Internet 0: Interdevice Internetworking - Publications
... guiding principles that it demonstrated; no one of these is new, but their intersection is unlike both the Internet as it exists today and all of the competing alternatives for networking things. Taken together, they provide the architecture for Internet 0: IP to leaf nodes. Each device in the Media ...
... guiding principles that it demonstrated; no one of these is new, but their intersection is unlike both the Internet as it exists today and all of the competing alternatives for networking things. Taken together, they provide the architecture for Internet 0: IP to leaf nodes. Each device in the Media ...
Networking
... function calls to the hardware’s specific required software in order to run • Can run in both kernel and user mode • Kernel mode used mainly for speed • User mode used mainly for stability ...
... function calls to the hardware’s specific required software in order to run • Can run in both kernel and user mode • Kernel mode used mainly for speed • User mode used mainly for stability ...
Network
... WAN Intercommunication over public networks Typically slower and more expensive than backbone or LAN ...
... WAN Intercommunication over public networks Typically slower and more expensive than backbone or LAN ...
part 5
... classes, encoded in IP’s ToS bits These bits can be set by ISP edge routers, handled by internal routers according to ISP ...
... classes, encoded in IP’s ToS bits These bits can be set by ISP edge routers, handled by internal routers according to ISP ...
20120423-boote-perfportal
... – Control-panel displaying services of interest to the specific user based on InCommon identity – Different levels of data access based on member institution assertions ...
... – Control-panel displaying services of interest to the specific user based on InCommon identity – Different levels of data access based on member institution assertions ...
Session2
... A worm is a self-replicating malware program, which uses a computer network to send copies of itself to other nodes and it may do so without any user involvement. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the ne ...
... A worm is a self-replicating malware program, which uses a computer network to send copies of itself to other nodes and it may do so without any user involvement. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the ne ...
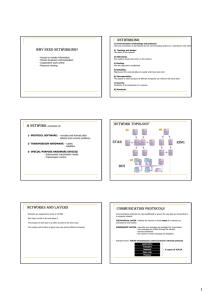
WHY NEED NETWORKING? NETWORKING NETWORK
... For example, all marketing personnel may be spread throughout a building. Yet if they are all assigned to a single VLAN, they can share resources and bandwidth as if they were connected to the same segment. ...
... For example, all marketing personnel may be spread throughout a building. Yet if they are all assigned to a single VLAN, they can share resources and bandwidth as if they were connected to the same segment. ...
Study Guide - Csulb.edu
... Packet switching: A technique used on computer networks for sending information that divides messages into small packets before sending. ...
... Packet switching: A technique used on computer networks for sending information that divides messages into small packets before sending. ...
Introduction
... The field of network security is about: how bad guys can attack computer networks how we can defend networks against attacks how to design architectures that are immune to attacks Internet not originally designed with ...
... The field of network security is about: how bad guys can attack computer networks how we can defend networks against attacks how to design architectures that are immune to attacks Internet not originally designed with ...
Kuliah Komunikasi Data
... defines the way in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected. A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions. ...
... defines the way in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected. A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions. ...
Networking
... The purpose of this basic IP technology training is to explain video over an IP network. This training describes how video can be used on a network using IP protocol and enables individuals to understand how the IP network can respond to today’s increasing need of sharing video at any time and from ...
... The purpose of this basic IP technology training is to explain video over an IP network. This training describes how video can be used on a network using IP protocol and enables individuals to understand how the IP network can respond to today’s increasing need of sharing video at any time and from ...
Chapter 1/Tutorial
... information across a single link that transfers data between adjacent network nodes. PPP : commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes . It can provide connection authentication , transmission encryption used over many types of physical networks including . ...
... information across a single link that transfers data between adjacent network nodes. PPP : commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes . It can provide connection authentication , transmission encryption used over many types of physical networks including . ...
Analytical work on 7DS
... 802.11 currently hard to deploy across city or large area 2.5G/3G wireless networks not suitable for large data volumes – cost and network design ...
... 802.11 currently hard to deploy across city or large area 2.5G/3G wireless networks not suitable for large data volumes – cost and network design ...
Job Description – Network Operations Engineer
... demonstrable skills needed to fulfill this role whilst experienced members of the team will help you develop your skills and confidence. We interact frequently with Technical Support, Managed Support, Service Provisioning and Sales teams so it's important that we are able to communicate ideas and in ...
... demonstrable skills needed to fulfill this role whilst experienced members of the team will help you develop your skills and confidence. We interact frequently with Technical Support, Managed Support, Service Provisioning and Sales teams so it's important that we are able to communicate ideas and in ...
Emerging Wireless Internet Standards
... “We make the net work” The mission of the IETF is to produce high quality, relevant technical and engineering documents that influence the way people design, use, and manage the Internet in such a way as to make the Internet work better. These documents include protocol standards, best current pract ...
... “We make the net work” The mission of the IETF is to produce high quality, relevant technical and engineering documents that influence the way people design, use, and manage the Internet in such a way as to make the Internet work better. These documents include protocol standards, best current pract ...
NetworkingReview
... 6. Explain the hidden terminal problem for wireless networks. What is a solution? 7. At what layer in the TCP/IP protocol hierarchy would a firewall be placed to filter messages based on a. Message content b. Source address c. Type of application 8. What is the internet2? Give an example that motiva ...
... 6. Explain the hidden terminal problem for wireless networks. What is a solution? 7. At what layer in the TCP/IP protocol hierarchy would a firewall be placed to filter messages based on a. Message content b. Source address c. Type of application 8. What is the internet2? Give an example that motiva ...
MPLS Based Web Switching
... Two-tier mesh networks First tier : access point for user Second tier : access points interconnected via a wireless mesh Backhaul to the Internet from a few points in the second tier mesh Eases deployment and cost ...
... Two-tier mesh networks First tier : access point for user Second tier : access points interconnected via a wireless mesh Backhaul to the Internet from a few points in the second tier mesh Eases deployment and cost ...
ch01
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
BigPond ElitE™ WiRElESS
... broadband network in Australia. It covers 2 million square kilometres, is more than twice as large as any of our competitors’ 3G networks and can reach 99% of Australia’s population*. Using a BigPond Elite™ device, customers can experience typical download speeds of 550kbps to 8Mbps and typical uplo ...
... broadband network in Australia. It covers 2 million square kilometres, is more than twice as large as any of our competitors’ 3G networks and can reach 99% of Australia’s population*. Using a BigPond Elite™ device, customers can experience typical download speeds of 550kbps to 8Mbps and typical uplo ...
Lecture 1 Introduction to the Computers
... • Tables of DNs & IP addresses are distributed throughout the Internet on numerous servers • There is a DNS server at most ISPs. It converts the domain names in our Internet requests to actual IP addresses • In case it does not have a particular domain name in its table, it makes a request to anothe ...
... • Tables of DNs & IP addresses are distributed throughout the Internet on numerous servers • There is a DNS server at most ISPs. It converts the domain names in our Internet requests to actual IP addresses • In case it does not have a particular domain name in its table, it makes a request to anothe ...