Study Guide for Exam - Centerville Public Schools
... Herpes (simplex type 2 virus: An STD in which a virus causes blisterlike sores, called genital herpes in the genital area) (simplex type I virus usually referred to as a cold sore) Either can occur on the mouth or genitals ...
... Herpes (simplex type 2 virus: An STD in which a virus causes blisterlike sores, called genital herpes in the genital area) (simplex type I virus usually referred to as a cold sore) Either can occur on the mouth or genitals ...
by body cells. - Shelton State
... Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Document
... change breath harder, blood vessels dilate, sweat glands secrete more less metabolic heat is retained body temp drops 2) Body temp falls muscles shiver, blood shunted to interior of body, more metabolic heat produced body temp rises ...
... change breath harder, blood vessels dilate, sweat glands secrete more less metabolic heat is retained body temp drops 2) Body temp falls muscles shiver, blood shunted to interior of body, more metabolic heat produced body temp rises ...
B6b Transport in Animals
... _______________ of blood. The blood inside is under _________ pressure and therefore the walls do not need to be as __________ as those of the arteries. They have a large __________ to allow the blood to flow quickly and rely on ___________ muscles close to the veins to help push the blood back towa ...
... _______________ of blood. The blood inside is under _________ pressure and therefore the walls do not need to be as __________ as those of the arteries. They have a large __________ to allow the blood to flow quickly and rely on ___________ muscles close to the veins to help push the blood back towa ...
30.3 The Heart and Circulation
... The circulatory system moves blood to all parts of the body. • The system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. – heart pumps blood throughout body – arteries move blood away from heart – veins move blood back to heart – capillaries get blood to and from ...
... The circulatory system moves blood to all parts of the body. • The system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. – heart pumps blood throughout body – arteries move blood away from heart – veins move blood back to heart – capillaries get blood to and from ...
Circulation and Gas Exchange
... the plasma is limited since it combines with water to form an acid. • Too much acid in the blood would lead to problems since blood functions best between pH 7.36 and 7.44. • Most carbon dioxide is transported in blood plasma as bicarbonate ions. (Some CO2 is carried in the red blood cells attached ...
... the plasma is limited since it combines with water to form an acid. • Too much acid in the blood would lead to problems since blood functions best between pH 7.36 and 7.44. • Most carbon dioxide is transported in blood plasma as bicarbonate ions. (Some CO2 is carried in the red blood cells attached ...
Biology 12 – Practice Final Exam 5) Describe the changes that occur
... 7) A student set up the experiment illustrated above and kept it at 37°C. After five minutes, the distilled water in the beaker was tested and found to contain a sugar but no starch. a) What had occurred inside the tube? (1 mark) Starch is too large of a molecule to cross the membrane, therefore no ...
... 7) A student set up the experiment illustrated above and kept it at 37°C. After five minutes, the distilled water in the beaker was tested and found to contain a sugar but no starch. a) What had occurred inside the tube? (1 mark) Starch is too large of a molecule to cross the membrane, therefore no ...
Chapter 1
... with acids or bases when either occurs in excess. The substances in these systems function by shedding or accepting hydrogen ions in the presence of strong bases or acids. This helps to neutralize substances that could alter the pH levels in the body. 20. Describe how the bicarbonate buffer system r ...
... with acids or bases when either occurs in excess. The substances in these systems function by shedding or accepting hydrogen ions in the presence of strong bases or acids. This helps to neutralize substances that could alter the pH levels in the body. 20. Describe how the bicarbonate buffer system r ...
Chapter 23 Respiratory System Functions: Provides for gas
... Transferring high-energy phosphate group from an intermediate directly to ADP 2. _______________________________ Remove electrons and pass them through electron transport chain to oxygen 3. _______________________________ Only in chlorophyll-containing plant cells ...
... Transferring high-energy phosphate group from an intermediate directly to ADP 2. _______________________________ Remove electrons and pass them through electron transport chain to oxygen 3. _______________________________ Only in chlorophyll-containing plant cells ...
Chapter 21
... when necessary. 23. Describe the function of hemoglobin as a buffer system. Red blood cells contain an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase that speeds the reaction of carbon dioxide and water. This reaction produces carbonic acid, which quickly dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Hemoglobin ...
... when necessary. 23. Describe the function of hemoglobin as a buffer system. Red blood cells contain an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase that speeds the reaction of carbon dioxide and water. This reaction produces carbonic acid, which quickly dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Hemoglobin ...
Physiology of Respiratory System
... • CO binds to the binding site that oxygen binds to on hemoglobin preventing gas transport of oxygen ...
... • CO binds to the binding site that oxygen binds to on hemoglobin preventing gas transport of oxygen ...
A-level
... Nervous and hormonal control of the heart beat I. Carbon dioxide – 1.Carbon dioxide in blood is high • pH of blood is low • It will stimulates the chemo-receptors in the carotid body and aortic arch • They send nerve impulse along the afferent nerve to the Cardio-acceleratory center • Nerve impul ...
... Nervous and hormonal control of the heart beat I. Carbon dioxide – 1.Carbon dioxide in blood is high • pH of blood is low • It will stimulates the chemo-receptors in the carotid body and aortic arch • They send nerve impulse along the afferent nerve to the Cardio-acceleratory center • Nerve impul ...
6.2 Transport system - HIS IB Biology 2011-2013
... muscle contraction... • This means that the myoctye (muscle cell) is the origin of the contraction and it is not controlled externally. A region of myocytes, called the sinoatrial node (SA node) controls the rate of the ...
... muscle contraction... • This means that the myoctye (muscle cell) is the origin of the contraction and it is not controlled externally. A region of myocytes, called the sinoatrial node (SA node) controls the rate of the ...
Hormonal Regulation of Sodium and Water Balance
... - inner medullary collecting duct contribute to reabsorbing ~4–5% of filtered Na+ hormonal regulation of salt and water balance ...
... - inner medullary collecting duct contribute to reabsorbing ~4–5% of filtered Na+ hormonal regulation of salt and water balance ...
Word Definition 1 chordate the phylum of animals with a notochord
... the phylum of animals with a notochord, nerve cord, and slits in their throats at 1 chordate some point in their lives 2 notochord a flexible rod that supports a chordate's back 3 cartilaginous/cartilage a tissue that is more flexible than bone 4 vertebra/vertebrae the bones that make up the backbon ...
... the phylum of animals with a notochord, nerve cord, and slits in their throats at 1 chordate some point in their lives 2 notochord a flexible rod that supports a chordate's back 3 cartilaginous/cartilage a tissue that is more flexible than bone 4 vertebra/vertebrae the bones that make up the backbon ...
digestive
... Food is ingested through the mouth. It is here where food is broken down into chewable and swallow able chunks by the teeth and the tongue (mechanical digestion). The teeth do much of the mechanical digestion by cutting, tearing, and crushing food into smaller fragments. The salivary glands secrete ...
... Food is ingested through the mouth. It is here where food is broken down into chewable and swallow able chunks by the teeth and the tongue (mechanical digestion). The teeth do much of the mechanical digestion by cutting, tearing, and crushing food into smaller fragments. The salivary glands secrete ...
Fill in the Blank - missmayerhealthscience20
... under a microscope. A blood vessel sends out a signal when it becomes ________. When platelets receive that signal, they will travel to the area and start to do their job by fixing it. To make contact with the ___________blood vessel, they grow long tentacles that are similar to an octopus or spider ...
... under a microscope. A blood vessel sends out a signal when it becomes ________. When platelets receive that signal, they will travel to the area and start to do their job by fixing it. To make contact with the ___________blood vessel, they grow long tentacles that are similar to an octopus or spider ...
Animal Form and Function (Ch. 40)
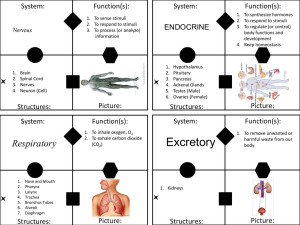
... a group of organs functioning together to perform a major body activity generally 11 major organ systems are recognized; in the order that we will cover them: skeletal muscular digestive circulatory respiratory urinary or excretory endocrine reproductive nervous integumentary ...
... a group of organs functioning together to perform a major body activity generally 11 major organ systems are recognized; in the order that we will cover them: skeletal muscular digestive circulatory respiratory urinary or excretory endocrine reproductive nervous integumentary ...
Chapter 42:Circulation - Volunteer State Community College
... Blood passes from cells through organs (liver, kidneys) that regulate the nutrient and waste content of the blood. ...
... Blood passes from cells through organs (liver, kidneys) that regulate the nutrient and waste content of the blood. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.