Evolution Test
... E. All of the above 17. A pattern of natural selection that favors average individuals A. Natural Selection B. Directional Selection C. Stabilizing Selection D. Disruptive Selection 18. A pattern of natural selection that favors both extremes A. Natural Selection B. Directional Selection C. Stabiliz ...
... E. All of the above 17. A pattern of natural selection that favors average individuals A. Natural Selection B. Directional Selection C. Stabilizing Selection D. Disruptive Selection 18. A pattern of natural selection that favors both extremes A. Natural Selection B. Directional Selection C. Stabiliz ...
HB Unit 11 History of Life and Classification
... • Lamarck- inheritance of acquired traits: individuals could acquire traits by behavior; traits could be passed on. ...
... • Lamarck- inheritance of acquired traits: individuals could acquire traits by behavior; traits could be passed on. ...
1DarwinianEvolution22_1
... Organisms that have advantageous heritable traits (fitness) survive and reproduce at a higher rate Environmental changes may result in adaptations, and sometimes speciation (the founder effect) Individuals do not evolve, Populations do! ...
... Organisms that have advantageous heritable traits (fitness) survive and reproduce at a higher rate Environmental changes may result in adaptations, and sometimes speciation (the founder effect) Individuals do not evolve, Populations do! ...
mutations - WordPress.com
... environments. Over time, the species will begin to diverge. Different traits will be successful in each environment. Eventually the two species will become so different they can no longer interbreed = speciation. 6. Which animal spurred Darwin’s thinking about how species might change over time duri ...
... environments. Over time, the species will begin to diverge. Different traits will be successful in each environment. Eventually the two species will become so different they can no longer interbreed = speciation. 6. Which animal spurred Darwin’s thinking about how species might change over time duri ...
populations - s3.amazonaws.com
... evolve in different environments – When this occurs, the similar species evolve to have different traits – These traits are said to be ...
... evolve in different environments – When this occurs, the similar species evolve to have different traits – These traits are said to be ...
Chapter 15
... 3. Gene flow – movement of genes in or out of a population. 4. Genetic drift – allele frequencies change as a result of random events, significant in small & medium populations. ...
... 3. Gene flow – movement of genes in or out of a population. 4. Genetic drift – allele frequencies change as a result of random events, significant in small & medium populations. ...
Evolution Bingo
... 25. He proposed the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous, slow gradual and uniform processes. 26. He proposed the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted chiefly from sudden violent and ...
... 25. He proposed the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous, slow gradual and uniform processes. 26. He proposed the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted chiefly from sudden violent and ...
evolution COB questions
... viability (genetics are incompatible), reduced hybrid fertility (offspring are sterile, like a mule), hybrid breakdown (offspring are fertile, but offspring of next generation are not) 2. allopatric speciation: speciation occurs in populations that live geographically separate a. conditions for: geo ...
... viability (genetics are incompatible), reduced hybrid fertility (offspring are sterile, like a mule), hybrid breakdown (offspring are fertile, but offspring of next generation are not) 2. allopatric speciation: speciation occurs in populations that live geographically separate a. conditions for: geo ...
EVOLUTION A. Origin of Life 1. Earth is ~ 4.6 bya
... 4. Gene Flow- individuals entering or leaving population 5. Sexual Selection- mates choose for particular traits. G. Speciation- forming new species 1. Species- interbreeding organisms that can produce fertile offspring 2. Speciation rates can vary, especially when adaptive radiation occurs and new ...
... 4. Gene Flow- individuals entering or leaving population 5. Sexual Selection- mates choose for particular traits. G. Speciation- forming new species 1. Species- interbreeding organisms that can produce fertile offspring 2. Speciation rates can vary, especially when adaptive radiation occurs and new ...
EVOLUTION A. Origin of Life 1. Earth is ~ 4.6 bya and life occurred
... and start new population; bottleneck effect- only certain individuals survive catastrophic event 2. Natural Selection- environment determines which traits are favorable and therefore are passed on because they live to make babies 3. Mutations- raw material for natural selection; can be positive, neg ...
... and start new population; bottleneck effect- only certain individuals survive catastrophic event 2. Natural Selection- environment determines which traits are favorable and therefore are passed on because they live to make babies 3. Mutations- raw material for natural selection; can be positive, neg ...
Survival of the Fittest
... predators, find a mate, etc. • These variations can be passed on to offspring. ...
... predators, find a mate, etc. • These variations can be passed on to offspring. ...
Evolution Notes
... Overproduction of offspring-more babies born than what the environment can support Variation-some individuals have the trait, some don’t Differential reproduction-individuals with the trait produce more offspring than individuals without it ...
... Overproduction of offspring-more babies born than what the environment can support Variation-some individuals have the trait, some don’t Differential reproduction-individuals with the trait produce more offspring than individuals without it ...
File
... 25. The dog breeds we have today were developed through: a. natural selection b. artificial selection (selective breeding) c. sexual selection d. acquired selection 26. The finches on the Galapagos island were similar in form except for variations of their beaks. Darwin observed that these variation ...
... 25. The dog breeds we have today were developed through: a. natural selection b. artificial selection (selective breeding) c. sexual selection d. acquired selection 26. The finches on the Galapagos island were similar in form except for variations of their beaks. Darwin observed that these variation ...
Bio 102 Practice Quiz 1
... 5. What was especially profound about the different beak types Darwin observed in his "finches" was that A) they allowed each bird to successfully inhabit several niches on the island. B) each beak type was seen on only one island. C) the beak type changed over the life time of each bird. D) this in ...
... 5. What was especially profound about the different beak types Darwin observed in his "finches" was that A) they allowed each bird to successfully inhabit several niches on the island. B) each beak type was seen on only one island. C) the beak type changed over the life time of each bird. D) this in ...
Evolution Unit Name:_KEY Study Guide _B_ Evolution _O_ Extinct _
... A large population of flightless birds lives on a massive island in the Pacific Ocean. The island sinks, isolating five populations of this species on different smaller islands that were once mountains. If the factors necessary for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium to work are active, what would we exp ...
... A large population of flightless birds lives on a massive island in the Pacific Ocean. The island sinks, isolating five populations of this species on different smaller islands that were once mountains. If the factors necessary for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium to work are active, what would we exp ...
File
... 22. Which of the following processes favors individuals having one of the extreme forms of a trait? a. directional selection b. geographic isolation c. reproductive isolation d. stabilizing selection 23. Formation of a new species from an existing one is called: a. convergent evolution b. extinction ...
... 22. Which of the following processes favors individuals having one of the extreme forms of a trait? a. directional selection b. geographic isolation c. reproductive isolation d. stabilizing selection 23. Formation of a new species from an existing one is called: a. convergent evolution b. extinction ...
Secondary Growth
... Populations produce more offspring than environment can support and therefore only a fraction survive (struggle for existence) Individuals best adapted to environment (more “fit”) will survive and leave more offspring • …..“Survival of the fittest” ...
... Populations produce more offspring than environment can support and therefore only a fraction survive (struggle for existence) Individuals best adapted to environment (more “fit”) will survive and leave more offspring • …..“Survival of the fittest” ...
Secondary Growth
... Populations produce more offspring than environment can support and therefore only a fraction survive (struggle for existence) Individuals best adapted to environment (more “fit”) will survive and leave more offspring • …..“Survival of the fittest” ...
... Populations produce more offspring than environment can support and therefore only a fraction survive (struggle for existence) Individuals best adapted to environment (more “fit”) will survive and leave more offspring • …..“Survival of the fittest” ...
2. Divergent Evolution
... - among the first to explain how organisms change over time - later disproved ...
... - among the first to explain how organisms change over time - later disproved ...
Unit 6 Essays
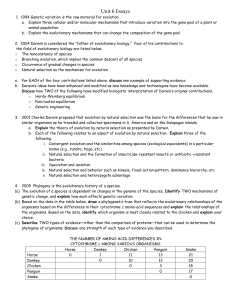
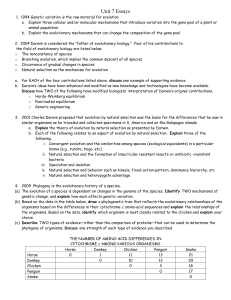
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
Evolution
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
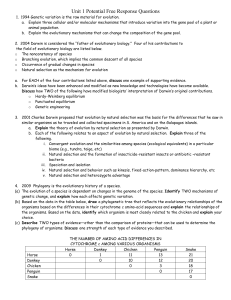
Unit 6 Essays
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. The biologist Orator F. Cook was the first to coin the term 'speciation' for the splitting of lineages or ""cladogenesis,"" as opposed to ""anagenesis"" or ""phyletic evolution"" occurring within lineages. Charles Darwin was the first to describe the role of natural selection in speciation. There is research comparing the intensity of sexual selection in different clades with their number of species.There are four geographic modes of speciation in nature, based on the extent to which speciating populations are isolated from one another: allopatric, peripatric, parapatric, and sympatric. Speciation may also be induced artificially, through animal husbandry, agriculture, or laboratory experiments. Whether genetic drift is a minor or major contributor to speciation is the subject matter of much ongoing discussion.