Learning objectives
... 24. Explain how osmotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure regulate the exchange of fluid and solutes across capillary walls. 25. Describe the composition of lymph and explain how the lymphatic system helps the normal functioning of the circulatory system. Explain the role of lymph nodes in body def ...
... 24. Explain how osmotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure regulate the exchange of fluid and solutes across capillary walls. 25. Describe the composition of lymph and explain how the lymphatic system helps the normal functioning of the circulatory system. Explain the role of lymph nodes in body def ...
Discussion Questions
... 24. Explain how osmotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure regulate the exchange of fluid and solutes across capillary walls. 25. Describe the composition of lymph and explain how the lymphatic system helps the normal functioning of the circulatory system. Explain the role of lymph nodes in body def ...
... 24. Explain how osmotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure regulate the exchange of fluid and solutes across capillary walls. 25. Describe the composition of lymph and explain how the lymphatic system helps the normal functioning of the circulatory system. Explain the role of lymph nodes in body def ...
29–2 Form and Function in Invertebrates To survive
... oxygen and nutrients, and cells must also remove metabolic wastes. The smallest and thinnest animals meet this requirement by simple diffusion between their body surface and the environment. But this system is usually insufficient for more complex animals. Most complex animals move blood through the ...
... oxygen and nutrients, and cells must also remove metabolic wastes. The smallest and thinnest animals meet this requirement by simple diffusion between their body surface and the environment. But this system is usually insufficient for more complex animals. Most complex animals move blood through the ...
Science TAKS Students
... 2. Compare mechanical digestion to chemical digestion, and where most of each occurs. 3. Explain enzymes and give an example. 4. Discuss the importance of the liver and pancreas in digestion. List the substances they produce and explain their function. 5. Describe the function of villi and explain h ...
... 2. Compare mechanical digestion to chemical digestion, and where most of each occurs. 3. Explain enzymes and give an example. 4. Discuss the importance of the liver and pancreas in digestion. List the substances they produce and explain their function. 5. Describe the function of villi and explain h ...
B7 quiz questions - Fakenham Academy Norfolk
... 5. Name two effectors involved in temperature regulation. 6. Describe what happens to the body at high temperatures. 7. During exercise the body produces more sweat. What negative effect can this have on the body? 8. Describe what happens to the body at low temperatures. 9. Explain with examples tha ...
... 5. Name two effectors involved in temperature regulation. 6. Describe what happens to the body at high temperatures. 7. During exercise the body produces more sweat. What negative effect can this have on the body? 8. Describe what happens to the body at low temperatures. 9. Explain with examples tha ...
What Is an Amphibian? - Nashua School District
... Amphibians in Danger Worldwide, amphibian populations are decreasing. One reason for the decrease is the destruction of amphibian habitats. An animal’s habitat is the specific environment in which it lives. When a swamp is filled in or a forest is cut, an area that was moist becomes drier. Few amphi ...
... Amphibians in Danger Worldwide, amphibian populations are decreasing. One reason for the decrease is the destruction of amphibian habitats. An animal’s habitat is the specific environment in which it lives. When a swamp is filled in or a forest is cut, an area that was moist becomes drier. Few amphi ...
Humans and animals - Beck-Shop
... You know what the outside of your body looks like. But what’s inside your body? Think of as many inside parts as you can. The parts inside your body are called organs . The body organs do different jobs to keep you alive and healthy. Different organs work together to form organ systems . ...
... You know what the outside of your body looks like. But what’s inside your body? Think of as many inside parts as you can. The parts inside your body are called organs . The body organs do different jobs to keep you alive and healthy. Different organs work together to form organ systems . ...
Organs
... function is to break down food into the nutrients needed to be absorbed into the blood? ...
... function is to break down food into the nutrients needed to be absorbed into the blood? ...
Energy Systems Live Show
... Anaerobic Respiration is how sprinters produce the energy that is used in short periods of ‘all out effort’ - high intensity. Oxygen cannot reach the muscles fast enough, so anaerobic respiration is used. Glucose Produces… ...
... Anaerobic Respiration is how sprinters produce the energy that is used in short periods of ‘all out effort’ - high intensity. Oxygen cannot reach the muscles fast enough, so anaerobic respiration is used. Glucose Produces… ...
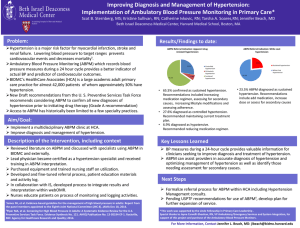
Implementation of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Primary
... • 6.9% diagnosed as hypotensive. Recommended reducing medication regimen. ...
... • 6.9% diagnosed as hypotensive. Recommended reducing medication regimen. ...
YEAR 11 IGCSE BIOLOGY REVISION GUIDE DBGS 1 Cells and
... 9 A student set up a potometer in the laboratory and measured the rate of movement of water in the capillary. An average of four readings gave a rate of 50mm per minute. The apparatus was then taken outside, where there was a light breeze. Four more readings were taken without delay. The average of ...
... 9 A student set up a potometer in the laboratory and measured the rate of movement of water in the capillary. An average of four readings gave a rate of 50mm per minute. The apparatus was then taken outside, where there was a light breeze. Four more readings were taken without delay. The average of ...
Second Semester Final Exam Study guide
... 10. Dendrites 21. Antigens 11. Axon 22. Vaccination B. How does a disruption of homeostasis lead to diabetes? C. What are stem cells? What is their importance to medical research? D. Know the levels of cellular organization within the body. E. Know the different types of tissue within the body. F. K ...
... 10. Dendrites 21. Antigens 11. Axon 22. Vaccination B. How does a disruption of homeostasis lead to diabetes? C. What are stem cells? What is their importance to medical research? D. Know the levels of cellular organization within the body. E. Know the different types of tissue within the body. F. K ...
Physio Lecture 5 Erythropoiesis
... When a RBC is old, it gets trapped in the reticular fibers of the spleen or liver, where a macrophage detects it and engulfs it. Within the macrophage, the globin chains, porphyrrin ring, and iron are detached from each other and liberated. What happens to each of these segments? The Iron is release ...
... When a RBC is old, it gets trapped in the reticular fibers of the spleen or liver, where a macrophage detects it and engulfs it. Within the macrophage, the globin chains, porphyrrin ring, and iron are detached from each other and liberated. What happens to each of these segments? The Iron is release ...
Endocrine System - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... but potentially disastrous), then besides the arousal of the sympathetic—adrenal-medullary system, the pituitary—adrenal—cortical arousal system is activated. The hypothalamus signals the pituitary by secreting a hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), into the portal system. Then CRH stimul ...
... but potentially disastrous), then besides the arousal of the sympathetic—adrenal-medullary system, the pituitary—adrenal—cortical arousal system is activated. The hypothalamus signals the pituitary by secreting a hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), into the portal system. Then CRH stimul ...
Frog Dissection Lab - Mr Dolan`s Science Page
... Frogs are amphibians, living both on land and in water. Their anatomy is very unique. Their bodies are similar to humans in that they have skin, bones, muscles, and organs. The body of a frog can be divided into a head, a short neck, and a trunk. The head contains the brain, mouth, eyes, ears and no ...
... Frogs are amphibians, living both on land and in water. Their anatomy is very unique. Their bodies are similar to humans in that they have skin, bones, muscles, and organs. The body of a frog can be divided into a head, a short neck, and a trunk. The head contains the brain, mouth, eyes, ears and no ...
rat dissection
... pancreatic duct). The pancreas also secretes insulin which is important in the regulation of glucose metabolism. The greater omentum is the membranous curtain of tissue that hangs from the stomach and contains lymph nodes, blood vessels, and fat. Find the pancreas by looking for a thin, almost membr ...
... pancreatic duct). The pancreas also secretes insulin which is important in the regulation of glucose metabolism. The greater omentum is the membranous curtain of tissue that hangs from the stomach and contains lymph nodes, blood vessels, and fat. Find the pancreas by looking for a thin, almost membr ...
Chapter 40 – Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function
... For instance, a parasitic tapeworm may be several meters long, but because it is very thin, most of its cells are bathed in the intestinal fluid of the worm’s vertebrate host from which it obtains nutrients. ...
... For instance, a parasitic tapeworm may be several meters long, but because it is very thin, most of its cells are bathed in the intestinal fluid of the worm’s vertebrate host from which it obtains nutrients. ...
breathing and exchange of gases
... intercostals and diaphragm. Volumes of air involved in these activities can be estimated with the help of spirometer and are of clinical significance. Exchange of O2 and CO2 at the alveoli and tissues occur by diffusion. Rate of diffusion is dependent on the partial pressure gradients of O2 (pO2) an ...
... intercostals and diaphragm. Volumes of air involved in these activities can be estimated with the help of spirometer and are of clinical significance. Exchange of O2 and CO2 at the alveoli and tissues occur by diffusion. Rate of diffusion is dependent on the partial pressure gradients of O2 (pO2) an ...
Frog dissection - Canyons District Biology Resources
... In the following laboratory exercise, you will examine in some detail the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig (Sus scrofa). As the pig is a mammal, many aspects of its structural and functional organization are identical with those of other mammals, including humans. Thus, a study of the fe ...
... In the following laboratory exercise, you will examine in some detail the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig (Sus scrofa). As the pig is a mammal, many aspects of its structural and functional organization are identical with those of other mammals, including humans. Thus, a study of the fe ...
the test - One Day Enrichment
... D. dehydration from lack of water intake E. frostbite on exposure to cold ...
... D. dehydration from lack of water intake E. frostbite on exposure to cold ...
הצעה למבנה הקוריקולום לקורסים הקדם
... biosynthesis and secretion by the ovary. Identify the cells responsible for their biosynthesis, the mechanism of their transport in the blood, and how they are degraded and removed from the body. 2) List the major target organs and cell types for estrogen action and describe its effects on each. 3) ...
... biosynthesis and secretion by the ovary. Identify the cells responsible for their biosynthesis, the mechanism of their transport in the blood, and how they are degraded and removed from the body. 2) List the major target organs and cell types for estrogen action and describe its effects on each. 3) ...
Introduction to the Amphibian Body
... Amphibian Partially Divided Heart • The top chambers of the amphibian heart are divided into left and right sides by the wall called the septum • The heart’s bottom chamber is not divided – This allows a mixture of oxygen-rich and oxygenpoor blood to be delivered to the amphibian’s tissues ...
... Amphibian Partially Divided Heart • The top chambers of the amphibian heart are divided into left and right sides by the wall called the septum • The heart’s bottom chamber is not divided – This allows a mixture of oxygen-rich and oxygenpoor blood to be delivered to the amphibian’s tissues ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.