Metabolic Pathway Flux Enhancement by Synthetic
... predictable control over gene expression (Pfleger et al., 2006; Salis et al., 2009; Win and Smolke, 2007), and directed evolution approaches for improved enzyme characteristics (Dougherty and Arnold, 2009; Zhang et al., 2008). In this chapter, we focus on ongoing efforts to improve pathway efficienc ...
... predictable control over gene expression (Pfleger et al., 2006; Salis et al., 2009; Win and Smolke, 2007), and directed evolution approaches for improved enzyme characteristics (Dougherty and Arnold, 2009; Zhang et al., 2008). In this chapter, we focus on ongoing efforts to improve pathway efficienc ...
Mechanisms Shaping the Membranes of Cellular Organelles
... stack of perforated sheets. Cellular membrane shapes are generally dynamic. They often change during processes such as cell movement, division, and growth, but also under steady state conditions. For example, many membrane-bound compartments have the ability to bud small vesicles and to fuse with ve ...
... stack of perforated sheets. Cellular membrane shapes are generally dynamic. They often change during processes such as cell movement, division, and growth, but also under steady state conditions. For example, many membrane-bound compartments have the ability to bud small vesicles and to fuse with ve ...
Escherichia coli Karl Skoog
... process in E. coli has been extensively studied for at least 50 years and a lot is known, however many details are still vague. New proteins involved in the process continue to be identified and the number of these proteins as well as the interactions among them are not yet fully known. It is theref ...
... process in E. coli has been extensively studied for at least 50 years and a lot is known, however many details are still vague. New proteins involved in the process continue to be identified and the number of these proteins as well as the interactions among them are not yet fully known. It is theref ...
How to move an amphipathic molecule across a lipid
... coupling helices contained within the long intracellular loops linking TM helices interact with the NBD of the opposite subunit in an arrangement termed ‘domain swapping’ [47]. Interestingly, ABCD proteins have a significant number of conserved hydrophilic residues in predicted transmembrane helices ...
... coupling helices contained within the long intracellular loops linking TM helices interact with the NBD of the opposite subunit in an arrangement termed ‘domain swapping’ [47]. Interestingly, ABCD proteins have a significant number of conserved hydrophilic residues in predicted transmembrane helices ...
e. Reference States are critical for the application of empirical
... The same set of energy parameters is therefore valid, to a good approximation, for both the intermolecular and intramolecular regimes, a result that removes reservations about adopting the same force fields for folding and for binding. k. Reduced set of parameters The specificity and robustness of W ...
... The same set of energy parameters is therefore valid, to a good approximation, for both the intermolecular and intramolecular regimes, a result that removes reservations about adopting the same force fields for folding and for binding. k. Reduced set of parameters The specificity and robustness of W ...
Biochem Jeopardy
... Explain how an enzyme works using the terms substrate and active site (correctly) in your explanation. A: What is “a substrate bonds to the active site of the enzyme causing a ...
... Explain how an enzyme works using the terms substrate and active site (correctly) in your explanation. A: What is “a substrate bonds to the active site of the enzyme causing a ...
Amino acid concentrations in fluids from the bovine oviduct and
... The results of individual amino acid concentrations and their relative abundance in bovine oviductal and uterine fluids recovered from slaughterhouse reproductive tracts are shown in Table 2. The non-essential amino acid group was the most abundant in OF and comprised 82% of the total amino acids me ...
... The results of individual amino acid concentrations and their relative abundance in bovine oviductal and uterine fluids recovered from slaughterhouse reproductive tracts are shown in Table 2. The non-essential amino acid group was the most abundant in OF and comprised 82% of the total amino acids me ...
PLANT PROTEIN PHOSPHATASES
... residues (107). Phosphohistidine phosphorylation has also been reported in plants (50), fungi (86), and animals (25), but its relative contribution to the total phosphoamino acid content of eukaryotic cells is not known. In animals, protein phosphorylation plays well-known roles in diverse cellular ...
... residues (107). Phosphohistidine phosphorylation has also been reported in plants (50), fungi (86), and animals (25), but its relative contribution to the total phosphoamino acid content of eukaryotic cells is not known. In animals, protein phosphorylation plays well-known roles in diverse cellular ...
Characterisation of the novel proteins expressed in corn line 1507
... carbohydrate, ash, fibre, fatty acids, amino acids, minerals and moisture) were similar in corn line 1507 and the non-transformed control corns. In addition, there were no observed differences in results from the analyses of four vitamins (Vitamins B1, B2, E and folate) measured in the transformed a ...
... carbohydrate, ash, fibre, fatty acids, amino acids, minerals and moisture) were similar in corn line 1507 and the non-transformed control corns. In addition, there were no observed differences in results from the analyses of four vitamins (Vitamins B1, B2, E and folate) measured in the transformed a ...
Energy metabolism reactions in ruminant muscle: responses to
... ATP/MJ ME, respectively (Baldwin, 1968; Lobley, 1986). Based on an average molecular weight of peptide amino acid of 110, minimum theoretical costs are 2.83.2 kJ per g protein synthesis. In practice a wider range of values has been used and often the figure of 4.5 kJ per g, as proposed by Webster (1 ...
... ATP/MJ ME, respectively (Baldwin, 1968; Lobley, 1986). Based on an average molecular weight of peptide amino acid of 110, minimum theoretical costs are 2.83.2 kJ per g protein synthesis. In practice a wider range of values has been used and often the figure of 4.5 kJ per g, as proposed by Webster (1 ...
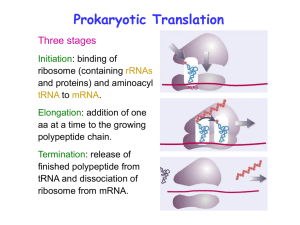
Class I tRNA
... Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
... Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
Full Text - Labs / Projects - Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
... Clones for Expressing Bacterial Proteins–-The GST-Hairy fusion proteins bHLH, Orange-WRPW, N30 (an N-terminal 30-amino acid fragment of Hairy), Basic (basic DNA-binding elements), and HLH have been described previously (5, 16). Dmp53 (obtained from M. Brodsky) is a BamHI/BglII fragment inserted in t ...
... Clones for Expressing Bacterial Proteins–-The GST-Hairy fusion proteins bHLH, Orange-WRPW, N30 (an N-terminal 30-amino acid fragment of Hairy), Basic (basic DNA-binding elements), and HLH have been described previously (5, 16). Dmp53 (obtained from M. Brodsky) is a BamHI/BglII fragment inserted in t ...
Nonruminant Nutrition: Amino Acids (Abstracts M204–M237)
... Statements of significance are based on testing at P < 0.05. No differences in breast weight or the number of days of enrichment between groups were determined. The 13C-lysine enrichment in breast muscle was not significantly higher than in control hens, however 15N-lysine enrichment was higher in g ...
... Statements of significance are based on testing at P < 0.05. No differences in breast weight or the number of days of enrichment between groups were determined. The 13C-lysine enrichment in breast muscle was not significantly higher than in control hens, however 15N-lysine enrichment was higher in g ...
Article - Inter Research
... R. pachyptila tube solubilisates suggests a multi-protein system (Fig. 3). There are numerous proteins evident, spanning the molecular weight range 120 000 to 12 000, but the 2 domlnant species occur at molecular weights 16 500 and 12 000, respectively. Both tube materials display considerable stabh ...
... R. pachyptila tube solubilisates suggests a multi-protein system (Fig. 3). There are numerous proteins evident, spanning the molecular weight range 120 000 to 12 000, but the 2 domlnant species occur at molecular weights 16 500 and 12 000, respectively. Both tube materials display considerable stabh ...
Classification and domain analysis of protein
... rate of human and chimpanzee genomes has also been discussed in several studies4,5. In addition to this, comparison of human and chimpanzee genomes has been done to discover the genetic basis of the anatomical, functional, habitable and genetic level variations among them6–13. In case of a particula ...
... rate of human and chimpanzee genomes has also been discussed in several studies4,5. In addition to this, comparison of human and chimpanzee genomes has been done to discover the genetic basis of the anatomical, functional, habitable and genetic level variations among them6–13. In case of a particula ...
Canola Meal for Pig Feeding
... able to demonstrate that under typical processing conditions as used by GrainCorp Oilseeds, the effects of processing have a minimal impact upon meal quality. It is during more extreme or less controlled oil extraction that protein heat damage occurs. Heat and pressure applied through canola process ...
... able to demonstrate that under typical processing conditions as used by GrainCorp Oilseeds, the effects of processing have a minimal impact upon meal quality. It is during more extreme or less controlled oil extraction that protein heat damage occurs. Heat and pressure applied through canola process ...
WW Domains Provide a Platform for the
... proteins are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including transcription, RNA processing, protein trafficking, receptor signaling, and control of the cytoskeleton (32, 33, 68). WW domain-mediated interactions have been implicated in cancer (4, 75), in hereditary disorders, such as Liddle’s ...
... proteins are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including transcription, RNA processing, protein trafficking, receptor signaling, and control of the cytoskeleton (32, 33, 68). WW domain-mediated interactions have been implicated in cancer (4, 75), in hereditary disorders, such as Liddle’s ...
Nutrient production by symbiotic bacteria
... subsequently raising them in isolation. All experiments were initiated by transferring adult apterae from plants to the complete diet either containing or lacking rifampicin. Larvae deposited over 1 day were retained on the diets for a second day. These aphids are termed 2 days old, ...
... subsequently raising them in isolation. All experiments were initiated by transferring adult apterae from plants to the complete diet either containing or lacking rifampicin. Larvae deposited over 1 day were retained on the diets for a second day. These aphids are termed 2 days old, ...
Disrupted mRNA sorting in CNS neurons
... translation, and provide a means for movement. To date, most studies have focused on the sequences and structural features of mRNAs which are sufficient to direct localization when introduced as reporter constructs (Mayford et al., 1996b; MacDonald and Kerr, 1998; Muslimov et al., 1997; for review s ...
... translation, and provide a means for movement. To date, most studies have focused on the sequences and structural features of mRNAs which are sufficient to direct localization when introduced as reporter constructs (Mayford et al., 1996b; MacDonald and Kerr, 1998; Muslimov et al., 1997; for review s ...
Sequence analysis of the Marburg virus nucleoprotein gene
... Fig. 2. Specificity of cDNA clones, MBG mRNAs and sequencing of the 5' end of the MBG NP mRNA. (a) Northern blot hybridization of 32P-labelled probes (nick translation) generated from eDNA clones MV-88 and MV-17 (see Fig. 1) to lanes of RNA resolved by electrophoresisin an acid-urea-agarose (1-5~) g ...
... Fig. 2. Specificity of cDNA clones, MBG mRNAs and sequencing of the 5' end of the MBG NP mRNA. (a) Northern blot hybridization of 32P-labelled probes (nick translation) generated from eDNA clones MV-88 and MV-17 (see Fig. 1) to lanes of RNA resolved by electrophoresisin an acid-urea-agarose (1-5~) g ...
-portal.org Journal of Molecular Biology
... α-Helical hairpins, consisting of a pair of closely spaced transmembrane (TM) helices that are connected by a short interfacial turn, are the simplest structural motifs found in multi-spanning membrane proteins. In naturally occurring hairpins, the presence of polar residues is common and predicted ...
... α-Helical hairpins, consisting of a pair of closely spaced transmembrane (TM) helices that are connected by a short interfacial turn, are the simplest structural motifs found in multi-spanning membrane proteins. In naturally occurring hairpins, the presence of polar residues is common and predicted ...
STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL STUDIES OF PYRIDOXINE 5’-PHOSPHATE SYNTHASE E. COLI Doctoral Thesis
... Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate is the biocatalytically active form of vitamin B6, being one of nature’s most versatile cofactors that plays a central role in the metabolism of amino acids. Whereas microorganisms and plants can synthetise vitamin B6 de novo, mammals have to obtain one of the B6 vitamers with ...
... Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate is the biocatalytically active form of vitamin B6, being one of nature’s most versatile cofactors that plays a central role in the metabolism of amino acids. Whereas microorganisms and plants can synthetise vitamin B6 de novo, mammals have to obtain one of the B6 vitamers with ...
Copyright Information of the Article Published Online
... peroxisomal import unique to several species, such as the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans[17]. In mammals, several proteins contain another type of PTS: Type 2 PTS. This motif is recognized by the Pex7 protein, and proteins carrying this PTS2 signal are transported into the peroxisome with the same ...
... peroxisomal import unique to several species, such as the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans[17]. In mammals, several proteins contain another type of PTS: Type 2 PTS. This motif is recognized by the Pex7 protein, and proteins carrying this PTS2 signal are transported into the peroxisome with the same ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.