2nd Nine Weeks Exam Review Unit 5
... The mold Aspergillus flavus grows on grain. A. flavus produces a toxin that binds to the DNA in the bodies of animals that eat the grain. The binding of the toxin to DNA blocks transcription, so it directly interferes with the ability of an animal cell to do which of the following? A. Transport gluc ...
... The mold Aspergillus flavus grows on grain. A. flavus produces a toxin that binds to the DNA in the bodies of animals that eat the grain. The binding of the toxin to DNA blocks transcription, so it directly interferes with the ability of an animal cell to do which of the following? A. Transport gluc ...
Document
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
C1. The common points of control are as follows: 1. DNA
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
Document
... mRNA: a copy of gene; with exactly the same sequence as one of the strands of the gene but substituting U for T Introns (内含子): parts of a gene / not used in protein synthesis; spliced out from mRNA>shortened mRNA leaves nucleus with exons (外 显子) plus regulatory region ...
... mRNA: a copy of gene; with exactly the same sequence as one of the strands of the gene but substituting U for T Introns (内含子): parts of a gene / not used in protein synthesis; spliced out from mRNA>shortened mRNA leaves nucleus with exons (外 显子) plus regulatory region ...
DNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... Which bases are complementary to each other? How are they held together in the double helix of DNA? ...
... Which bases are complementary to each other? How are they held together in the double helix of DNA? ...
Biochemistry Exam Molecular Biology Lecture 1 – An Introduction to
... • Open reading frames à segments that don’t have a stop codon for at least 50 codons. • Every mRNA has three possible reading frames, because after three nucleotides the codons are the same again. ...
... • Open reading frames à segments that don’t have a stop codon for at least 50 codons. • Every mRNA has three possible reading frames, because after three nucleotides the codons are the same again. ...
What is latency? - California State University, Fullerton
... • Added to some are an antiTAR polyamide nucleotide analog with/wo link to transportin that gets it into cell • Bottom row - scrambled nucleotide sequence • What do results show? • Why might this approach have an advantage over targeting Tat? • How would you show that it prevents virus replication? ...
... • Added to some are an antiTAR polyamide nucleotide analog with/wo link to transportin that gets it into cell • Bottom row - scrambled nucleotide sequence • What do results show? • Why might this approach have an advantage over targeting Tat? • How would you show that it prevents virus replication? ...
SPECIFIKÁCIÓS TÁBLÁZAT Vegyszer neve Specifikáció Kiszerelés
... rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep additional dyes, for color indication for reaction setup as w ...
... rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep additional dyes, for color indication for reaction setup as w ...
Protein synthesis 2015 TranscritpionTranslation.notebook
... • Single stranded • Ribose sugar • Bases: C,G,A,U • Uracil replaces Thymine • 3 types ...
... • Single stranded • Ribose sugar • Bases: C,G,A,U • Uracil replaces Thymine • 3 types ...
Closed Loop DNA Operating System Migration
... that stringing together a simple alphabet of four characters together we can get enough information to create a complex organism!. ...
... that stringing together a simple alphabet of four characters together we can get enough information to create a complex organism!. ...
1 BIOS 1300 SI SI WORKSHEET 8 (Chapter 3 Cont.) SI Leader
... -Alternate RNA splicing allows 1 pre mRNA to code for multiple proteins III. Translation: 1. Initiation: mRNA, a tRNA corresponding to the __________ codon, and 2 ribosomal subunits unite to form a translation initiation complex with the help of _________________ factors 2. Elongation: Amino a ...
... -Alternate RNA splicing allows 1 pre mRNA to code for multiple proteins III. Translation: 1. Initiation: mRNA, a tRNA corresponding to the __________ codon, and 2 ribosomal subunits unite to form a translation initiation complex with the help of _________________ factors 2. Elongation: Amino a ...
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
... Most primitive life forms are the prokaryotes found in or near these vents. ...
... Most primitive life forms are the prokaryotes found in or near these vents. ...
problem set
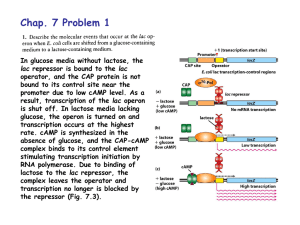
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
Matching review Connect with lines
... planaria shrimp sea urchin sponges nautilus coral pinworms ...
... planaria shrimp sea urchin sponges nautilus coral pinworms ...
Presentation 1 Guidelines
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
Chapter 15 - Translation of mRNA
... 1. The genetic basis for protein synthesis a. Archibald Garrod proposed that some genes code for the production of a single enzyme b. Beadle and Tatum’s experiments with Neurospora led them to propose the one-gene/oneenzyme hypothesis 2. The relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesi ...
... 1. The genetic basis for protein synthesis a. Archibald Garrod proposed that some genes code for the production of a single enzyme b. Beadle and Tatum’s experiments with Neurospora led them to propose the one-gene/oneenzyme hypothesis 2. The relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesi ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.