Natural Genetic Variation Modifies Gene Expression
... skeletal variation in stickleback fish (4), genetic variation commonly acts on traits by altering when, where, and how much genes are expressed (5,6). Understanding the mechanisms by which genetic variation acts on gene expression patterns is therefore a major goal for the biological sciences. The e ...
... skeletal variation in stickleback fish (4), genetic variation commonly acts on traits by altering when, where, and how much genes are expressed (5,6). Understanding the mechanisms by which genetic variation acts on gene expression patterns is therefore a major goal for the biological sciences. The e ...
Cell-Free Phospholipid Biosynthesis by Gene
... and implementation of complex genetic and metabolic pathways that can support essential cellular functions. Here, we show that phospholipid biosynthesis, a multiple-step process involved in cell membrane homeostasis, can be reconstituted starting from the genes encoding for all necessary proteins. A ...
... and implementation of complex genetic and metabolic pathways that can support essential cellular functions. Here, we show that phospholipid biosynthesis, a multiple-step process involved in cell membrane homeostasis, can be reconstituted starting from the genes encoding for all necessary proteins. A ...
The proposed channel-enzyme transient receptor potential
... eLife digest Ion channels are proteins that allow specific charged particles to move across the membranes of cells – for example to travel in or out of a cell, or between different parts of the same cell. Almost all ion channels are gated, meaning that they can open and close in response to differen ...
... eLife digest Ion channels are proteins that allow specific charged particles to move across the membranes of cells – for example to travel in or out of a cell, or between different parts of the same cell. Almost all ion channels are gated, meaning that they can open and close in response to differen ...
tr-kit promotes the formation of a multimolecular complex composed
... for Src-like kinases in mitosis (Taylor and Shalloway, 1994); it has been demonstrated that the interaction with the SH3 domain of Fyn is necessary for Fyn-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sam68 (Shen et al., 1999). Once phosphorylated in the carboxyterminal region, Sam68 recruits the SH2 domai ...
... for Src-like kinases in mitosis (Taylor and Shalloway, 1994); it has been demonstrated that the interaction with the SH3 domain of Fyn is necessary for Fyn-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sam68 (Shen et al., 1999). Once phosphorylated in the carboxyterminal region, Sam68 recruits the SH2 domai ...
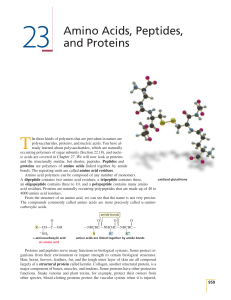
23 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. You have already learned about polysaccharides, which are naturally occurring polymers of sugar subunits (Section 22.18), and nucleic acids are covered in Chapter 27. We will now look at proteins and the structurally similar, but shorter, peptides. Pepti ...
... polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. You have already learned about polysaccharides, which are naturally occurring polymers of sugar subunits (Section 22.18), and nucleic acids are covered in Chapter 27. We will now look at proteins and the structurally similar, but shorter, peptides. Pepti ...
Soil Biology and Biochemistry
... were made to quantify indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) excreted by different wild type strains of Azospirilhun spp. The microorganisms produce IAA, during the late stationary growth phase and show a significant increase in IAA production when tryptophan is present in the medium. Under these conditions wit ...
... were made to quantify indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) excreted by different wild type strains of Azospirilhun spp. The microorganisms produce IAA, during the late stationary growth phase and show a significant increase in IAA production when tryptophan is present in the medium. Under these conditions wit ...
Plant Cell
... The Plant Cell Preview, www.aspb.org ã 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
... The Plant Cell Preview, www.aspb.org ã 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
Stress-Induced Chloroplast Degradation in
... The Plant Cell Preview, www.aspb.org ã 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
... The Plant Cell Preview, www.aspb.org ã 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
CHAPTER 1 SAMPLE TEST
... a. the disulfide and hydrogen bonds that determine molecular shape b. the action of the ribosomes c. the precise location of specific amino acids, common to all proteins d. different numbers, kinds, and sequences of amino acids e. different kinds of bonds between successive amino acids Proteins tend ...
... a. the disulfide and hydrogen bonds that determine molecular shape b. the action of the ribosomes c. the precise location of specific amino acids, common to all proteins d. different numbers, kinds, and sequences of amino acids e. different kinds of bonds between successive amino acids Proteins tend ...
Preference for and learning of amino acids in larval
... in first-instar and in third-instar larvae. Our data suggest that this preference profile changes across larval instars, and that starvation during the third instar also alters this profile. Only aspartic acid turns out to be robustly attractive across all our experiments. The essentiality of amino ...
... in first-instar and in third-instar larvae. Our data suggest that this preference profile changes across larval instars, and that starvation during the third instar also alters this profile. Only aspartic acid turns out to be robustly attractive across all our experiments. The essentiality of amino ...
A mRNA localized to the vegetal cortex of Xenopus
... Pasceri, 1989; Yuge et al., 1990). Embryological experiments have also mapped the specification of endoderm (Wylie et al., 1987), the germ cell lineage (Whitington and Dixon, 1975) and mesoderm (Nieuwkoop, 1973) to the vegetal hemisphere. Of all these processes, only mesoderm induction has been char ...
... Pasceri, 1989; Yuge et al., 1990). Embryological experiments have also mapped the specification of endoderm (Wylie et al., 1987), the germ cell lineage (Whitington and Dixon, 1975) and mesoderm (Nieuwkoop, 1973) to the vegetal hemisphere. Of all these processes, only mesoderm induction has been char ...
Globins in Nonvertebrate Species: Dispersal by Horizontal Gene
... John Czeluzniak, 5 Morris Goodman, 5 Mark Blaxter,ll and Serge Vinogradofl *Department of Biochemistry, University of Antwerp; TDepartment of Morphology, Systematics and Ecology, University of Ghent; *Department of Radiology and Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago; SDepartment of Anatomy, ...
... John Czeluzniak, 5 Morris Goodman, 5 Mark Blaxter,ll and Serge Vinogradofl *Department of Biochemistry, University of Antwerp; TDepartment of Morphology, Systematics and Ecology, University of Ghent; *Department of Radiology and Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago; SDepartment of Anatomy, ...
... Specific activity is the ratio of the activity of the target protein divided by the total protein. It is useful because after each purification step the total protein decreases, therefore the specific activity increases. 10. (12 pts) Briefly describe the structural features of either and alpha helix ...
Proteins RCA Gene Cluster and Functional RCA Locus in Chicken
... A 150-kb DNA fragment, which contains the gene of the chicken complement regulatory protein CREM (formerly named Cremp), was isolated from a microchromosome by screening bacterial artificial chromosome library. Within 100 kb of the cloned region, three complete genes encoding short consensus repeats ...
... A 150-kb DNA fragment, which contains the gene of the chicken complement regulatory protein CREM (formerly named Cremp), was isolated from a microchromosome by screening bacterial artificial chromosome library. Within 100 kb of the cloned region, three complete genes encoding short consensus repeats ...
Adipocyte metabolic pathways regulated by diet control
... in adipocytes, and the survival of early germline cysts. Enzymes catalyzing fatty acid oxidation and ...
... in adipocytes, and the survival of early germline cysts. Enzymes catalyzing fatty acid oxidation and ...
First Title - Buckeye Valley
... The Nucleus Protein Synthesis • Translation—the assembling of a protein by ribosomes, using the information carried by the mRNA molecule • tRNAs carry amino acids • Anticodons bind to mRNA • Occurs in cytoplasm ...
... The Nucleus Protein Synthesis • Translation—the assembling of a protein by ribosomes, using the information carried by the mRNA molecule • tRNAs carry amino acids • Anticodons bind to mRNA • Occurs in cytoplasm ...
End-product control of enzymes of branched
... the latter strain do not therefore imply specific genes. Results reported below show that 966 is not deficient in AHAS.) Media and growth conditions. Growth was in all cases at 30 OC. Spores of S.coelicolor strains grown on R5 medium were obtained as described by Hopwood e t al. (1985). T o inoculat ...
... the latter strain do not therefore imply specific genes. Results reported below show that 966 is not deficient in AHAS.) Media and growth conditions. Growth was in all cases at 30 OC. Spores of S.coelicolor strains grown on R5 medium were obtained as described by Hopwood e t al. (1985). T o inoculat ...
Sulfur Metabolism in Escherichia coli and Related Bacteria: Facts
... physiological importance of this activity. However, as we shall see later, there exist numerous sulfonatases that may act on this molecule, yielding cysteine and a sulfate ion, which would thus enter the normal pathway. It is useful to understand the synthesis of O acetylserine and its regulation, b ...
... physiological importance of this activity. However, as we shall see later, there exist numerous sulfonatases that may act on this molecule, yielding cysteine and a sulfate ion, which would thus enter the normal pathway. It is useful to understand the synthesis of O acetylserine and its regulation, b ...
1 Nucleoli: Composition, Function and Dynamics
... chromatin. This is an indication that the active rDNA is highly dispersed within the nucleolus. On the basis of their appearance in electron microscope images, the nucleoli in many animal cells have been described in terms of a tripartite structure, with small, lightly staining regions called fibril ...
... chromatin. This is an indication that the active rDNA is highly dispersed within the nucleolus. On the basis of their appearance in electron microscope images, the nucleoli in many animal cells have been described in terms of a tripartite structure, with small, lightly staining regions called fibril ...
Connection of the Mitochondrial Outer and Inner Membranes by
... Wickner, 1996; Jahn and Südhof, 1999). Fusion of mitochondrial membranes has been observed in a great variety of different cell types. These include budding yeast, filamentous fungi, mammalian cells in culture, and various plant cells (Bereiter-Hahn, 1990; Bereiter-Hahn and Vöth, 1994; Steinberg, 19 ...
... Wickner, 1996; Jahn and Südhof, 1999). Fusion of mitochondrial membranes has been observed in a great variety of different cell types. These include budding yeast, filamentous fungi, mammalian cells in culture, and various plant cells (Bereiter-Hahn, 1990; Bereiter-Hahn and Vöth, 1994; Steinberg, 19 ...
Engineering carbonic anhydrase for highly selective ester hydrolysis Gunnar Höst
... important topic in biochemistry, where a lot of effort is put into structure determination of proteins. Several approaches for exploring the relation between form and function exist. The absolute majority of enzyme engineering work takes advantage of the possibility to clone a gene and incorporate m ...
... important topic in biochemistry, where a lot of effort is put into structure determination of proteins. Several approaches for exploring the relation between form and function exist. The absolute majority of enzyme engineering work takes advantage of the possibility to clone a gene and incorporate m ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.