the forward (ADPGlc synthesis) and reverse reactions (ATP and Glc1P formation) with relative equilibrium values close to 1, the reaction is essent ...
... Espada, at the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina.6 The enzyme requires a divalent metal ion, such as Mg2+ or Mn2+. Although the enzyme catalyzes both the forward (ADPGlc synthesis) and reverse reactions (ATP and Glc1P formation) with relative equilibrium values close to 1, the reaction is essent ...
Growth independent rhamnolipid production from glucose using the
... rhamnose moiety requires b-oxidation and gluconeogenic reactions. Notably, in simulations with low growth rates and maintenance metabolism, rhamnolipid yield on glycerol equaled yields on sugars; with higher growth rate and maintenance metabolism, the yield on glycerol equaled the yield on octanoate ...
... rhamnose moiety requires b-oxidation and gluconeogenic reactions. Notably, in simulations with low growth rates and maintenance metabolism, rhamnolipid yield on glycerol equaled yields on sugars; with higher growth rate and maintenance metabolism, the yield on glycerol equaled the yield on octanoate ...
Metabolic flux profiling of recombinant protein secreting Pichia
... phenomenon might be related to higher energy demand caused by Rol secretion, resulting in higher maintenance-energy requirements. Since Rol amounts were very small relative to the total cell protein, one is tempted to speculate that such metabolic burden was mainly associated to the secretion stress ...
... phenomenon might be related to higher energy demand caused by Rol secretion, resulting in higher maintenance-energy requirements. Since Rol amounts were very small relative to the total cell protein, one is tempted to speculate that such metabolic burden was mainly associated to the secretion stress ...
brv12140 - Cambridge Repository
... important to maintain carbon homoeostasis, to provide precursors for nucleotide and amino acid biosynthesis, to provide reducing molecules for anabolism, and to defeat oxidative stress. The PPP shares reactions with the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and Calvin cycle and divides into an oxidative and non- ...
... important to maintain carbon homoeostasis, to provide precursors for nucleotide and amino acid biosynthesis, to provide reducing molecules for anabolism, and to defeat oxidative stress. The PPP shares reactions with the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and Calvin cycle and divides into an oxidative and non- ...
General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis and Maud
... in amino acid sequence yet catalyze the same reaction. Usually, these enzymes display different kinetic parameters, such as K M, or different regulatory properties. They are encoded by different genetic loci, which usually arise through gene duplication and divergence. ...
... in amino acid sequence yet catalyze the same reaction. Usually, these enzymes display different kinetic parameters, such as K M, or different regulatory properties. They are encoded by different genetic loci, which usually arise through gene duplication and divergence. ...
Book Review - Journal of Experimental Biology
... precise. The text is complemented by schematic artwork and a number of text boxes summarizing important facts and examples. References are limited but present a well-selected and up-to-date set for additional reading. This book is unique among publications that are relevant to metabolism, primarily ...
... precise. The text is complemented by schematic artwork and a number of text boxes summarizing important facts and examples. References are limited but present a well-selected and up-to-date set for additional reading. This book is unique among publications that are relevant to metabolism, primarily ...
Glucose-6-Phosphate Fluorometric Assay Kit
... On entry into cells, glucose is converted by hexokinase (or glucokinase) into glucose-6-phosphate (G6P, D-glucose-6-phosphate, Robison ester). G6P has three principal intracellular fates.1 It can: 1) enter glycolysis via phosphoglucose isomerase to provide cellular energy or carbon skeletons for bio ...
... On entry into cells, glucose is converted by hexokinase (or glucokinase) into glucose-6-phosphate (G6P, D-glucose-6-phosphate, Robison ester). G6P has three principal intracellular fates.1 It can: 1) enter glycolysis via phosphoglucose isomerase to provide cellular energy or carbon skeletons for bio ...
The acetyl-CoA pathway of autotrophic growth
... The most direct conceivable route for synthesis of multicarbon compounds from CO: is to join two molecules of CO 2 together to make a 2-carbon compound and then polymerize the 2-carbon compound or add CO 2 successively to the 2-carbon compound to make multicarbon compounds. Recently, it has been dem ...
... The most direct conceivable route for synthesis of multicarbon compounds from CO: is to join two molecules of CO 2 together to make a 2-carbon compound and then polymerize the 2-carbon compound or add CO 2 successively to the 2-carbon compound to make multicarbon compounds. Recently, it has been dem ...
Beneficial effects of L-arginine on reducing obesity
... generate heat (Cannon and Nedergaard 2004). Of particular interest, BAT produces 150–300 times more heat per kg tissue than non-BAT organs (Power 1989). Excitingly, new evidence shows that functional BAT exists in adult humans (Cypess et al. 2009; Virtanen et al. 2009). In addition, BAT activity is ...
... generate heat (Cannon and Nedergaard 2004). Of particular interest, BAT produces 150–300 times more heat per kg tissue than non-BAT organs (Power 1989). Excitingly, new evidence shows that functional BAT exists in adult humans (Cypess et al. 2009; Virtanen et al. 2009). In addition, BAT activity is ...
uncorrected page proofs
... bound together by high-energy chemical bonds (see figure 5.1). The energy that powers the mechanisms involved in muscular contraction is obtained from the catabolism (breaking down) of ATP. However, the body stores only a very small quantity of this ‘energy currency’ within the cells, enough to powe ...
... bound together by high-energy chemical bonds (see figure 5.1). The energy that powers the mechanisms involved in muscular contraction is obtained from the catabolism (breaking down) of ATP. However, the body stores only a very small quantity of this ‘energy currency’ within the cells, enough to powe ...
Energy systems and interplay of energy systems
... bound together by high-energy chemical bonds (see figure 5.1). The energy that powers the mechanisms involved in muscular contraction is obtained from the catabolism (breaking down) of ATP. However, the body stores only a very small quantity of this ‘energy currency’ within the cells, enough to powe ...
... bound together by high-energy chemical bonds (see figure 5.1). The energy that powers the mechanisms involved in muscular contraction is obtained from the catabolism (breaking down) of ATP. However, the body stores only a very small quantity of this ‘energy currency’ within the cells, enough to powe ...
Role of NAD+-Dependent Malate Dehydrogenase in the Metabolism
... the Alpha and Gamma classes of Proteobacteria and the phylum Verrucomicrobia [1,2]. Since these bacteria are able to obtain energy from the oxidation of reduced C1 compounds, the TCA cycle would not be an obligatory way for energy generation. The complete oxidative TCA cycle could function in the al ...
... the Alpha and Gamma classes of Proteobacteria and the phylum Verrucomicrobia [1,2]. Since these bacteria are able to obtain energy from the oxidation of reduced C1 compounds, the TCA cycle would not be an obligatory way for energy generation. The complete oxidative TCA cycle could function in the al ...
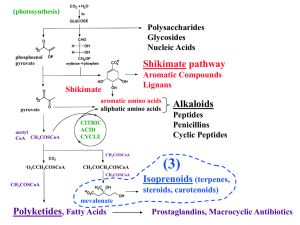
Biosynthesis of Isoprenoids
... In contrast, rubber has an all-cis configuration because its synthesis is controlled by another type of prenyl transferase enzyme. ...
... In contrast, rubber has an all-cis configuration because its synthesis is controlled by another type of prenyl transferase enzyme. ...
Potato Bubbles: Intro to Enzymes Laboratory
... An enzyme has to fit together perfectly with its substrate. So if an enzyme loses its shape it won’t work anymore. Some things that can make an enzyme lose its shape are changes in temperature or pH. When an enzyme loses its shape we say that it has denatured. ...
... An enzyme has to fit together perfectly with its substrate. So if an enzyme loses its shape it won’t work anymore. Some things that can make an enzyme lose its shape are changes in temperature or pH. When an enzyme loses its shape we say that it has denatured. ...
fulltext
... This review article presents a survey of selected principal biosynthetic pathways that lead to the most important monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, sugar alcohols, and cyclitols in foods and in food raw materials and informs nonspecialist readers about new scientific advances as reported in recentl ...
... This review article presents a survey of selected principal biosynthetic pathways that lead to the most important monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, sugar alcohols, and cyclitols in foods and in food raw materials and informs nonspecialist readers about new scientific advances as reported in recentl ...
Enzyme Activities Support the Use of Liver Lipid–Derived Ketone
... isolated from red muscle of I. oxyrinchus (Ballantyne et al. 1992). Palmitoyl carnitine was not oxidized, indicating that fatty acids were probably not used for fuel in the red muscle of this species. No other studies that we know of have measured mitochondrial enzyme activities or examined other as ...
... isolated from red muscle of I. oxyrinchus (Ballantyne et al. 1992). Palmitoyl carnitine was not oxidized, indicating that fatty acids were probably not used for fuel in the red muscle of this species. No other studies that we know of have measured mitochondrial enzyme activities or examined other as ...
A multi-tissue type genome-scale metabolic network for analysis of
... gluconeogenesis, glycogen storage, urea production and ketogenesis. Though the liver consists of many different cell types, the major cell type pertaining to metabolism is the hepatocyte. Skeletal muscle, one of the most abundant tissues in the human body, has high metabolic requirements, and plays ...
... gluconeogenesis, glycogen storage, urea production and ketogenesis. Though the liver consists of many different cell types, the major cell type pertaining to metabolism is the hepatocyte. Skeletal muscle, one of the most abundant tissues in the human body, has high metabolic requirements, and plays ...
Tn917 insertion site in the 2C4 mutant
... mobility by the faecium toxin can be duplicated with purified H2O2. 5. Glycerol stimulataes faecium killing while Glucose inhibits faecium killing. 6. Changes in Oxygen levels leads to faecium toxin production 7. Addition of Catalase completely rescues faecium toxicity ...
... mobility by the faecium toxin can be duplicated with purified H2O2. 5. Glycerol stimulataes faecium killing while Glucose inhibits faecium killing. 6. Changes in Oxygen levels leads to faecium toxin production 7. Addition of Catalase completely rescues faecium toxicity ...
Comparison of cell-wall teichoic acid with high-molecular
... of concentrated HC1 was added. To extract free fatty acids, petroleum ether was added and the top layer was removed; this process was repeated three times and these layers were mixed together and concentrated to 0-2ml. Methylation was done by adding 0-1ml of BF, (Sigma) in methanol 14YOw/v to the co ...
... of concentrated HC1 was added. To extract free fatty acids, petroleum ether was added and the top layer was removed; this process was repeated three times and these layers were mixed together and concentrated to 0-2ml. Methylation was done by adding 0-1ml of BF, (Sigma) in methanol 14YOw/v to the co ...
Decreased expression of plastidial adenylate kinase in potato tubers
... plastidial adenylate kinase, catalysing the interconversion of ATP and AMP to ADP, leads to increased adenylate pools and starch content in transgenic potato tubers. However, the underlying mechanisms were not elucidated. Here, it is shown that decreased expression of plastidial adenylate kinase in ...
... plastidial adenylate kinase, catalysing the interconversion of ATP and AMP to ADP, leads to increased adenylate pools and starch content in transgenic potato tubers. However, the underlying mechanisms were not elucidated. Here, it is shown that decreased expression of plastidial adenylate kinase in ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑