BIOCHEMISTRY
... Hydrocarbons $30 What is the removing of water to join monomers called? What is the addition of water to split polymers called? Dehydration synthesis Hydrolysis Cinda Sheldon ...
... Hydrocarbons $30 What is the removing of water to join monomers called? What is the addition of water to split polymers called? Dehydration synthesis Hydrolysis Cinda Sheldon ...
Room-temperature-curable resin composition
... proportions that the proportion of the active hydrogen The vinyl polymer (B) having both of the above containing group in the compound (a-4) is about 0.5 to 20 reactive groups may be prepared by applying any known methods. Examples of simple methods include 3 equivalents per equivalent of the acid a ...
... proportions that the proportion of the active hydrogen The vinyl polymer (B) having both of the above containing group in the compound (a-4) is about 0.5 to 20 reactive groups may be prepared by applying any known methods. Examples of simple methods include 3 equivalents per equivalent of the acid a ...
NITROGEN METABOLISM
... ammonia is called nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation, is a reductive process i.e., nitrogen fixation will stop if there is no reducing condition or if oxygen is present. This nitrogen fixation may take place by two different methods – abiological and biological. 10.2.1 Abiological nitrogen fixatio ...
... ammonia is called nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation, is a reductive process i.e., nitrogen fixation will stop if there is no reducing condition or if oxygen is present. This nitrogen fixation may take place by two different methods – abiological and biological. 10.2.1 Abiological nitrogen fixatio ...
2. Lect. Urea cycle
... For example, the malate can be transported into the mitochondria via the malate shuttle, reenter the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and get oxidized to oxaloacetate (OAA), which can be used for gluconeogenesis . Alternatively, the OAA can be converted to aspartate via transamination , and can enter the ...
... For example, the malate can be transported into the mitochondria via the malate shuttle, reenter the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and get oxidized to oxaloacetate (OAA), which can be used for gluconeogenesis . Alternatively, the OAA can be converted to aspartate via transamination , and can enter the ...
On the origin of biochemistry at an alkaline hydrothermal vent
... activity). CO from the C cluster traverses the enzyme and binds at the A cluster, presumably to the methylbearing Ni atom (Volbeda & Fontecilla-Camps 2006). The bound carbonyl is thought to be attacked by the methyl to yield a transition metal-bound acetyl moiety that is subsequently removed from th ...
... activity). CO from the C cluster traverses the enzyme and binds at the A cluster, presumably to the methylbearing Ni atom (Volbeda & Fontecilla-Camps 2006). The bound carbonyl is thought to be attacked by the methyl to yield a transition metal-bound acetyl moiety that is subsequently removed from th ...
as a PDF
... Systemic pH regulation was seen to involve two principal organs: the lungs, which adjust the pCO2 and the kidneys excreting acid or generating bicarbonate. The kidney of omnivorous mammals provides several mechanisms to counteract the development of metabolic acidosis: proximal tubular bicarbonate r ...
... Systemic pH regulation was seen to involve two principal organs: the lungs, which adjust the pCO2 and the kidneys excreting acid or generating bicarbonate. The kidney of omnivorous mammals provides several mechanisms to counteract the development of metabolic acidosis: proximal tubular bicarbonate r ...
FATTY ACID METABOLISM
... mitochondrial matrix. 2. Intermediates in fatty acid synthesis are covalently linked to the sulfhydryl groups of an acyl carrier protein (ACP), whereas intermediates in fatty acid breakdown are covalently attached to the sulfhydryl group of coenzyme A. 3. The enzymes of fatty acid synthesis in highe ...
... mitochondrial matrix. 2. Intermediates in fatty acid synthesis are covalently linked to the sulfhydryl groups of an acyl carrier protein (ACP), whereas intermediates in fatty acid breakdown are covalently attached to the sulfhydryl group of coenzyme A. 3. The enzymes of fatty acid synthesis in highe ...
Unit 6 Vitamins Defining a vitamin Essential
... Rare; Listlessness, fatigue, headache, sleep disturbance, nausea, abdominal distress; Alcoholics at risk Usually in combination with other deficiencies Vitamin B5: _____________________ Exists in free and protein-bound (biocytin) forms; biocytin must be cleaved from protein by biotinidase before bei ...
... Rare; Listlessness, fatigue, headache, sleep disturbance, nausea, abdominal distress; Alcoholics at risk Usually in combination with other deficiencies Vitamin B5: _____________________ Exists in free and protein-bound (biocytin) forms; biocytin must be cleaved from protein by biotinidase before bei ...
Glutathione as an endogenous sulphur source in the
... Besides thiol compounds, the intracellular concentrations of certain amino acids were also affected by the mutation leading to GSH deficiency, especially when S. cerevisiae cells were grown on MM medium using ammonia as the nitrogen source (Table 1). Among the amino acids affected were threonine, se ...
... Besides thiol compounds, the intracellular concentrations of certain amino acids were also affected by the mutation leading to GSH deficiency, especially when S. cerevisiae cells were grown on MM medium using ammonia as the nitrogen source (Table 1). Among the amino acids affected were threonine, se ...
12_chemistry_impq_CH13_amines_02
... Acetylation (or ethanoylation) is the process of introducing an acetyl group into a molecule. Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines undergo acetylation reaction by nucleophilic substitution when treated with acid chlorides, anhydrides or esters. This reaction involves the replacement o ...
... Acetylation (or ethanoylation) is the process of introducing an acetyl group into a molecule. Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines undergo acetylation reaction by nucleophilic substitution when treated with acid chlorides, anhydrides or esters. This reaction involves the replacement o ...
Full-Text PDF
... the total hydrophobic amino acids content in SPH constituted 34.71%. Udenigwe et al. [14] indicated that acidic amino acids such as Glu and Asp contributed to the antioxidant activities of peptides due to the presence of excess electrons which could be donated during interaction with free radicals. ...
... the total hydrophobic amino acids content in SPH constituted 34.71%. Udenigwe et al. [14] indicated that acidic amino acids such as Glu and Asp contributed to the antioxidant activities of peptides due to the presence of excess electrons which could be donated during interaction with free radicals. ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... • Mono-, di-, and triacylglycerols consist of one, two, or three molecules of fatty acid esterified to a molecule of glycerol. • Fatty acids are esterified through their carboxyl groups, resulting in a loss of negative charge and formation of “neutral fat.” [Note: If a species of acylglycerol is sol ...
... • Mono-, di-, and triacylglycerols consist of one, two, or three molecules of fatty acid esterified to a molecule of glycerol. • Fatty acids are esterified through their carboxyl groups, resulting in a loss of negative charge and formation of “neutral fat.” [Note: If a species of acylglycerol is sol ...
Determination of amino acid enantiomers in human urine and blood
... with ninhydrin according to Spackman et al., (1958). Chiral resolution and determination of relative amounts of D-AAs was performed by GC of N(O)-pentafluoropropionyl amino acid (2)-propyl esters on Chirasil-L-Val (N-propionyl-L-valinetert-butylamide polysiloxane; Chrompack, Middelburg, The Netherla ...
... with ninhydrin according to Spackman et al., (1958). Chiral resolution and determination of relative amounts of D-AAs was performed by GC of N(O)-pentafluoropropionyl amino acid (2)-propyl esters on Chirasil-L-Val (N-propionyl-L-valinetert-butylamide polysiloxane; Chrompack, Middelburg, The Netherla ...
Oxidation and biosynthesis of fatty acids
... Domain 1 contains transacylases, ketoacyl-ACP synthase (condensing enzyme) Domain 2 contains acyl carrier protein, b-ketoacyl reductase, dehydratase, and enoyl reductase. Domain 3 contains thioesterase activity. ...
... Domain 1 contains transacylases, ketoacyl-ACP synthase (condensing enzyme) Domain 2 contains acyl carrier protein, b-ketoacyl reductase, dehydratase, and enoyl reductase. Domain 3 contains thioesterase activity. ...
Lecture 1 - "Hudel" Luecke
... http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html (1 of 4)5/24/2007 12:49:06 PM ...
... http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html (1 of 4)5/24/2007 12:49:06 PM ...
Unique amino acid signatures that are evolutionarily conserved
... homodimers is unclear. The abundance of keratin polypeptides, coupled with their cellspecific expression suggests that keratins have evolved to fulfill specific requirements for specialized epithelial tissues. To support this hypothesis, several studies have demonstrated that the loss of a particula ...
... homodimers is unclear. The abundance of keratin polypeptides, coupled with their cellspecific expression suggests that keratins have evolved to fulfill specific requirements for specialized epithelial tissues. To support this hypothesis, several studies have demonstrated that the loss of a particula ...
Carbon metabolism in transgenic roots with altered levels
... different levels of hexokinase (HK) or cytosolic triosephosphate isomerase (cTPI) growing under different nitrogen regimes. The flux of carbon through the oxPPP in cTPI antisense roots is higher than control roots growing under high supply of N. On the other hand, the conversion of Glucose (Glc) to ...
... different levels of hexokinase (HK) or cytosolic triosephosphate isomerase (cTPI) growing under different nitrogen regimes. The flux of carbon through the oxPPP in cTPI antisense roots is higher than control roots growing under high supply of N. On the other hand, the conversion of Glucose (Glc) to ...
SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION STUDY OF PHYSICAL MIXTURE OF CARBAMAZEPINE AND
... absorption. Consequently CBZ absorption becomes slow when used orally to be erratic bioavailability [10-12]. The dissolution rate is proportional to the saturation solubility of the drug and the surface area of the drug particles under hydrodynamic conditions. Dissolution rate can be increased by de ...
... absorption. Consequently CBZ absorption becomes slow when used orally to be erratic bioavailability [10-12]. The dissolution rate is proportional to the saturation solubility of the drug and the surface area of the drug particles under hydrodynamic conditions. Dissolution rate can be increased by de ...
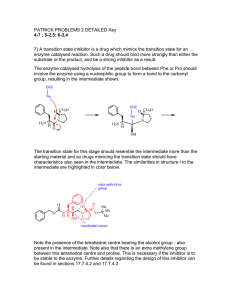
PATRICK PROBLEMS 2 Key
... be stable to the enzyme. Further details regarding the design of this inhibitor can be found in sections 17.7.4.2 and 17.7.4.3 ...
... be stable to the enzyme. Further details regarding the design of this inhibitor can be found in sections 17.7.4.2 and 17.7.4.3 ...
CP1 Domain in Escherichia coli Leucyl
... described above. Aminoacylation activity of LeuRS and LeuRS-B was measured in the standard buffer containing 0.1 mM [14C]leucine with the addition of methionine or isoleucine at concentrations ranging from 10 to 50 mM, which will compete with leucine for activation and transfer to tRNALeu. These mis ...
... described above. Aminoacylation activity of LeuRS and LeuRS-B was measured in the standard buffer containing 0.1 mM [14C]leucine with the addition of methionine or isoleucine at concentrations ranging from 10 to 50 mM, which will compete with leucine for activation and transfer to tRNALeu. These mis ...
Regulation of Acetyl-Coenzyme A Carboxylase and Acetyl
... acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in rapidly Triton X-100 lysed spinach chloroplasts show an activation by light and deactivation in the dark. The stim ulation o f acetyl-CoA carboxylase by dithiothreitol in darkened chloroplasts points to an involvem ent o f reducing equivalents in ...
... acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in rapidly Triton X-100 lysed spinach chloroplasts show an activation by light and deactivation in the dark. The stim ulation o f acetyl-CoA carboxylase by dithiothreitol in darkened chloroplasts points to an involvem ent o f reducing equivalents in ...
Regulation of Acetyl-Coenzyme A Carboxylase and
... acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in rapidly Triton X-100 lysed spinach chloroplasts show an activation by light and deactivation in the dark. The stim ulation o f acetyl-CoA carboxylase by dithiothreitol in darkened chloroplasts points to an involvem ent o f reducing equivalents in ...
... acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in rapidly Triton X-100 lysed spinach chloroplasts show an activation by light and deactivation in the dark. The stim ulation o f acetyl-CoA carboxylase by dithiothreitol in darkened chloroplasts points to an involvem ent o f reducing equivalents in ...