* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Session2
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
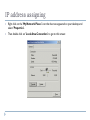
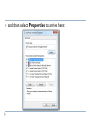
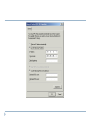
Content Overview of Computer Networks (Wireless and Wired) IP Address, MAC Address and Workgroups LAN Setup and Creating Workgroup Concept on typical Servers (Proxy, DNS, Web, Mail) File, Folder, Printer, Scanner Sharing over LAN Browser Configuration and Internet Options File download and popup unblock Internet virus, spyware, malware, spam Searching in the web E-mail Computer Networks Computer network connects two or more autonomous computers. The computers can be geographically located anywhere. Overview of Computer Networks (Wireless & Wired) Connection among computer for Information/ data and resource sharing. Wireless and Wired A popular example of a computer network is the internet, which allows millions of users to share information Computer networks can be classified according to their size: Local Area Network (LAN) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Wide Area Network (WAN) LAN, MAN & WAN Network in small geographical Area (Room, Building or a Campus) is called LAN (Local Area Network) Network in a City is call MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) Network spread geographically (Country or across Globe) is called WAN (Wide Area Network) Also know as Internet Applications of Networks Resource Sharing Information Sharing Easy accessibility from anywhere (files, databases) Search Capability (WWW) Communication Hardware (computing resources, disks, printers) Software (application software) Email Message broadcast Remote computing Distributed processing (GRID Computing) Networking Media Networking media can be defined simply as the means by which signals (data) are sent from one computer to another (either by cable or wireless means). Wireless Wired IP Address, MAC Address and Workgroups IP Address- a unique number which identifies a computer and its location on the internet. Like mobile number 32 bits (4 bytes) in length (0-255) MAC Address- Media Access Control address is a unique identifier assigned to most network adapters or network interface cards (NICs) by the manufacturer… Workgroups- like room Local Area Network (LAN) A LAN is a network that is used for communicating among computer devices, usually within an office building or home LAN’s enable the sharing of resources such as files or hardware devices that may be needed by multiple users. (printer, scanner sharing) Two types of LAN: server-client base, simple LAN Setup Hardware: NIC Card, UTP Cable, RJ 45 connector Two steps IP address assigning Workgroup creating Start Control Panel Network Connections Create a new connection IP address assigning Right click on the 'My Network Places' icon that has now appeared on your desktop and select 'Properties'. Then double click on 'Local Area Connection' to get to this screen: and then select Properties to arrive here: Use the following an IP address Selected IP Address 192.168.1-254.1-254 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 File, Folder, Printer, Scanner Sharing over LAN Lets see Concept on typical Servers (Proxy, DNS, Web, Mail) Proxy Server Server that stands between an external network (such as Internet) and an organization's internal (private) networks and serves as a firewall. It prevents external users from directly accessing the internal information resources, or even knowing their location. Server that stores frequently requested information (documents or files) from elsewhere in the network and makes it available to the users. While this arrangement results in higher access speed. It is possible to filter unwanted website (nude or adult website). A proxy server improves Internet access speeds from a network primarily by using a caching system. When we use internet through proxy server then we need to configure our web browser by setting proxy IP DNS Server: Converting/mapping web address to IP address. www.google.com 152.76.93.12 Web Server: hold website/ webpage (http protocol) Mail Server: for email (POP3, SMTP protocol) Browser Configuration and Internet Options Home page adding Firefox menu Options Options General (for Mozilla Firefox Browser) (New version) Or menu tools Options General Popup unblock Firefox menu Options Options Content (for Mozilla Firefox Browser) Font Size Proxy setup: menu tools Options Advance Network Settings (manual proxy configuration) 192.168.1.1 (Proxy server address) JavaScript block/ unblock menu tools Options contents Internet virus, spyware, malware, spam A computer virus is a harmful program that is secretly introduced into a system in order to corrupt it or destroy data. Its has self replication and spread capability. Malware, short for malicious software, is a software designed to harm or secretly access a computer system without the owner's informed consent. Spyware is a type of malware that can be installed on computers, and which collects small pieces of information about users without their knowledge. The presence of spyware is typically hidden from the user, and can be difficult to detect. A worm is a self-replicating malware program, which uses a computer network to send copies of itself to other nodes and it may do so without any user involvement. Unlike a computer virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer. Adware, or advertising-supported software, is any software package which automatically plays, displays, or downloads advertisements to a computer. ??