Ch33 nervous system reading essentials
... Maybe your heart began to pound and your palms became sweaty. This type of reaction is involuntary—you do not think about it, it just happens. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for this reaction. The autonomic nervous system carries impulses from the CNS to the heart and other internal org ...
... Maybe your heart began to pound and your palms became sweaty. This type of reaction is involuntary—you do not think about it, it just happens. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for this reaction. The autonomic nervous system carries impulses from the CNS to the heart and other internal org ...
Sensory Receptors
... – Lamellar (Pacinian) corpuscles—deep pressure and vibration – Bulbous corpuscles (Ruffini endings)—deep continuous pressure – Muscle spindles—muscle stretch – Tendon organs—stretch in tendons – Joint kinesthetic receptors—joint position and motion © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... – Lamellar (Pacinian) corpuscles—deep pressure and vibration – Bulbous corpuscles (Ruffini endings)—deep continuous pressure – Muscle spindles—muscle stretch – Tendon organs—stretch in tendons – Joint kinesthetic receptors—joint position and motion © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Study guide (Word Document)
... 2. This is because rods are only located at the sides of your retina; when you look directly at something, you are using the cells in the middle of your retina, which are cones p. 102 activity 7 1. The person should not be able to hit the character at first (unless they were cheating!) 2. The goggle ...
... 2. This is because rods are only located at the sides of your retina; when you look directly at something, you are using the cells in the middle of your retina, which are cones p. 102 activity 7 1. The person should not be able to hit the character at first (unless they were cheating!) 2. The goggle ...
Spinal Cord Injury - Deranged Physiology
... Primary afferent information (small diameter, often unmyelinated fibres) synapse on second order neurons, located primarily in laminae I or V. The axons of these 2nd order lamina I and V neurons, then both ascend (not more than 1 or 2 segments) and cross to the opposite side to enter the "spinothala ...
... Primary afferent information (small diameter, often unmyelinated fibres) synapse on second order neurons, located primarily in laminae I or V. The axons of these 2nd order lamina I and V neurons, then both ascend (not more than 1 or 2 segments) and cross to the opposite side to enter the "spinothala ...
From Sensation to Perception
... Adaptation of Sensory Receptors • Receptors responding to _____________________________________ adapt quickly • Receptors responding slowly include Merkel’s discs, Ruffini’s corpuscles, and interoceptors that respond to chemical levels in the blood • _____________________________________ and propri ...
... Adaptation of Sensory Receptors • Receptors responding to _____________________________________ adapt quickly • Receptors responding slowly include Merkel’s discs, Ruffini’s corpuscles, and interoceptors that respond to chemical levels in the blood • _____________________________________ and propri ...
Motor Pathways
... – Vestibulospinal tract: balance (axial muscles); automatic postural adjustments ...
... – Vestibulospinal tract: balance (axial muscles); automatic postural adjustments ...
Sensory feedback for upper limb prostheses
... peripheral afferents to produce the necessary pattern of stimulation. As described later, a more reasonable candidate is to directly stimulate neurons in cortex where the integration between the different afferent types encoding joint angle has already occurred. Besides the SA2 afferents there are t ...
... peripheral afferents to produce the necessary pattern of stimulation. As described later, a more reasonable candidate is to directly stimulate neurons in cortex where the integration between the different afferent types encoding joint angle has already occurred. Besides the SA2 afferents there are t ...
stretch reflex 2
... • Also deviation of the upright attitude toward any direction → will cause additional stretching of the postural ms →↑ ms tone of these ms → restores equilibrium before it is disturbed. ...
... • Also deviation of the upright attitude toward any direction → will cause additional stretching of the postural ms →↑ ms tone of these ms → restores equilibrium before it is disturbed. ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy Lecture
... 2) _____________ (peroneal) - lateral to fibula; innervates fibularis muscles (Note: Sciatica involves injury to the sciatic nerve, causing pain to radiate from the buttock down the posterior leg; may be caused by herniated disc, dislocated hip, lumbosacral osteoarthritis, pregnancy, and gluteal mus ...
... 2) _____________ (peroneal) - lateral to fibula; innervates fibularis muscles (Note: Sciatica involves injury to the sciatic nerve, causing pain to radiate from the buttock down the posterior leg; may be caused by herniated disc, dislocated hip, lumbosacral osteoarthritis, pregnancy, and gluteal mus ...
08 Electrophysiology of muscles
... Since charge activity is faster than mechanical activity – the action potentials initiate first followed fairly quickly by the initiation of the mechanical activity of contraction. ...
... Since charge activity is faster than mechanical activity – the action potentials initiate first followed fairly quickly by the initiation of the mechanical activity of contraction. ...
This article was originally published in the Encyclopedia of
... The combination of muscles (force production mechanisms) and skeletons enable animals to move in a variety of ways. There are basically three types of skeletons: endoskeletons, the rigid internal skeleton of vertebrates; exoskeletons, the rigid external skeleton of arthropods; and hydrostatic skelet ...
... The combination of muscles (force production mechanisms) and skeletons enable animals to move in a variety of ways. There are basically three types of skeletons: endoskeletons, the rigid internal skeleton of vertebrates; exoskeletons, the rigid external skeleton of arthropods; and hydrostatic skelet ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... Sensory Pathways for Transmitting Somatic Signals into the CNS ...
... Sensory Pathways for Transmitting Somatic Signals into the CNS ...
NEURO PresentationWORKING students B
... • Subcortical fibers from adjacent areas of the cortex especially from somatic sensory areas of parietal cortex and visual and auditory cortex. • Subcortical fibers from opposite hemisphere which pass through corpus callosum. • Somatic sensory fibers from ventrobasal complex of the thalamus (i.e., c ...
... • Subcortical fibers from adjacent areas of the cortex especially from somatic sensory areas of parietal cortex and visual and auditory cortex. • Subcortical fibers from opposite hemisphere which pass through corpus callosum. • Somatic sensory fibers from ventrobasal complex of the thalamus (i.e., c ...
13-2nd, 3rd, 4th & 6th cranial nerves
... • Fibers in the optic tracts: Mainly terminate in the (LGB), lateral geniculate body of the thalamus (3rd order neuron). A few fibers terminate in pretectal area and superior colliculus. These fibers are related to light reflexes. ...
... • Fibers in the optic tracts: Mainly terminate in the (LGB), lateral geniculate body of the thalamus (3rd order neuron). A few fibers terminate in pretectal area and superior colliculus. These fibers are related to light reflexes. ...
Orthopedic and Physical Therapy Objectives in
... which has received much attention, there i s described a pseudoparalysis or muscle stretch paralysis (or alienated musde-in one of the several uses of the word "alienated"). The weakness or paralysis is described as being due to the fact that the muscles are maintained in a stretch position by an op ...
... which has received much attention, there i s described a pseudoparalysis or muscle stretch paralysis (or alienated musde-in one of the several uses of the word "alienated"). The weakness or paralysis is described as being due to the fact that the muscles are maintained in a stretch position by an op ...
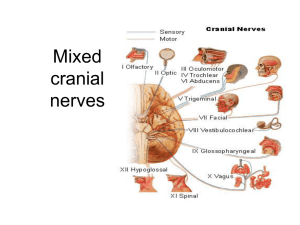
26. Mixed cranial nervest
... combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance). ...
... combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance). ...
The Effects of Beta-alanine Supplementation on the Aging Population
... physical work capacity test (PWC) during the presupplementation visit (visit 2), thus eliminating the potential of a learning effect. After the pre-supplementation visit, subjects will receive the beta-alanine or the placebo and follow the designed supplementation plan for 28 days. Upon completion o ...
... physical work capacity test (PWC) during the presupplementation visit (visit 2), thus eliminating the potential of a learning effect. After the pre-supplementation visit, subjects will receive the beta-alanine or the placebo and follow the designed supplementation plan for 28 days. Upon completion o ...
8165 Brain Nervous Sys CE 8x11
... the body and limbs. Neurons also conduct sensory impulses from the skin to the spinal chord. They serve to relay impulses from receptors and outlying parts to the CNS, and then return the signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands. Q: Name the three types of neurons. A: Sensory, motor, and assoc ...
... the body and limbs. Neurons also conduct sensory impulses from the skin to the spinal chord. They serve to relay impulses from receptors and outlying parts to the CNS, and then return the signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands. Q: Name the three types of neurons. A: Sensory, motor, and assoc ...
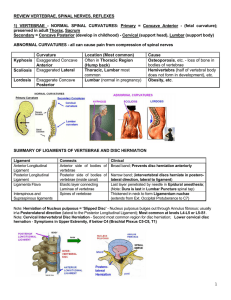
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... not pathological but due to increased activation of Gamma motor neurons associated with nervousness and anxiety. Which of the following is an action of Gamma motor neurons that could produce the mild hyperreflexia? A. Increase sensitivity of Golgi tendon organs B. Increase sensitivity of Ia fibers i ...
... not pathological but due to increased activation of Gamma motor neurons associated with nervousness and anxiety. Which of the following is an action of Gamma motor neurons that could produce the mild hyperreflexia? A. Increase sensitivity of Golgi tendon organs B. Increase sensitivity of Ia fibers i ...
Pain bare
... • Act by blocking the production of substances produced in the inflammatory response (eg prostaglandins or bradykinins) which stimulate pain receptors ...
... • Act by blocking the production of substances produced in the inflammatory response (eg prostaglandins or bradykinins) which stimulate pain receptors ...
15 2nd,3rd, 4th &6th..
... The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers run superficially in the nerve and are therefore the first axons to suffer when a nerve is affected by external pressure. Consequently, the first sign of compression of the occulomotor nerve is ipsilateral slowness of the pupillary response to light. ...
... The preganglionic parasympathetic fibers run superficially in the nerve and are therefore the first axons to suffer when a nerve is affected by external pressure. Consequently, the first sign of compression of the occulomotor nerve is ipsilateral slowness of the pupillary response to light. ...
Muscle fiber and motor end plate involvement in the
... partial functional denervation induced by the decreased available area of postjunctional synaptic contact. The presence of dense granules between axon and muscle has been reported in mice paralyzed by tetanus toxin.25 It was suggested that they might have originated from lysosomes of muscle fibers w ...
... partial functional denervation induced by the decreased available area of postjunctional synaptic contact. The presence of dense granules between axon and muscle has been reported in mice paralyzed by tetanus toxin.25 It was suggested that they might have originated from lysosomes of muscle fibers w ...
Brachial Plexus
... Godard Prize by the Academy of Medicine for her work on a particular type of brachial plexus radicular palsy named in her honor. ...
... Godard Prize by the Academy of Medicine for her work on a particular type of brachial plexus radicular palsy named in her honor. ...
Quiz Answers
... cell from depolarizing and block the cell from generating an action potential. Since the action potential is the signal that neurons use in cell-to-cell communication, the ability of a neuron to communicate would be inhibited. 14. Now that you have addressed some of the basic biology of this case, e ...
... cell from depolarizing and block the cell from generating an action potential. Since the action potential is the signal that neurons use in cell-to-cell communication, the ability of a neuron to communicate would be inhibited. 14. Now that you have addressed some of the basic biology of this case, e ...
Document
... Damage to a corresponding spinal nerve will produce loss of sensation the region of skin supplied by a dermatome. 2 and 3 are correct. ...
... Damage to a corresponding spinal nerve will produce loss of sensation the region of skin supplied by a dermatome. 2 and 3 are correct. ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.