Improving Function Prediction Using Patterns of Native Disorder in
... Instrinsically unstructured (disordered) proteins adopt little or no stable secondary structure in their native state. Proteins containing long disordered regions are abundant within eukaryotic genomes and can be predicted successfully from amino sequence. Disordered regions have been shown to be im ...
... Instrinsically unstructured (disordered) proteins adopt little or no stable secondary structure in their native state. Proteins containing long disordered regions are abundant within eukaryotic genomes and can be predicted successfully from amino sequence. Disordered regions have been shown to be im ...
Protein Synthesis
... Protein synthesis occurs at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of a cell. But--DNA is in the nucleus. ...
... Protein synthesis occurs at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of a cell. But--DNA is in the nucleus. ...
Unit1-KA4-Revision
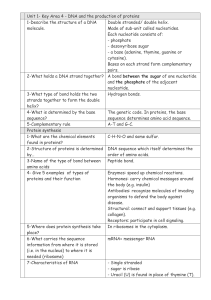
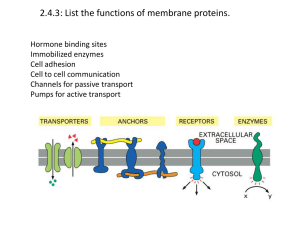
... 2-Structure of proteins is determined DNA sequence which itself determines the by… order of amino acids. 3-Name of the type of bond between Peptide bond. amino acids 4- Give 5 examples of types of Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions. proteins and their function Hormones: carry chemical messages aro ...
... 2-Structure of proteins is determined DNA sequence which itself determines the by… order of amino acids. 3-Name of the type of bond between Peptide bond. amino acids 4- Give 5 examples of types of Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions. proteins and their function Hormones: carry chemical messages aro ...
Heller’s-ring-test
... A white ring is formed at the junction of two solutions. This ring is made up of denatured protein. Yellow colour in the ring is due to nitro compound of ...
... A white ring is formed at the junction of two solutions. This ring is made up of denatured protein. Yellow colour in the ring is due to nitro compound of ...
Life’s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon 8/25/2011 1
... • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
... • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
http://gslc. genetics. utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/
... http:// gslc. genetics. utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/ Defme the following terms: Transcription, Translation, Codon Complete the "Build a Protein" Activity You will need to record the sequence of bases in the mRNA as well as the sequence of amino acids on a separate piece of paper that I will col ...
... http:// gslc. genetics. utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/ Defme the following terms: Transcription, Translation, Codon Complete the "Build a Protein" Activity You will need to record the sequence of bases in the mRNA as well as the sequence of amino acids on a separate piece of paper that I will col ...
Document
... Form structures such as hair and fur, make up muscles, and provide long term nutrient storage. Circulate in the blood and defend the body from harmful microorganisms, act as signals. Control chemical reactions in a cell. ...
... Form structures such as hair and fur, make up muscles, and provide long term nutrient storage. Circulate in the blood and defend the body from harmful microorganisms, act as signals. Control chemical reactions in a cell. ...
Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
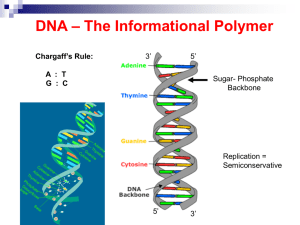
... Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 di ...
... Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 di ...
Protein
... Protein Foods high in protein are Animal products, nuts, lentils, soy, dairy, cheese ...
... Protein Foods high in protein are Animal products, nuts, lentils, soy, dairy, cheese ...
On the Origin of Language
... intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
... intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
Major Organic Groups - Lemon Bay High School
... Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
... Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
Proteins - Kaikoura High School
... • Primary structure = order of amino acids • Secondary structure = how tight the coil or chain is • Tertiary structure = how the chains loop back on themselves again and again. • Quaternary structure = how separate ...
... • Primary structure = order of amino acids • Secondary structure = how tight the coil or chain is • Tertiary structure = how the chains loop back on themselves again and again. • Quaternary structure = how separate ...
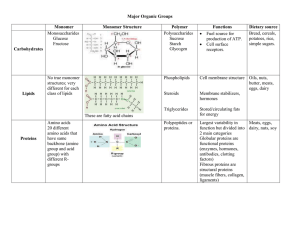
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer
... Outline of Information to pull out of pp. 46-50 in Text book ...
... Outline of Information to pull out of pp. 46-50 in Text book ...
Protein

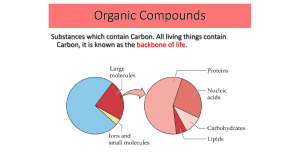
Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.