A One- or Two-Day Course for Your Campus on
... ligands, substrates, and drugs, and protein evolutionary conservation. Handson experience will be largely with molecules of each participant's choosing. Participants will learn easy methods for creating publication-quality molecular images, and how to put snapshots or rotating animations in Powerpoi ...
... ligands, substrates, and drugs, and protein evolutionary conservation. Handson experience will be largely with molecules of each participant's choosing. Participants will learn easy methods for creating publication-quality molecular images, and how to put snapshots or rotating animations in Powerpoi ...
Proteins – where do they come from?
... • The mRNA is either read by another ribosome or it is recycled so its nucleotides can be used again. • The ribosome large and small subunit falls apart from each other ...
... • The mRNA is either read by another ribosome or it is recycled so its nucleotides can be used again. • The ribosome large and small subunit falls apart from each other ...
THE CENTRAL DOGMA THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... about its properties/function? For example: 1. A protein that is rich in hydrophobic amino acids 2. Histones – rich in Arg, Lys ...
... about its properties/function? For example: 1. A protein that is rich in hydrophobic amino acids 2. Histones – rich in Arg, Lys ...
Day 2: Protein Sequence Analysis
... Used to predict whether a protein is localized in the cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, or is retained in the ER, or destined for lysosome (vacuolar) or the peroxisome. ...
... Used to predict whether a protein is localized in the cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, or is retained in the ER, or destined for lysosome (vacuolar) or the peroxisome. ...
Proteins - Science Learning Hub
... This dipeptide (two amino acids linked together) is known as glycylalanine and is represented as Gly-Ala using the three-letter amino acid coding system. Peptides and proteins Chains with fewer than 50 amino acids are called peptides, while the term protein is reserved for longer chains which, unlik ...
... This dipeptide (two amino acids linked together) is known as glycylalanine and is represented as Gly-Ala using the three-letter amino acid coding system. Peptides and proteins Chains with fewer than 50 amino acids are called peptides, while the term protein is reserved for longer chains which, unlik ...
chemistry_and_proteins
... the sequence aminoacids in the proteins. Series of three nucleotides specifies one amino acid. • This chart identifies each amino acid by its three-letter codon(s). For example, G under the "first letter" column, C under the "second letter" column, and A under the "third letter" column intersect at ...
... the sequence aminoacids in the proteins. Series of three nucleotides specifies one amino acid. • This chart identifies each amino acid by its three-letter codon(s). For example, G under the "first letter" column, C under the "second letter" column, and A under the "third letter" column intersect at ...
Protein Folding and Quality Control
... Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide being synthesized. Proteins will fold during s ...
... Function: making specific functional domains critical for function (occurs following or coincident with synthesis) Sequence dependence: Final structure of protein is dependent on amino acid sequence and properties of amino acids that make up polypeptide being synthesized. Proteins will fold during s ...
Slide 1
... Protein synthesis: series of steps that convert the DNA code into an organism’s features. Steps… 1. Focus on a single gene on a chromosome in the nucleus 2. DNA code gets converted to mRNA code by transcription (C-G, G-C, T-A, A-U) ...
... Protein synthesis: series of steps that convert the DNA code into an organism’s features. Steps… 1. Focus on a single gene on a chromosome in the nucleus 2. DNA code gets converted to mRNA code by transcription (C-G, G-C, T-A, A-U) ...
Classification of Amino Acids
... SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) binds to proteins roughly proportional to the molecular weight of the protein Binding of 1 SDS/ 2 amino acids ...
... SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) binds to proteins roughly proportional to the molecular weight of the protein Binding of 1 SDS/ 2 amino acids ...
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS IN THE BODY FUNCTIONS OF
... will determine the cell's water content, as water is attracted to protein. When protein levels are low, fluid imbalances result. This type of system is important to prevent dehydration , as well as to enhance muscle and nerve cell function. SOURCES OF PROTEIN "Amino acids" is the name given to the b ...
... will determine the cell's water content, as water is attracted to protein. When protein levels are low, fluid imbalances result. This type of system is important to prevent dehydration , as well as to enhance muscle and nerve cell function. SOURCES OF PROTEIN "Amino acids" is the name given to the b ...
Ch 5 ppt
... In the case of Thalidomide, it was discovered that only one of the two enantiomeric ...
... In the case of Thalidomide, it was discovered that only one of the two enantiomeric ...
Clp proteins in photosynthetic organisms: An essential family of
... structure of most proteins within a cell. They are found in all organisms and are separated into many different families. One such family is Clp, which in photosynthetic organisms plays an essential role for cell function and overall survival. My group has been studying the Clp family of molecular c ...
... structure of most proteins within a cell. They are found in all organisms and are separated into many different families. One such family is Clp, which in photosynthetic organisms plays an essential role for cell function and overall survival. My group has been studying the Clp family of molecular c ...
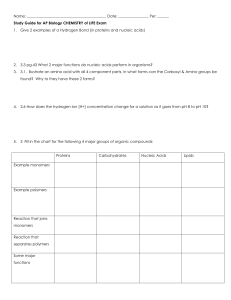
Name: Date: Per: ______ Study Guide for AP Biology CHEMISTRY
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins pr ...
... Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins pr ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins pr ...
... Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins pr ...
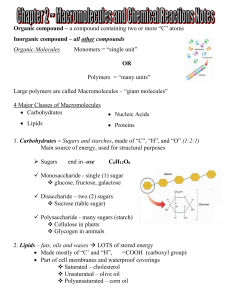
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.