Chapter 3
... – This causes kinks or bends in the carbon chain because the maximum number of hydrogen atoms cannot bond to the carbons at the double bond – These compounds are called unsaturated fats because they have fewer than the maximum number of hydrogens – Fats with the maximum number of hydrogens are calle ...
... – This causes kinks or bends in the carbon chain because the maximum number of hydrogen atoms cannot bond to the carbons at the double bond – These compounds are called unsaturated fats because they have fewer than the maximum number of hydrogens – Fats with the maximum number of hydrogens are calle ...
Proteins in nutrition
... Deamination and urea forming are reaction, which are very demanding to liver function. The urea must be consecutive removed from the organism by kidneys. The excessive intake of proteins entails problems for liver and kidneys. Denaturation Denaturation of proteins is very important reaction from nu ...
... Deamination and urea forming are reaction, which are very demanding to liver function. The urea must be consecutive removed from the organism by kidneys. The excessive intake of proteins entails problems for liver and kidneys. Denaturation Denaturation of proteins is very important reaction from nu ...
Translasyon
... bind GTP to bind tRNA. • IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3 bind to 30S subunit to form initiation complex • Once 50S subunit binds initiation complex, GTP is hydrolyzed, initiator tRNA enters P-site and IFs ...
... bind GTP to bind tRNA. • IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3 bind to 30S subunit to form initiation complex • Once 50S subunit binds initiation complex, GTP is hydrolyzed, initiator tRNA enters P-site and IFs ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
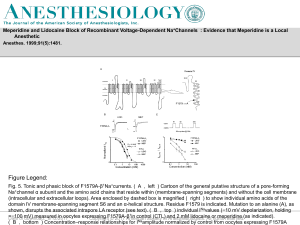
... Fig. 5. Tonic and phasic block of F1579A-β1Na+currents. ( A , left ) Cartoon of the general putative structure of a pore-forming Na+channel α subunit and the amino acid chains that reside within (membrane-spanning segments) and without the cell membrane (intracellular and extracellular loops). Area ...
... Fig. 5. Tonic and phasic block of F1579A-β1Na+currents. ( A , left ) Cartoon of the general putative structure of a pore-forming Na+channel α subunit and the amino acid chains that reside within (membrane-spanning segments) and without the cell membrane (intracellular and extracellular loops). Area ...
Problem 1
... Assume you cannot perform step 2 as described above because your lab ran out of chymotrypsin supply. You are desperate to have the answer and you are looking for an alternative method to use in step 2. Consider the following possibilities: (c) Can you use any of the other three cleavage agents liste ...
... Assume you cannot perform step 2 as described above because your lab ran out of chymotrypsin supply. You are desperate to have the answer and you are looking for an alternative method to use in step 2. Consider the following possibilities: (c) Can you use any of the other three cleavage agents liste ...
Document
... The other crucial contributing factor is that interaction between two hydrophobic surfaces in a solution reduces the hydrophobic surface area and therby INCREASES the number of water-to-water solvent hydrogen bonds!!! ...
... The other crucial contributing factor is that interaction between two hydrophobic surfaces in a solution reduces the hydrophobic surface area and therby INCREASES the number of water-to-water solvent hydrogen bonds!!! ...
Self-Organizing Bio
... DNA in Nanotechnologies Self-Assembly of Polypeptides Proteins in Nanotechnologies ...
... DNA in Nanotechnologies Self-Assembly of Polypeptides Proteins in Nanotechnologies ...
1. Identify the structural formula. Use these choices - burgess
... For each statement, write the letter of one of the structural formulas in number 1 above. A letter can be used more than once. _B_ 2. When many are bonded together, a protein is formed. _C_ 3. It is a disaccharide with the formula C12H22O11 _A_ 4. It is an isomer of fructose and galactose [each have ...
... For each statement, write the letter of one of the structural formulas in number 1 above. A letter can be used more than once. _B_ 2. When many are bonded together, a protein is formed. _C_ 3. It is a disaccharide with the formula C12H22O11 _A_ 4. It is an isomer of fructose and galactose [each have ...
Physical Properties - Winthrop University
... •Steric hindrances may prevent Sn2 reactions •The concentration of both reactants affects the rate ...
... •Steric hindrances may prevent Sn2 reactions •The concentration of both reactants affects the rate ...
... 9. (10 pts) There are only three stable secondary structures. i) What are their names? ii) Describe, or sketch, one of them, indicating the location of H-bonds and sidechains. iii) Assuming that your secondary structure faced the core of the protein, what distribution of polar and nonpolar amino aci ...
Datasheet - LifeSensors
... Interferon stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) is a member of the ubiquitin-like protein family whose expression is increased following stimulation with type 1 Interferons. ISG15-VME is synthesized by the conjugation of 4-amino-but-2-enoic acid methyl ester to the C-terminus of ISG15G156. Binding of ISG15-V ...
... Interferon stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) is a member of the ubiquitin-like protein family whose expression is increased following stimulation with type 1 Interferons. ISG15-VME is synthesized by the conjugation of 4-amino-but-2-enoic acid methyl ester to the C-terminus of ISG15G156. Binding of ISG15-V ...
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 20: Organic bases
... 2. Kb , the base ionization constant, is the equilibrium constant for the reaction of the base with water: ...
... 2. Kb , the base ionization constant, is the equilibrium constant for the reaction of the base with water: ...
LESSON
... they contain weakly acidic and weakly basic groups. C. they are able to absorb great amounts of carbon dioxide during condensation reactions. D. they produce carbonic acid upon hydrolysis. E. All of these. ...
... they contain weakly acidic and weakly basic groups. C. they are able to absorb great amounts of carbon dioxide during condensation reactions. D. they produce carbonic acid upon hydrolysis. E. All of these. ...
Proteins
... • β-pleated sheets: area where 2 or more regions of the polypeptide chain lie in parallel ...
... • β-pleated sheets: area where 2 or more regions of the polypeptide chain lie in parallel ...
IIIb
... 6. (14 pts) The biosynthetic pathways for tryptophan and cystathionine utilize a betaelimination/beta addition process for their synthesis. 1- What is the amino acid that undergoes elimination in each case? 2- What is the component that adds in each case? 3- Pick one of these processes and draw the ...
... 6. (14 pts) The biosynthetic pathways for tryptophan and cystathionine utilize a betaelimination/beta addition process for their synthesis. 1- What is the amino acid that undergoes elimination in each case? 2- What is the component that adds in each case? 3- Pick one of these processes and draw the ...
CHAPTERS 19 AND 20
... Isoelectric point - the pH at which the zwitterion forms Learning check 19.1 Oxidation of cysteine – The -SH on two cysteines lose the hydrogen's through oxidation to form a -S-S-(disulfide bond) and water ...
... Isoelectric point - the pH at which the zwitterion forms Learning check 19.1 Oxidation of cysteine – The -SH on two cysteines lose the hydrogen's through oxidation to form a -S-S-(disulfide bond) and water ...
2. Solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) - RSC Publishing
... The general process for synthesizing peptides on a resin starts by attaching the first amino acid (AA), from the C-terminal residue (carboxyl group), then proceeding with the peptide sequence construction to the N-terminal end. The amino acids are coupled to the supported peptide sequence by the alp ...
... The general process for synthesizing peptides on a resin starts by attaching the first amino acid (AA), from the C-terminal residue (carboxyl group), then proceeding with the peptide sequence construction to the N-terminal end. The amino acids are coupled to the supported peptide sequence by the alp ...
From Gene to Protein Chapter Questions 7) Which of the following
... D) leu-pro-asp-lys-gly E) phe-ser-tyr-cys-leu 19) A particular eukaryotic protein is 300 amino acids long. Which of the following could be the maximum number of nucleotides in the DNA that codes for the amino acids in this protein? A) 3 B) 100 C) 300 D) 900 E) 1,800 20) A codon A) consists of two nu ...
... D) leu-pro-asp-lys-gly E) phe-ser-tyr-cys-leu 19) A particular eukaryotic protein is 300 amino acids long. Which of the following could be the maximum number of nucleotides in the DNA that codes for the amino acids in this protein? A) 3 B) 100 C) 300 D) 900 E) 1,800 20) A codon A) consists of two nu ...
Class Notes 2
... Peptide units are joined by covalent bonds between Cα atoms. Thus – Peptides can rotate along 2 bonds: • N-Cα and Cα-C ...
... Peptide units are joined by covalent bonds between Cα atoms. Thus – Peptides can rotate along 2 bonds: • N-Cα and Cα-C ...
Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Culture (SILAC)
... amino acid is supplied to cells in culture instead of the natural amino acid, it is incorporated into all newly synthesized proteins. After a number of cell divisions, each instance of this particular amino acid will be replaced by its isotope-labeled analog. Since there is hardly any chemical diffe ...
... amino acid is supplied to cells in culture instead of the natural amino acid, it is incorporated into all newly synthesized proteins. After a number of cell divisions, each instance of this particular amino acid will be replaced by its isotope-labeled analog. Since there is hardly any chemical diffe ...
Document
... • Tertiary structure – Interaction among the R groups of amino acids – Interactions include ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and covalent bonds – What type of amino acids involved in each? ...
... • Tertiary structure – Interaction among the R groups of amino acids – Interactions include ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and covalent bonds – What type of amino acids involved in each? ...
Sample Exam #1 ( file)
... Which of the following is NOT correct about amino acids? A. Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms. B. Amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group fastened to an asymmetric carbon. C. Amino acids can make peptide bonds. D. There are over 30 kinds of individual amino acids found in t ...
... Which of the following is NOT correct about amino acids? A. Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms. B. Amino acids contain an amino group and a carboxyl group fastened to an asymmetric carbon. C. Amino acids can make peptide bonds. D. There are over 30 kinds of individual amino acids found in t ...
Chapter 1
... • Lysine – Ketogenic - catabolism yields acetyl CoA – Disorders of lysine metabolism ...
... • Lysine – Ketogenic - catabolism yields acetyl CoA – Disorders of lysine metabolism ...