Acoelomates_2-1
... story than just parasites: •Pesticides affect a frog’s immune response to the parasite. ...
... story than just parasites: •Pesticides affect a frog’s immune response to the parasite. ...
Spinal Nerves - Buckeye Valley
... dorsal root ganglion • Whole nerve "trunk" lies in intervertebral foramen ...
... dorsal root ganglion • Whole nerve "trunk" lies in intervertebral foramen ...
Primary afferent neurons of the gut
... Vagal and spinal afferent fibers each respond to mechanical stimulation such as distension and contraction. Vagal afferent encode events within the physiological range. Some spinal afferents respond over a wide dynamic range extending from physiological to pathophysiological levels of distensi ...
... Vagal and spinal afferent fibers each respond to mechanical stimulation such as distension and contraction. Vagal afferent encode events within the physiological range. Some spinal afferents respond over a wide dynamic range extending from physiological to pathophysiological levels of distensi ...
Cranial Nerves: Assessment of Functions
... Ask the subject to stopper one ear canal with his or her finger while you test hearing in the other ear. At a distance of 50 cm directly lateral to the tested ear, whisper a two-digit number (e.g., 29, 35) and ask the subject to identify the number by writing it on a sheet of paper. Repeat the test ...
... Ask the subject to stopper one ear canal with his or her finger while you test hearing in the other ear. At a distance of 50 cm directly lateral to the tested ear, whisper a two-digit number (e.g., 29, 35) and ask the subject to identify the number by writing it on a sheet of paper. Repeat the test ...
Nociceptive sensation
... Pain reception Damage stimuli perception created by the brain from electrochemical nerve impulses delivered to it from sensory receptors. These receptors transfuse (or change) different influences of both internal processes in organism and surrounding environment into the electric impulses. ► Pai ...
... Pain reception Damage stimuli perception created by the brain from electrochemical nerve impulses delivered to it from sensory receptors. These receptors transfuse (or change) different influences of both internal processes in organism and surrounding environment into the electric impulses. ► Pai ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... nerve plexuses. ii. The anterior ramus also gives off a pair of communicating rami that connect with a string of sympathetic chain glanglia in spinal nerves T1 through L2. (Fig. 13.13) E. Except in the thoracic region, the anterior rami branch and merge to form five weblike nerve plexuses: the cervi ...
... nerve plexuses. ii. The anterior ramus also gives off a pair of communicating rami that connect with a string of sympathetic chain glanglia in spinal nerves T1 through L2. (Fig. 13.13) E. Except in the thoracic region, the anterior rami branch and merge to form five weblike nerve plexuses: the cervi ...
Upgrade Nerve Reflexology Migraine. Is the Trigeminal
... very sure that it is the Trigeminal nerve that is responsible for all this ongoing suffering, why is there such a lack of very effective treatment and medication? Despite all the progress in medication, focusing on the nerve-blood connections, migraine still stays hard to control. From our experienc ...
... very sure that it is the Trigeminal nerve that is responsible for all this ongoing suffering, why is there such a lack of very effective treatment and medication? Despite all the progress in medication, focusing on the nerve-blood connections, migraine still stays hard to control. From our experienc ...
POWERPOINT VERSION ()
... • regions of cortex that are not primary motor or primary sensory areas • widespread throughout the cerebral cortex • analyze and interpret sensory experiences • provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment, emotions ...
... • regions of cortex that are not primary motor or primary sensory areas • widespread throughout the cerebral cortex • analyze and interpret sensory experiences • provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment, emotions ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY B.Sc. Counselling Psychology
... depth or distance in vision. Both processes involve spatial aspects of sensory input. Many features contribute to auditory localization of which the following are most important: Having two ears In the same way that having two eyes allows for greater visual abilities through stereoscopic vision, so ...
... depth or distance in vision. Both processes involve spatial aspects of sensory input. Many features contribute to auditory localization of which the following are most important: Having two ears In the same way that having two eyes allows for greater visual abilities through stereoscopic vision, so ...
Spinal Cord
... Cord contusion is the best response because there is gross traumatic injury to the spinal column with disruption of the C4-C5 ligamenta flava, interspinous ligaments, and posterior longitudinal ligament. There is fracture deformity of C5 vertebra consistent with a flexion teardrop fracture and fra ...
... Cord contusion is the best response because there is gross traumatic injury to the spinal column with disruption of the C4-C5 ligamenta flava, interspinous ligaments, and posterior longitudinal ligament. There is fracture deformity of C5 vertebra consistent with a flexion teardrop fracture and fra ...
Neurologic System The nervous system Central and peripheral
... Evaluate both primary and cortical discriminatory sensation. Sensory Function (Cont.) Primary sensory functions Superficial touch Cotton wisp or fingertip Superficial pain Broken tongue blade or the point and hub of a sterile needle Temperature and deep pressure Tested only when superficial pain sen ...
... Evaluate both primary and cortical discriminatory sensation. Sensory Function (Cont.) Primary sensory functions Superficial touch Cotton wisp or fingertip Superficial pain Broken tongue blade or the point and hub of a sterile needle Temperature and deep pressure Tested only when superficial pain sen ...
Spinal Sensorimotor System: An Overview
... locomotion application. While I do not propose that we try to duplicate or biomimic a system as complex as the SSMS, I do propose that a bipedal system modeled somewhat along the lines of the biological example makes an appealing research pathway. The bipedal locomotion system we investigate would b ...
... locomotion application. While I do not propose that we try to duplicate or biomimic a system as complex as the SSMS, I do propose that a bipedal system modeled somewhat along the lines of the biological example makes an appealing research pathway. The bipedal locomotion system we investigate would b ...
Chapter 2: The synapse – regulating communication and
... are abnormal. We learned how information flow can be disrupted: Disorders of electrical signaling such as those that affect myelin, can directly affect the speed that the electrical signal is conveyed. Disorders of transport mechanisms, such as those that affect the nerve terminal, can directly ...
... are abnormal. We learned how information flow can be disrupted: Disorders of electrical signaling such as those that affect myelin, can directly affect the speed that the electrical signal is conveyed. Disorders of transport mechanisms, such as those that affect the nerve terminal, can directly ...
Autonomic
... blood vessels in your skeletal muscles dilate, blood vessels in the visceral muscles constrict, digestion is ceased, your liver ramps up glucose release, your pupils dilate, ...
... blood vessels in your skeletal muscles dilate, blood vessels in the visceral muscles constrict, digestion is ceased, your liver ramps up glucose release, your pupils dilate, ...
Power Point CH 15
... a longitudinal fissure that extends along the midsagittal plane. • The hemispheres are separate from one another except at a few locations where bundles of axons called tracts form white matter regions that allow for communication between them. • The corpus callosum is the largest tract and the main ...
... a longitudinal fissure that extends along the midsagittal plane. • The hemispheres are separate from one another except at a few locations where bundles of axons called tracts form white matter regions that allow for communication between them. • The corpus callosum is the largest tract and the main ...
Animal Physiology, Chapter 10
... or ACh and the effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory – ANS effect on the target organ is dependent upon the neurotransmitter released and the receptor type of the effector ...
... or ACh and the effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory – ANS effect on the target organ is dependent upon the neurotransmitter released and the receptor type of the effector ...
Creatine
... and phosphate, and the energy released is used to regenerate the primary source of energy, ATP Extra creatine in the muscle may also increase the rate of regeneration of phosphocreatine following exercise, which should mean less fatigue with repeated bursts of activity in training or in many sport ...
... and phosphate, and the energy released is used to regenerate the primary source of energy, ATP Extra creatine in the muscle may also increase the rate of regeneration of phosphocreatine following exercise, which should mean less fatigue with repeated bursts of activity in training or in many sport ...
Central Nervous System I. Brain - Function A. Hindbrain 1. Medulla
... This area is located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe. It extends from the longitudinal fissure on the superior cerebrum to the lateral sulcus. It is separated from the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe by the central sulcus. The primary somatic sensory area receives nerve impulses f ...
... This area is located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe. It extends from the longitudinal fissure on the superior cerebrum to the lateral sulcus. It is separated from the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe by the central sulcus. The primary somatic sensory area receives nerve impulses f ...
Answer on Question#47890 - Biology - Other
... fiber contains numerous bundles of protein filaments. These bundles, called myofibrils, are organized into repeating contractile units called sarcomeres. A sarcomere contains two types of protein filaments: actin filaments and myosin filaments. The thin actin filaments are attached to Z line, the en ...
... fiber contains numerous bundles of protein filaments. These bundles, called myofibrils, are organized into repeating contractile units called sarcomeres. A sarcomere contains two types of protein filaments: actin filaments and myosin filaments. The thin actin filaments are attached to Z line, the en ...
Cranial Nerves: Assessment of Functions
... Ask the subject to stopper one ear canal with his or her finger while you test hearing in the other ear. At a distance of 50 cm directly lateral to the tested ear, whisper a two-digit number (e.g., 29, 35) and ask the subject to identify the number by writing it on a sheet of paper. Repeat the test ...
... Ask the subject to stopper one ear canal with his or her finger while you test hearing in the other ear. At a distance of 50 cm directly lateral to the tested ear, whisper a two-digit number (e.g., 29, 35) and ask the subject to identify the number by writing it on a sheet of paper. Repeat the test ...
ALS, MS AND MD - ALS Society of Canada
... the spinal cord and those that travel to the voluntary muscles, so there are symptoms of both central and peripheral involvement, with weakness and wasting in arms, legs, and mouth/throat ...
... the spinal cord and those that travel to the voluntary muscles, so there are symptoms of both central and peripheral involvement, with weakness and wasting in arms, legs, and mouth/throat ...
Cranial Nerves
... • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera ...
... • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera • Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord • Somatic fibers connecting to the skin and skeletal muscles • Autonomic fibers connecting to viscera ...
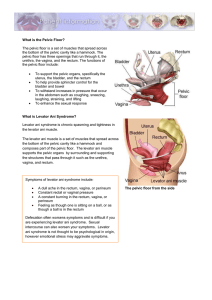
What is the Pelvic Floor? The pelvic floor is a set of muscles that
... the levator ani muscle. The levator ani muscle is a set of muscles that spread across the bottom of the pelvic cavity like a hammock and composes part of the pelvic floor. The levator ani muscle supports the pelvic organs by surrounding and supporting the structures that pass through it such as the ...
... the levator ani muscle. The levator ani muscle is a set of muscles that spread across the bottom of the pelvic cavity like a hammock and composes part of the pelvic floor. The levator ani muscle supports the pelvic organs by surrounding and supporting the structures that pass through it such as the ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.