What Is Canine Chiropractic Care
... care for more than 100 years. Many people see their chiropractor for more than just back pain. People visit their chiropractor for more energy, improved sports performance, better resistance to disease, and to help insure drug-free lives for themselves and their families. This is known as wellness c ...
... care for more than 100 years. Many people see their chiropractor for more than just back pain. People visit their chiropractor for more energy, improved sports performance, better resistance to disease, and to help insure drug-free lives for themselves and their families. This is known as wellness c ...
Sermon Presentation
... love, hate, joy and sadness, are mammalian inventions, originated in the limbic system. • When we speak of “chemistry” between people that is literally true. • The Limbic system sends signals to the appropriate glands to secret certain hormones into the blood to induce certain feelings and their cor ...
... love, hate, joy and sadness, are mammalian inventions, originated in the limbic system. • When we speak of “chemistry” between people that is literally true. • The Limbic system sends signals to the appropriate glands to secret certain hormones into the blood to induce certain feelings and their cor ...
Chapter 15
... Corticospinal Pathway • Sometimes called the pyramidal system • Provides voluntary control over skeletal muscles: – system begins at pyramidal cells of primary motor cortex – axons of these upper motor neurons descend into brain stem and spinal cord to synapse on lower motor neurons that control sk ...
... Corticospinal Pathway • Sometimes called the pyramidal system • Provides voluntary control over skeletal muscles: – system begins at pyramidal cells of primary motor cortex – axons of these upper motor neurons descend into brain stem and spinal cord to synapse on lower motor neurons that control sk ...
Chapter 14 ()
... a. specialized dendritic endings of sensory neurons used for general senses free / unencapsulated example: root hair plexus (also called hair follicle receptor) encapsulated - dendrites enclosed in c.t. capsule that amplifies or filters stimuli example: Pacinian corpuscle ...
... a. specialized dendritic endings of sensory neurons used for general senses free / unencapsulated example: root hair plexus (also called hair follicle receptor) encapsulated - dendrites enclosed in c.t. capsule that amplifies or filters stimuli example: Pacinian corpuscle ...
control of body movement
... Afferent fibers from many sources synapse on interneurons: i) the same muscles controlled by the motor neuron, ii) other nearby muscles, iii) tendons, joints and skin surrounding the muscles. Thus, afferent input from these sources provide negative-feedback and awareness of limb and body position. ...
... Afferent fibers from many sources synapse on interneurons: i) the same muscles controlled by the motor neuron, ii) other nearby muscles, iii) tendons, joints and skin surrounding the muscles. Thus, afferent input from these sources provide negative-feedback and awareness of limb and body position. ...
Notes - The Nervous System
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
middle ear
... - Info from receptors below head enters spinal cord and travels through spinal nerves to brain ...
... - Info from receptors below head enters spinal cord and travels through spinal nerves to brain ...
Document
... Refraction The bending of light around an object. Images viewed by the eye are upside down, our brain interprets them properly! ...
... Refraction The bending of light around an object. Images viewed by the eye are upside down, our brain interprets them properly! ...
nervous5
... If tagged with a fluorescent label could be used to detect the presence and locations of inotropic and metabotropic AChRs. ...
... If tagged with a fluorescent label could be used to detect the presence and locations of inotropic and metabotropic AChRs. ...
File - Mrs. Walston Science
... and the brain. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system, it it the pathway to the peripheral nervous system. ...
... and the brain. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system, it it the pathway to the peripheral nervous system. ...
Nervous System Overview
... • Cylinder of nerve tissue within the vertebral canal (thick as a finger) • The spinal cord has 31 pairs of spinal nerves. – sensory component which enters the back of the cord – motor component that exits the front of the spinal cord to their specific muscles or glands. ...
... • Cylinder of nerve tissue within the vertebral canal (thick as a finger) • The spinal cord has 31 pairs of spinal nerves. – sensory component which enters the back of the cord – motor component that exits the front of the spinal cord to their specific muscles or glands. ...
Structural elements and mechanisms involved in the transformation
... Two main categories : Somatic / Visceral motor neurons Somatic motor neurons: Originate from CNS direct axons to skeletal muscles control locomotion Types of efferent motor neurons: Alpha / Beta / Gamma motor neurons Types of muscle fibers they innervate: Intrafusal / Extrafusal muscle fiber ...
... Two main categories : Somatic / Visceral motor neurons Somatic motor neurons: Originate from CNS direct axons to skeletal muscles control locomotion Types of efferent motor neurons: Alpha / Beta / Gamma motor neurons Types of muscle fibers they innervate: Intrafusal / Extrafusal muscle fiber ...
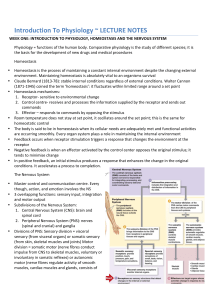
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Unit Four Essential Questions
... The epimysium is the outer layer of connective tissue. The perimysium is made of connective tissue and forms casings for bundles of muscle fibers. The endomysium is connective tissue surrounding each individual muscle fiber. ...
... The epimysium is the outer layer of connective tissue. The perimysium is made of connective tissue and forms casings for bundles of muscle fibers. The endomysium is connective tissue surrounding each individual muscle fiber. ...
Chapter 6
... *Receptive field = area within which a receptor can detect a stimulus Lateral inhibition; to facilitate localization and sharpen contrast, the most strongly activated pathway at the center inhibits the less excited pathways from the fringe areas Adaptation occurs when sensory receptors are subjected ...
... *Receptive field = area within which a receptor can detect a stimulus Lateral inhibition; to facilitate localization and sharpen contrast, the most strongly activated pathway at the center inhibits the less excited pathways from the fringe areas Adaptation occurs when sensory receptors are subjected ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous (5days)
... language. Possibly involved with intellect and personality. ...
... language. Possibly involved with intellect and personality. ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
... Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
Neuro Quiz 4 – Notes from April 9 to April 16 First order neurons
... T or F: Even in the simple monosynaptic reflex, there is interneuron involved. It is never a one-on-one connection. 5. The majority of proprioception gets carried predominantly in the ________ column, which explains their large size. 6. Position Sense aka _____________. 7. The remaining propriocepti ...
... T or F: Even in the simple monosynaptic reflex, there is interneuron involved. It is never a one-on-one connection. 5. The majority of proprioception gets carried predominantly in the ________ column, which explains their large size. 6. Position Sense aka _____________. 7. The remaining propriocepti ...
Movement
... • Spinal Cord Circuits – These are the neuronal circuits that make up the final common pathway for the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation. All central, or higher order, regulation of movement must be mediated through these neurons. • Descending Systems – These are neural system ...
... • Spinal Cord Circuits – These are the neuronal circuits that make up the final common pathway for the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation. All central, or higher order, regulation of movement must be mediated through these neurons. • Descending Systems – These are neural system ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Peripheral nervous system (PNS): All of the neurons that extend from the CNS How the two work together Information is passed from sensory receptors to PNS o Special senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste) o General sensory receptors (touch, light, external heat, pain) o Visceral receptors (monitorin ...
... Peripheral nervous system (PNS): All of the neurons that extend from the CNS How the two work together Information is passed from sensory receptors to PNS o Special senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste) o General sensory receptors (touch, light, external heat, pain) o Visceral receptors (monitorin ...
Nervous Dia rams
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
PCL - mmc7
... brainstem and conducts nerve impulses down to the appropriate spinal level. An upper motor neuron lesion is also known as a pyramidal lesion. Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper m ...
... brainstem and conducts nerve impulses down to the appropriate spinal level. An upper motor neuron lesion is also known as a pyramidal lesion. Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper m ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.