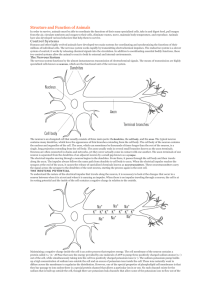
1 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Types of Circulatory Systems
... units and secretes them as pigment in the bile, responsible for the color of feces. Each second two million red blood cells are produced to replace those thus taken out of circulation. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are larger than erythrocytes, have a nucleus, and lack hemoglobin. The ...
... units and secretes them as pigment in the bile, responsible for the color of feces. Each second two million red blood cells are produced to replace those thus taken out of circulation. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are larger than erythrocytes, have a nucleus, and lack hemoglobin. The ...
Circulation and Gas Exchange
... 3. List two ways that fish osmoregulate in freshwater. 4. List two ways that fish osmoregulate in seawater. 5. List two ways in which lobe-finned fishes differ physically from ray-finned fishes. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... 3. List two ways that fish osmoregulate in freshwater. 4. List two ways that fish osmoregulate in seawater. 5. List two ways in which lobe-finned fishes differ physically from ray-finned fishes. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The Skeleton - Cecchini Cuore
... cells use oxygen to break down the nutrients we get from the food we eat to release energy. the respiratory and circulatory systems are responsible for delivering oxygen and food to all cells of the body. an efficient respiratory system ensures that the maximum amount of oxygen reaches the lungs and ...
... cells use oxygen to break down the nutrients we get from the food we eat to release energy. the respiratory and circulatory systems are responsible for delivering oxygen and food to all cells of the body. an efficient respiratory system ensures that the maximum amount of oxygen reaches the lungs and ...
Urinary System Physiology
... • Renin released from JG cells when – blood pressure declines – osmolarity of distal convoluted tubule decreases ...
... • Renin released from JG cells when – blood pressure declines – osmolarity of distal convoluted tubule decreases ...
Nervous tissue
... 5. What is homeostasis & how is it achieved? 6. What are the 2 types of thermoregulation? 7. How do organisms exchange heat with their environment? 8. How can organisms exchange heat within their bodies? 9. How do we achieve homeostasis for body temperature? 10. How do animals thermoregulate in temp ...
... 5. What is homeostasis & how is it achieved? 6. What are the 2 types of thermoregulation? 7. How do organisms exchange heat with their environment? 8. How can organisms exchange heat within their bodies? 9. How do we achieve homeostasis for body temperature? 10. How do animals thermoregulate in temp ...
invertebrates_th_grade
... The planarian’s food is digested in the gastroderm. Nondigestible material is pushed out of the intestine though the mouth. The planarian’s intestines extend to every area of the worm’s body and food is moved throughout the intestine by the twisting movements of the planarian and by flagella. ...
... The planarian’s food is digested in the gastroderm. Nondigestible material is pushed out of the intestine though the mouth. The planarian’s intestines extend to every area of the worm’s body and food is moved throughout the intestine by the twisting movements of the planarian and by flagella. ...
Respiratory System Chapter 24
... Carbon dioxide levels- main regulatory chemical for respiration ↑ CO2 = ↓ blood pH Increased CO2 increases respiration Changes in CO2 act on central chemoreceptors in the medulla oblongata Oxygen levels Peripheral chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery detect oxygen concentration cha ...
... Carbon dioxide levels- main regulatory chemical for respiration ↑ CO2 = ↓ blood pH Increased CO2 increases respiration Changes in CO2 act on central chemoreceptors in the medulla oblongata Oxygen levels Peripheral chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery detect oxygen concentration cha ...
respiratory
... Bicarbonate ions move into the RBCs and bind with hydrogen ions to form carbonic acid Carbonic acid is then split by carbonic anhydrase to release carbon dioxide and water Carbon dioxide then diffuses from the blood into the alveoli ...
... Bicarbonate ions move into the RBCs and bind with hydrogen ions to form carbonic acid Carbonic acid is then split by carbonic anhydrase to release carbon dioxide and water Carbon dioxide then diffuses from the blood into the alveoli ...
Cardiovascular System
... • These are conduit vessels that are near the heart which carry blood for circulation. • The major example of an elastic artery is the aorta. • These are large lumen vessels (low resistance) that contain more elastin than the muscular arteries. • This allows them to be “pressure reservoirs” ‒‒ they ...
... • These are conduit vessels that are near the heart which carry blood for circulation. • The major example of an elastic artery is the aorta. • These are large lumen vessels (low resistance) that contain more elastin than the muscular arteries. • This allows them to be “pressure reservoirs” ‒‒ they ...
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals: Gas Exchange
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
Supported by: Body Systems and ABO blood types Grade 6 Lesson
... i. What are the four blood types of people? ii. What does blood do? iii. How does it do it? Make sure you talk about the small molecules in the blood that carry oxygen to the body cells (Hemoglobin, myoglobin), clotting particles, dissolved substances in the blood like sugars, etc. iv. Why is blood ...
... i. What are the four blood types of people? ii. What does blood do? iii. How does it do it? Make sure you talk about the small molecules in the blood that carry oxygen to the body cells (Hemoglobin, myoglobin), clotting particles, dissolved substances in the blood like sugars, etc. iv. Why is blood ...
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals: Gas Exchange
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
First Aid Manual
... May assist in the administration of aspirin if available for suspected cardiac chest pain. Ask 4 questions first (age, allergy, stomach ulcers, blood disorder) Heart Attack: The heart is about the size of your fist located on the left side of your chest. It lies between the right and left lungs, in ...
... May assist in the administration of aspirin if available for suspected cardiac chest pain. Ask 4 questions first (age, allergy, stomach ulcers, blood disorder) Heart Attack: The heart is about the size of your fist located on the left side of your chest. It lies between the right and left lungs, in ...
Maintaining a Balance - The Bored of Studies Community
... pH of 7 is neutral e.g. water, 0-6 is acidic .e.g. lemon juice, 8-14 is basic .e.g. sodium bicarbonate ...
... pH of 7 is neutral e.g. water, 0-6 is acidic .e.g. lemon juice, 8-14 is basic .e.g. sodium bicarbonate ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... Mechanisms that prevent alveoli from filling with fluid: 1) cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together 2) the relatively high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 3) there is low pressure in the pulmonary circuit ...
... Mechanisms that prevent alveoli from filling with fluid: 1) cells of alveolar wall are tightly joined together 2) the relatively high osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid draws water out of them 3) there is low pressure in the pulmonary circuit ...
File
... Protects & supports body organs Framework for muscles & movement Hematopoiesis; store minerals ...
... Protects & supports body organs Framework for muscles & movement Hematopoiesis; store minerals ...
Structure and Function of Animals syllabus
... The somatic nervous system is responsible for voluntary, or conscious, movement. The neurons only target the skeletal muscles responsible for body movement. All of the neurons in the somatic system release acetylcholine, an excitatory neurotransmitter that causes skeletal muscles to contract. None o ...
... The somatic nervous system is responsible for voluntary, or conscious, movement. The neurons only target the skeletal muscles responsible for body movement. All of the neurons in the somatic system release acetylcholine, an excitatory neurotransmitter that causes skeletal muscles to contract. None o ...
BILAN DE SANTÉ
... Repetitive infections (cold, flu, fungus, etc.) Frequent use of antibiotics. Have you suffered mononucleosis? Allergies : food, respiratory, others specify : ...
... Repetitive infections (cold, flu, fungus, etc.) Frequent use of antibiotics. Have you suffered mononucleosis? Allergies : food, respiratory, others specify : ...
Notes Key
... Endocrine – the hypothalamus (gland in the brain) sends messages to the pituitary (gland in the brain)to make hormones. Reproductive – receives the hormones and produces sperm and eggs. 7. Which Three systems work together to remove excess water from the body? Endocrine, Circulatory, and Excretory E ...
... Endocrine – the hypothalamus (gland in the brain) sends messages to the pituitary (gland in the brain)to make hormones. Reproductive – receives the hormones and produces sperm and eggs. 7. Which Three systems work together to remove excess water from the body? Endocrine, Circulatory, and Excretory E ...
Mechanisms of Action
... Law. This phenomenon allows oxygen to effortlessly cross cell membranes and enter all of the body’s fluid systems, including plasma, synovial, lymphatic, and interstitial (between cells) and cerebrospinal fluids. Normally, only the red blood cells are capable of transporting oxygen throughout the bo ...
... Law. This phenomenon allows oxygen to effortlessly cross cell membranes and enter all of the body’s fluid systems, including plasma, synovial, lymphatic, and interstitial (between cells) and cerebrospinal fluids. Normally, only the red blood cells are capable of transporting oxygen throughout the bo ...
respiratory powerpoint
... The Physiology of Breathing Inspiration •Respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata •Neurons in the RC fire automatically in a rhythmic cycle •Carbon dioxide levels in blood, lungs, or brain can cause changes in the activity of the RC •When carbon dioxide levels rise, receptors in body ...
... The Physiology of Breathing Inspiration •Respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata •Neurons in the RC fire automatically in a rhythmic cycle •Carbon dioxide levels in blood, lungs, or brain can cause changes in the activity of the RC •When carbon dioxide levels rise, receptors in body ...
Heart and Blood Vessels
... Blood Pressure When the heart contracts, it produces a wave of fluid pressure in the arteries. The force of the blood on the arteries’ walls is blood pressure. ...
... Blood Pressure When the heart contracts, it produces a wave of fluid pressure in the arteries. The force of the blood on the arteries’ walls is blood pressure. ...
Modeling Drug Delivery in the Rhesus Monkey - LPPD
... The male rhesus monkeys weighed between 3.1 and 6.8 kg. Using Kirchoff’s conservation (current and voltage) laws, Darcy’s law, and the HagenPoiseuille equation to derive the calculations, we modeled blood flow through compartments and constructed a static one-dimensional model to simulate blood dist ...
... The male rhesus monkeys weighed between 3.1 and 6.8 kg. Using Kirchoff’s conservation (current and voltage) laws, Darcy’s law, and the HagenPoiseuille equation to derive the calculations, we modeled blood flow through compartments and constructed a static one-dimensional model to simulate blood dist ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.