Carbon dioxide transport - e-safe
... which is made available when oxygen is released; therefore, free hydrogen ions are removed from solution. Reduced haemoglobin is less acidic than oxygenated haemoglobin. This is another way of stating the Haldane effect, which explains that, at any given PCO2, the carbon dioxide content of deoxygena ...
... which is made available when oxygen is released; therefore, free hydrogen ions are removed from solution. Reduced haemoglobin is less acidic than oxygenated haemoglobin. This is another way of stating the Haldane effect, which explains that, at any given PCO2, the carbon dioxide content of deoxygena ...
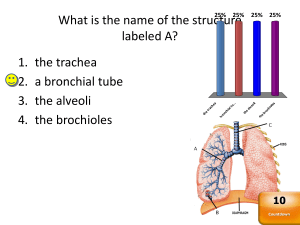
What is the name of the structure labeled A? 1. the trachea 2. a
... 1. It cleans blood that moves through the circulatory system. 2. It makes blood that is pumped by the circulatory system. 3. It allows gas exchange between the air and blood. 4. It helps to move the blood from the lungs to heart. ...
... 1. It cleans blood that moves through the circulatory system. 2. It makes blood that is pumped by the circulatory system. 3. It allows gas exchange between the air and blood. 4. It helps to move the blood from the lungs to heart. ...
respiratory compensation - King Edward Medical University
... 1. Note whether the pH is low (acidosis) or high (alkalosis) 2. Decide which value, pCO2 or HCO3- , is outside the normal range and could be the cause of the problem. If the cause is a change in pCO2, the problem is respiratory. If the cause is HCO3- the problem ...
... 1. Note whether the pH is low (acidosis) or high (alkalosis) 2. Decide which value, pCO2 or HCO3- , is outside the normal range and could be the cause of the problem. If the cause is a change in pCO2, the problem is respiratory. If the cause is HCO3- the problem ...
Your Heart Anatomy And Procedures
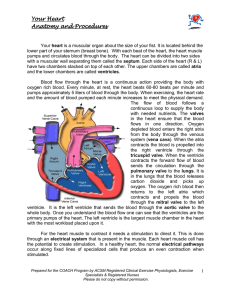
... oxygen rich blood to the heart muscle. There are two main coronary arteries the left and the right. The left artery divides into two arteries the anterior descending branch, which supplies blood to most of the left side of the heart and also the septum. The other branch is called the circumflex and ...
... oxygen rich blood to the heart muscle. There are two main coronary arteries the left and the right. The left artery divides into two arteries the anterior descending branch, which supplies blood to most of the left side of the heart and also the septum. The other branch is called the circumflex and ...
Key Terms
... Preface With each breath, we take in oxygen that feeds our cells and fuels the production of energy. Water nourishes our tissues and helps regulate the level of chemicals in the body. The carbohydrates, proteins and fats that we ingest in food supply energy, as well as building materials the body us ...
... Preface With each breath, we take in oxygen that feeds our cells and fuels the production of energy. Water nourishes our tissues and helps regulate the level of chemicals in the body. The carbohydrates, proteins and fats that we ingest in food supply energy, as well as building materials the body us ...
1430748233.
... The hard exoskeleton of insects is unsuitable for gas exchange but their internal gas exchange surfaces differ significantly from those of mammals. The most significant difference is the lack of a transport system. Gases diffuse passively through the spiracles, trachea and tracheoles directly to the ...
... The hard exoskeleton of insects is unsuitable for gas exchange but their internal gas exchange surfaces differ significantly from those of mammals. The most significant difference is the lack of a transport system. Gases diffuse passively through the spiracles, trachea and tracheoles directly to the ...
File
... • Provide a layer of protection from abrasion and excessive water loss • Aid in the absorption and transportation of filtered substances ...
... • Provide a layer of protection from abrasion and excessive water loss • Aid in the absorption and transportation of filtered substances ...
sodium phenylacetate/sodium benzoate
... therapy. Caloric intake of ⬎80 cal/kg/day should be attempted. Non-protein calories should be supplied as glucose (8– 10 mg/kg/min) with Intralipid added. ● Once elevated ammonia levels have been reduced to normal range, oral therapy, such as sodium phenylbutyrate, dietary management and protein res ...
... therapy. Caloric intake of ⬎80 cal/kg/day should be attempted. Non-protein calories should be supplied as glucose (8– 10 mg/kg/min) with Intralipid added. ● Once elevated ammonia levels have been reduced to normal range, oral therapy, such as sodium phenylbutyrate, dietary management and protein res ...
APBiology 12
... o As the animal acclimatizes, changes in kidney function result in excretion of more alkaline urine, returning blood pH to its normal range. o Other changes during acclimatization include increased production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen. ...
... o As the animal acclimatizes, changes in kidney function result in excretion of more alkaline urine, returning blood pH to its normal range. o Other changes during acclimatization include increased production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen. ...
Carbon dioxide transport
... which is made available when oxygen is released; therefore, free hydrogen ions are removed from solution. Reduced haemoglobin is less acidic than oxygenated haemoglobin. This is another way of stating the Haldane effect, which explains that, at any given PCO2, the carbon dioxide content of deoxygena ...
... which is made available when oxygen is released; therefore, free hydrogen ions are removed from solution. Reduced haemoglobin is less acidic than oxygenated haemoglobin. This is another way of stating the Haldane effect, which explains that, at any given PCO2, the carbon dioxide content of deoxygena ...
Paediatric shock
... in physiological equilibrium with each other. A diagnosis of dehydration, by comparison, usually implies a more gradual, prolonged loss of fluid which comes from all fluid compartments. It is frequently associated with electrolyte disturbance, which is unusual in the early stages of shock – at least ...
... in physiological equilibrium with each other. A diagnosis of dehydration, by comparison, usually implies a more gradual, prolonged loss of fluid which comes from all fluid compartments. It is frequently associated with electrolyte disturbance, which is unusual in the early stages of shock – at least ...
growth hormone releasing hormone
... Neurotransmitters and other molecules affecting neurosecretory activity of the hypothalamus (toxins, inflammatory agents) are found also in the circulation. Hypothalamus is protected from these influences by blood brain barrier (BBB). BBB is a complex mechanism regulating exchange of mediators betwe ...
... Neurotransmitters and other molecules affecting neurosecretory activity of the hypothalamus (toxins, inflammatory agents) are found also in the circulation. Hypothalamus is protected from these influences by blood brain barrier (BBB). BBB is a complex mechanism regulating exchange of mediators betwe ...
11Physiology of human body systems
... containing altogether about 20 000 genes. As it divides again and again, a ball of cells forms. These cells pass over a special area, within the developing embryo, and certain genes get switched on or off. As a result the cells become different from each other. They are each specialised to carry out ...
... containing altogether about 20 000 genes. As it divides again and again, a ball of cells forms. These cells pass over a special area, within the developing embryo, and certain genes get switched on or off. As a result the cells become different from each other. They are each specialised to carry out ...
Lecture 8 Microcirculation
... 1. Learn the basis of fluid movement through capillary walls. 2. Learn the different types of capillaries with the tissue types they are found in. 3. Learn the factors directly effect bulk fluid flow. 4. Learn the Starling hypothesis for bulk fluid flow through the tissues. 5. Learn the basic functi ...
... 1. Learn the basis of fluid movement through capillary walls. 2. Learn the different types of capillaries with the tissue types they are found in. 3. Learn the factors directly effect bulk fluid flow. 4. Learn the Starling hypothesis for bulk fluid flow through the tissues. 5. Learn the basic functi ...
body_system_relationships_chart
... Respiratory System- Provides oxygen and removes carbon dioxide ...
... Respiratory System- Provides oxygen and removes carbon dioxide ...
Mini Med School
... giving off gases such as methane and hydrogen sulfide as natural by-products of their activities). This is the cause of the discomfort and flatulence associated with eating beans, cabbage, and other gaspromoting foods. Fortunately for gas sufferers, the enzymes that enable our microbes to break down ...
... giving off gases such as methane and hydrogen sulfide as natural by-products of their activities). This is the cause of the discomfort and flatulence associated with eating beans, cabbage, and other gaspromoting foods. Fortunately for gas sufferers, the enzymes that enable our microbes to break down ...
B3 Text book - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... of a red blood cell. These vessels are called capillaries. As they leave the organs, the capillaries join together again and again to form wider vessels called veins. By the time they reach the heart all the veins have joined up to form only two large blood vessels. Diagram A shows a generalised pla ...
... of a red blood cell. These vessels are called capillaries. As they leave the organs, the capillaries join together again and again to form wider vessels called veins. By the time they reach the heart all the veins have joined up to form only two large blood vessels. Diagram A shows a generalised pla ...
edema
... • Fluid collections in different body cavities are variously designated hydrothorax, hydropericardium, or hydroperitoneum (the last is more commonly called ascites). Anasarca is a severe and generalized edema with profound subcutaneous tissue swelling. ...
... • Fluid collections in different body cavities are variously designated hydrothorax, hydropericardium, or hydroperitoneum (the last is more commonly called ascites). Anasarca is a severe and generalized edema with profound subcutaneous tissue swelling. ...
Edema
... • Fluid collections in different body cavities are variously designated hydrothorax, hydropericardium, or hydroperitoneum (the last is more commonly called ascites). Anasarca is a severe and generalized edema with profound subcutaneous tissue swelling. ...
... • Fluid collections in different body cavities are variously designated hydrothorax, hydropericardium, or hydroperitoneum (the last is more commonly called ascites). Anasarca is a severe and generalized edema with profound subcutaneous tissue swelling. ...
valves
... • In humans, the main breathing control centers are in two regions of the brain, the medulla oblongata and the pons • The medulla regulates the rate and depth of breathing in response to pH changes (as indicator of blood CO2 conc. The main determenant of pH in the CSF) in the cerebrospinal fluid (th ...
... • In humans, the main breathing control centers are in two regions of the brain, the medulla oblongata and the pons • The medulla regulates the rate and depth of breathing in response to pH changes (as indicator of blood CO2 conc. The main determenant of pH in the CSF) in the cerebrospinal fluid (th ...
7th Grade Practice iLEAP Questions
... The human body is very complex. Below is information about how parts of the human body function to keep a person alive. Read the information and study the diagrams. Then answer questions 1 through 5. Materials Exchange from Blood The blood has the job of moving materials such as food molecules, vita ...
... The human body is very complex. Below is information about how parts of the human body function to keep a person alive. Read the information and study the diagrams. Then answer questions 1 through 5. Materials Exchange from Blood The blood has the job of moving materials such as food molecules, vita ...
Patient Assessment
... •Periodically take a refresher course in Wilderness First Aid •Emphasis should always be on PREVENTION ...
... •Periodically take a refresher course in Wilderness First Aid •Emphasis should always be on PREVENTION ...
Ch 22 The Respiratory System
... The chloride shift – to counterbalance the outrush of negative bicarbonate ions from the RBCs, chloride ions (Cl–) move from the plasma into the erythrocytes ...
... The chloride shift – to counterbalance the outrush of negative bicarbonate ions from the RBCs, chloride ions (Cl–) move from the plasma into the erythrocytes ...
Study Guide
... systems Explain the gastrovascular cavity ‘s role in distribution of substances throughout the body Explain an open circulatory system and how substances are distributed throughout the body Explain a closed circulatory system and why they are more advanced than other systems Be able to discuss the d ...
... systems Explain the gastrovascular cavity ‘s role in distribution of substances throughout the body Explain an open circulatory system and how substances are distributed throughout the body Explain a closed circulatory system and why they are more advanced than other systems Be able to discuss the d ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.