A perturbation-based method for calculating explicit likelihood of
... Their interdependence should be apparent in the evolutionary record of each protein family: positions in the sequence of a protein family that are intimately associated in space or in function should co-vary in evolution. A recent approach by Ranganathan and colleagues proposes to look at subsets of ...
... Their interdependence should be apparent in the evolutionary record of each protein family: positions in the sequence of a protein family that are intimately associated in space or in function should co-vary in evolution. A recent approach by Ranganathan and colleagues proposes to look at subsets of ...
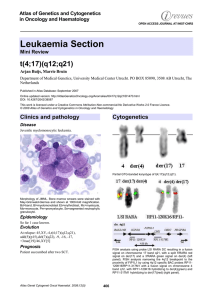
Leukaemia Section t(4;17)(q12;q21) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... amino-terminal amino acids of FIP1L, including the FIP homology domain and 403 carboxyl-terminal amino acids of RARA, including the DNA and ligand binding domains, with replacement of FIP1L1 amino acid 429 (Valine) and RARA amino acid 60 (Threonine) into an Alanine. Oncogenesis All known chimeric RA ...
... amino-terminal amino acids of FIP1L, including the FIP homology domain and 403 carboxyl-terminal amino acids of RARA, including the DNA and ligand binding domains, with replacement of FIP1L1 amino acid 429 (Valine) and RARA amino acid 60 (Threonine) into an Alanine. Oncogenesis All known chimeric RA ...
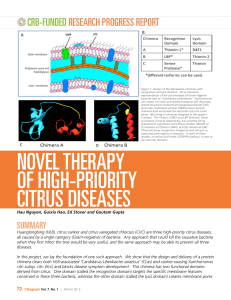
novel therapy of high-priority citrus diseases
... category, thereby allowing us to choose the chimera with the highest anti-bacterial activity. Thionin1-D4E1 chimera was the first one that we started working on three years ago. At that time, the sequence of the citrus genome was not completed, and hence complete screening of citrus Thionins was not ...
... category, thereby allowing us to choose the chimera with the highest anti-bacterial activity. Thionin1-D4E1 chimera was the first one that we started working on three years ago. At that time, the sequence of the citrus genome was not completed, and hence complete screening of citrus Thionins was not ...
Hemoglobin Receptor in Leishmania Is a Hexokinase Located in the
... isolated from Leishmania promastigotes using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) was used for cDNA synthesis using Super ScriptII reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Subsequently, PCR was performed using the above-mentioned primers and Platinum HiFidelity Taq pol ...
... isolated from Leishmania promastigotes using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) was used for cDNA synthesis using Super ScriptII reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Subsequently, PCR was performed using the above-mentioned primers and Platinum HiFidelity Taq pol ...
High pKa variability of cysteine residues in structural databases and
... these oxidations are effectively counteracted through natural defensive mechanisms [9]; however, intense and/or persistent levels of ROS stress ultimately lead to protein damage (misfolding, cross-linkages, inactivation of functional residues) [10,11]. A critically important aspect of Cys reactivity ...
... these oxidations are effectively counteracted through natural defensive mechanisms [9]; however, intense and/or persistent levels of ROS stress ultimately lead to protein damage (misfolding, cross-linkages, inactivation of functional residues) [10,11]. A critically important aspect of Cys reactivity ...
Safety Assessment of Soy Proteins and Peptides as Used in
... 71 kDa) and β (ca 50 kDa). The 11S globulin is a hexamer, and is made up of five different subunits, each of which consists of an acidic subunit A (ca 35 kDa) and a basic subunit B (ca 20 kDa), linked by a disulfide bond. The 11S globulin was found to dissociate into 2S, 3S or 7S forms in solutions ...
... 71 kDa) and β (ca 50 kDa). The 11S globulin is a hexamer, and is made up of five different subunits, each of which consists of an acidic subunit A (ca 35 kDa) and a basic subunit B (ca 20 kDa), linked by a disulfide bond. The 11S globulin was found to dissociate into 2S, 3S or 7S forms in solutions ...
Cellular uptake of long-chain fatty acids: role of membrane
... energy source, building blocks for membrane lipids and cellular signalling molecules such as eicosanoids [2–6]. In addition, fatty acids may directly or indirectly interact with membranes, transporters, ion channels, enzymes or hormone receptors and thus regulate various cell functions [2 – 6]. Esse ...
... energy source, building blocks for membrane lipids and cellular signalling molecules such as eicosanoids [2–6]. In addition, fatty acids may directly or indirectly interact with membranes, transporters, ion channels, enzymes or hormone receptors and thus regulate various cell functions [2 – 6]. Esse ...
OptCDR: a general computational method for the design
... majority of antibody-binding interactions. Humanization (Almagro and Fransson, 2008) is a common experimental technique where the CDRs from a non-human antibody are attached to the framework of a human antibody, thereby retaining the binding properties of the non-human antibody while decreasing or e ...
... majority of antibody-binding interactions. Humanization (Almagro and Fransson, 2008) is a common experimental technique where the CDRs from a non-human antibody are attached to the framework of a human antibody, thereby retaining the binding properties of the non-human antibody while decreasing or e ...
Renin Precursor Synthesis and Renin
... If pure submaxillary renin is mixed with mouse plasma it does not bind to other proteins. This facilitates its enzymatic activity in mouse plasma, but does not offer an explanation for the highmolecular-weight forms. In order to mimic complex-formation of renin with plasma proteins 1251-labelled pur ...
... If pure submaxillary renin is mixed with mouse plasma it does not bind to other proteins. This facilitates its enzymatic activity in mouse plasma, but does not offer an explanation for the highmolecular-weight forms. In order to mimic complex-formation of renin with plasma proteins 1251-labelled pur ...
Protein transfer of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Vir proteins to
... containing cre::vir fusion plasmids were grown overnight in 5 ml of LC media supplemented with spectinomycin (250 g/ml) and gentamycin (40 g/ml) or incubated for two days on agar plates at 29C. At the onset of the experiments A.tumefaciens strain KE1(LBA2575) (Sundberg et al., 1996) was used as a ...
... containing cre::vir fusion plasmids were grown overnight in 5 ml of LC media supplemented with spectinomycin (250 g/ml) and gentamycin (40 g/ml) or incubated for two days on agar plates at 29C. At the onset of the experiments A.tumefaciens strain KE1(LBA2575) (Sundberg et al., 1996) was used as a ...
Chapter 8: Fibrous Proteins
... Mutation affects protofilament and/or protofibril formation Aberrant protofilament or protofibril formation results in a loss of mechanical integrity of basal skin cells ...
... Mutation affects protofilament and/or protofibril formation Aberrant protofilament or protofibril formation results in a loss of mechanical integrity of basal skin cells ...
Prediction of protease substrates using sequence
... Received on January 25, 2010; revised on May 4, 2010; accepted on May 18, 2010 ...
... Received on January 25, 2010; revised on May 4, 2010; accepted on May 18, 2010 ...
Towards the construction of Escherichia coli cell
... Cell-free protein systems are described as the in vitro expression of recombinant proteins without the use of living cells. This approach uses a cell lysate containing a wide array of biological and chemical components for transcription, translation, protein folding, and energy metabolism; all requi ...
... Cell-free protein systems are described as the in vitro expression of recombinant proteins without the use of living cells. This approach uses a cell lysate containing a wide array of biological and chemical components for transcription, translation, protein folding, and energy metabolism; all requi ...
Full-Text PDF
... homologues have also been found in fungi, insects, and vertebrates including human. Together they form a superfamily of secreted proteins named CAP (from cystein rich secretory protein (CRISP), antigen 5, and PR1 proteins; [5]). Even though PR1s have been extensively studied, their exact function re ...
... homologues have also been found in fungi, insects, and vertebrates including human. Together they form a superfamily of secreted proteins named CAP (from cystein rich secretory protein (CRISP), antigen 5, and PR1 proteins; [5]). Even though PR1s have been extensively studied, their exact function re ...
Deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae and on the
... The purine guanine and the p yrimidincs cytosine, thymine and uracil were found not to affect growth or colour of, or the contents of nucleic acids and protein in. biotin-deficient yeast. Each of the pyrmidincs was incorporated in biotin-deficient medium in concentrations up i o 1-0 x lW3iv; because ...
... The purine guanine and the p yrimidincs cytosine, thymine and uracil were found not to affect growth or colour of, or the contents of nucleic acids and protein in. biotin-deficient yeast. Each of the pyrmidincs was incorporated in biotin-deficient medium in concentrations up i o 1-0 x lW3iv; because ...
The Specificity of Enzymes Adding Amino Acids in the
... UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu. Table I shows that both UDP-Mur-NAc-Gly and UDPMurNAc-L-Ala are good substrates for the D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme. The glutamic acid occurring as amino acid residue 2 of the muramyl pentapeptide chain of all bacterial peptidoglycans is present in the D-configuration (Schl ...
... UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu. Table I shows that both UDP-Mur-NAc-Gly and UDPMurNAc-L-Ala are good substrates for the D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme. The glutamic acid occurring as amino acid residue 2 of the muramyl pentapeptide chain of all bacterial peptidoglycans is present in the D-configuration (Schl ...
tutorial_structurech..
... described plugins are designed to work with proteins and nucleic acids and understand atom names as used by the force fields CHARMM and AMBER as well as the standard PDB naming convention for non-hydrogen atoms. WARNING: The current implementation of the chirality plugin does not support DNA yet. Th ...
... described plugins are designed to work with proteins and nucleic acids and understand atom names as used by the force fields CHARMM and AMBER as well as the standard PDB naming convention for non-hydrogen atoms. WARNING: The current implementation of the chirality plugin does not support DNA yet. Th ...
Slide 1
... high level of annotation (such as the description of the function of a protein, its domains structure, post-translational modifications, variants, etc.) ...
... high level of annotation (such as the description of the function of a protein, its domains structure, post-translational modifications, variants, etc.) ...
Feeding Lysine: A Nutritionist and Dairy Producer`s Perspective
... easily forms covalent bonds with other AA and reducing sugars known as the Maillard reaction. Lysine’s basic side chain is so reactive that even when it is part of a peptide or protein, its ε-amino group remains reactive and can still form covalent bonds (Nursten, 2005). Although all AA, peptides, a ...
... easily forms covalent bonds with other AA and reducing sugars known as the Maillard reaction. Lysine’s basic side chain is so reactive that even when it is part of a peptide or protein, its ε-amino group remains reactive and can still form covalent bonds (Nursten, 2005). Although all AA, peptides, a ...
2.2.3 Enzymes Worksheet
... If enzymes are used freely _________________ in a vessel it can be very wasteful as they are ________ at the end of the process To prevent this problem enzymes are often _____________________ or fixed. This means they are ________________ to ______________ or an _________ _______________ and can be ...
... If enzymes are used freely _________________ in a vessel it can be very wasteful as they are ________ at the end of the process To prevent this problem enzymes are often _____________________ or fixed. This means they are ________________ to ______________ or an _________ _______________ and can be ...
The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models
... α-helices (amino acids 144–154, 175–193 and 200–219) and a small antiparallel β-sheet (amino acids 128–131 and 161–164) [78]. It has an amino-terminal signal peptide (amino acids 1–23), a more or less flexible N-terminal domain (amino acids 23–120), a folded C-terminal domain (amino acids 121–231), ...
... α-helices (amino acids 144–154, 175–193 and 200–219) and a small antiparallel β-sheet (amino acids 128–131 and 161–164) [78]. It has an amino-terminal signal peptide (amino acids 1–23), a more or less flexible N-terminal domain (amino acids 23–120), a folded C-terminal domain (amino acids 121–231), ...
Bil 255 – CMB
... Some Native Examples of Enzyme Inhibition: Irreversible Enzyme Inhibition & Mechanism of Action of an Antibiotic... Antibiotic - a natural molecule (often made by bacterial cells) that can kill other bacterial cells (& without hurting eukaryotic cells: they're insensitive) Penicillin - any one of a ...
... Some Native Examples of Enzyme Inhibition: Irreversible Enzyme Inhibition & Mechanism of Action of an Antibiotic... Antibiotic - a natural molecule (often made by bacterial cells) that can kill other bacterial cells (& without hurting eukaryotic cells: they're insensitive) Penicillin - any one of a ...
Fal1p Is an Essential DEAD-Box Protein Involved in 40S
... A previously uncharacterized Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene, FAL1, was found by sequence comparison as a homolog of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A (eIF4A). Fal1p has 55% identity and 73% similarity on the amino acid level to yeast eIF4A, the prototype of ATP-dependent RNA helicases o ...
... A previously uncharacterized Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene, FAL1, was found by sequence comparison as a homolog of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A (eIF4A). Fal1p has 55% identity and 73% similarity on the amino acid level to yeast eIF4A, the prototype of ATP-dependent RNA helicases o ...
Similarities and Differences in the Glycosylation Mechanisms in
... numbering about 12 in archaea, 14 in yeast, and up to 19 in mammals. Bacteria also have a polyisoprene as their LLO lipid but, instead of dolichol, they use undecaprenol (11 isoprene units) which has one more double bond than the same length dolichol. This double bond is located between carbons 2 an ...
... numbering about 12 in archaea, 14 in yeast, and up to 19 in mammals. Bacteria also have a polyisoprene as their LLO lipid but, instead of dolichol, they use undecaprenol (11 isoprene units) which has one more double bond than the same length dolichol. This double bond is located between carbons 2 an ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.