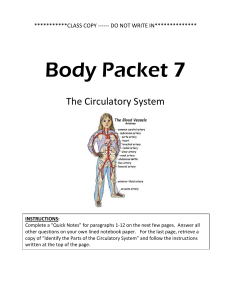
Kingdom_Animalia_Notes
... contracts, blood is pumped away from the heart to the body, lungs, or gills. Circulatory System of Fish: Fish have a two-chambered heart with one atrium and one ventricle. The gills contain many capillaries for gas exchange, so the blood pressure is low after going through the gills. Low-pressure ...
... contracts, blood is pumped away from the heart to the body, lungs, or gills. Circulatory System of Fish: Fish have a two-chambered heart with one atrium and one ventricle. The gills contain many capillaries for gas exchange, so the blood pressure is low after going through the gills. Low-pressure ...
Name: Period: _____ Date
... openings, unlike cnidarians, ctenophores and flatworms. Why is this a significant ...
... openings, unlike cnidarians, ctenophores and flatworms. Why is this a significant ...
Unit 1, Lessons 1-3 Review Set
... B. Takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen C. Transports blood throughout the body D. Removes waste from the body through the liver ...
... B. Takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen C. Transports blood throughout the body D. Removes waste from the body through the liver ...
TEKS 5 - Net Start Class
... The Integumentary System The largest single organ in the body is our skin, which makes up a large part of the integumentary system. In many animals, skin may be covered with scales, fur, or even thick, bony plates, forming a first line of defense against injury and attack. But for many animals, the ...
... The Integumentary System The largest single organ in the body is our skin, which makes up a large part of the integumentary system. In many animals, skin may be covered with scales, fur, or even thick, bony plates, forming a first line of defense against injury and attack. But for many animals, the ...
Kingdom Animalia 1. Several characteristics are used to classify
... ventricle. Blood from the lungs (pulmonary circuit) goes to one atrium while blood from the body (systemic circuit) goes to the other atrium. Both atria empty into the ventricle where the blood is mixed. (b) The advantage of this system is that there is higher pressure in vessels that lead to both t ...
... ventricle. Blood from the lungs (pulmonary circuit) goes to one atrium while blood from the body (systemic circuit) goes to the other atrium. Both atria empty into the ventricle where the blood is mixed. (b) The advantage of this system is that there is higher pressure in vessels that lead to both t ...
PCRRT
... Issues with Infused Fluid Rates • 2000 – 3000 ml/hr/1.73m2 • Effluent flow (infused fluids + UF) approximately equals CRRT clearance – Unlike IHD, solution rate is limiting factor – Too low: poor clearance, accumulation of unwanted molecules (e.g. citrate) – Too high: more loss of electrolytes, dru ...
... Issues with Infused Fluid Rates • 2000 – 3000 ml/hr/1.73m2 • Effluent flow (infused fluids + UF) approximately equals CRRT clearance – Unlike IHD, solution rate is limiting factor – Too low: poor clearance, accumulation of unwanted molecules (e.g. citrate) – Too high: more loss of electrolytes, dru ...
the human body
... and carrying, distributing and collecting. Part of the circulation is through the kidneys and there it is balanced, filtered, purified, cleaned and adjusted. Like a treatment plant, non-stop. Unwanted substances are then disposed of via the bladder. For the filtering process, hundreds of pints of ...
... and carrying, distributing and collecting. Part of the circulation is through the kidneys and there it is balanced, filtered, purified, cleaned and adjusted. Like a treatment plant, non-stop. Unwanted substances are then disposed of via the bladder. For the filtering process, hundreds of pints of ...
Chapter 42 Circulation and Gas Exchange
... 2. Distinguish between open and closed circulatory systems 3. Using an arthropod as an example, describe the circulation of hemolymph 4. Explain how hemolymph differs from blood 5. Using an earthworm as an example, describe circulation of blood and explain how it exchanges materials with interstitia ...
... 2. Distinguish between open and closed circulatory systems 3. Using an arthropod as an example, describe the circulation of hemolymph 4. Explain how hemolymph differs from blood 5. Using an earthworm as an example, describe circulation of blood and explain how it exchanges materials with interstitia ...
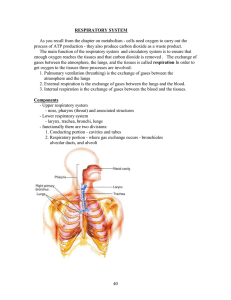
Respiratory System
... in a bronchiole secondary to prolonged irritation from a substance like tobacco smoke -Cancer cells eventually form tumor masses that obstruct air passages and decrease gas exchange -These cancers spread easily to the circulation leading to lymph node, liver, bones brain or kidney metastasis. ...
... in a bronchiole secondary to prolonged irritation from a substance like tobacco smoke -Cancer cells eventually form tumor masses that obstruct air passages and decrease gas exchange -These cancers spread easily to the circulation leading to lymph node, liver, bones brain or kidney metastasis. ...
Human Body Project
... Describe the basic structure and function of the endocrine system. List the endocrine glands . (Diagram) List the hormones released by each gland. Discuss the functions of the hormones. Explain how a hormone only affects its target cells and not other cells (Diagram) Explain two malfunctions of the ...
... Describe the basic structure and function of the endocrine system. List the endocrine glands . (Diagram) List the hormones released by each gland. Discuss the functions of the hormones. Explain how a hormone only affects its target cells and not other cells (Diagram) Explain two malfunctions of the ...
Human Body Systems
... • Cells are organized by the activities they do – Cells that contract = muscle tissue – Cells that carry messages = nerve tissue ...
... • Cells are organized by the activities they do – Cells that contract = muscle tissue – Cells that carry messages = nerve tissue ...
Week 1 - Speyside High School
... What you need to learn this week: The need to maintain conditions within tolerable limits Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment Negative feedback is the way in which homeostasis is achieved Negative feedback describes a process in which any deviation from the normal ...
... What you need to learn this week: The need to maintain conditions within tolerable limits Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment Negative feedback is the way in which homeostasis is achieved Negative feedback describes a process in which any deviation from the normal ...
Respiratory system
... • The mucus membrane of the larynx becomes inflamed and swollen due to infection or an irritation from inhaled vapors • Prevents the vocal chords from vibrating freely ...
... • The mucus membrane of the larynx becomes inflamed and swollen due to infection or an irritation from inhaled vapors • Prevents the vocal chords from vibrating freely ...
Slide 1
... • The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. Information from the body is carried to the brain via the spinal cord. • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and brain, out to the rest of the body. Information is carrie ...
... • The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. Information from the body is carried to the brain via the spinal cord. • The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and brain, out to the rest of the body. Information is carrie ...
Body Organization: Working Together
... toward the heart. Veins have thinner walls, and they look purple or blue when you see them through your skin. They are really very dark red, but we will learn more about that later. Veins have help carrying the blood back toward the heart. If you think about your legs for a minute, it is a long way ...
... toward the heart. Veins have thinner walls, and they look purple or blue when you see them through your skin. They are really very dark red, but we will learn more about that later. Veins have help carrying the blood back toward the heart. If you think about your legs for a minute, it is a long way ...
Gas Exchange
... When carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the blood, only a small amount of it (9%) reaching the blood is held in simple solution. (as dissolved carbon dioxide) Another 27 % attaches directly to the Hemoglobin to form carbonamino-hemoglobin. The remaining 64% combines with water to form bicar ...
... When carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the blood, only a small amount of it (9%) reaching the blood is held in simple solution. (as dissolved carbon dioxide) Another 27 % attaches directly to the Hemoglobin to form carbonamino-hemoglobin. The remaining 64% combines with water to form bicar ...
Physiological Adjustments to Exercise
... prediction because standing did increase the pulse rate and blood pressure in comparison to reclining. The main point of this trial comparison was to show that even the slight exertion of having the body stand upright rather than recline laying down slightly increased the pulse and blood pressure. T ...
... prediction because standing did increase the pulse rate and blood pressure in comparison to reclining. The main point of this trial comparison was to show that even the slight exertion of having the body stand upright rather than recline laying down slightly increased the pulse and blood pressure. T ...
Respiratory System
... • If you were exercising, the levels of carbon dioxide increase so breathing rate increases. ...
... • If you were exercising, the levels of carbon dioxide increase so breathing rate increases. ...
chapter_vertebrates
... Metamorphosis – the process that changes an amphibian from a gilled, aquatic organism to an air-breathing organism Young amphibians possess gills, but adults usually have lungs Gills and lungs are not the only organs used for respiration Most have thin, moist skin They can exchange gases t ...
... Metamorphosis – the process that changes an amphibian from a gilled, aquatic organism to an air-breathing organism Young amphibians possess gills, but adults usually have lungs Gills and lungs are not the only organs used for respiration Most have thin, moist skin They can exchange gases t ...
CHAPTER 23
... RESPIRATORY SYSTEM As you recall from the chapter on metabolism - cells need oxygen to carry out the process of ATP production - they also produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. The main function of the respiratory system and circulatory system is to ensure that enough oxygen reaches the tissues ...
... RESPIRATORY SYSTEM As you recall from the chapter on metabolism - cells need oxygen to carry out the process of ATP production - they also produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. The main function of the respiratory system and circulatory system is to ensure that enough oxygen reaches the tissues ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.