Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
Molecular Genetics - Madison County Schools
... In the broth with the sulfur, radioactivity was only measured in the liquid, which indicated that the protein was not incorporated into the bacterium. In the phosphorus broth, radioavtivity was measured in the pellet (bacteria), which indicated that the viral DNA was incorporated into the bacterium. ...
... In the broth with the sulfur, radioactivity was only measured in the liquid, which indicated that the protein was not incorporated into the bacterium. In the phosphorus broth, radioavtivity was measured in the pellet (bacteria), which indicated that the viral DNA was incorporated into the bacterium. ...
homepage/tkazanecki/file/Deoxyribonucleic Acid - Parkway C-2
... • Nucleic Acids – Nucleotide-Phosphate, 5carbon sugar and N base – Carry the genetic code of life ...
... • Nucleic Acids – Nucleotide-Phosphate, 5carbon sugar and N base – Carry the genetic code of life ...
chapter 10 bio analysis
... 1. How many nucleotides did the original DNA model contain? The original DNA model contained approximately 12 nucleotides in each double helix. 2. Write the base-pair order for the DNA molecule you created using the following code: red=adenine, blue-guanine, yellow=cytosine, and green= thymine. Guan ...
... 1. How many nucleotides did the original DNA model contain? The original DNA model contained approximately 12 nucleotides in each double helix. 2. Write the base-pair order for the DNA molecule you created using the following code: red=adenine, blue-guanine, yellow=cytosine, and green= thymine. Guan ...
AP Biology - HPHSAPBIO
... 4. Describe the semiconservative model of replication and the significance of the experiments by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Note the structure of the many origins of replication and replication forks and explain the role of DNA polymerase. 6. Def ...
... 4. Describe the semiconservative model of replication and the significance of the experiments by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Note the structure of the many origins of replication and replication forks and explain the role of DNA polymerase. 6. Def ...
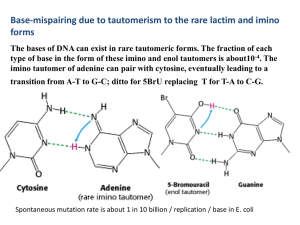
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It is likely that mutations in DNA repair genes will lead to the accumulation of mutations throughout the genome. In time, genes important in controlling cell ...
... deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It is likely that mutations in DNA repair genes will lead to the accumulation of mutations throughout the genome. In time, genes important in controlling cell ...
Molecular Bio Questions1
... other. b. The two strands have complementary sequences and are parallel to each other. c. The two strands have identical sequences and are antiparallel to each other. d. The two strands have complementary sequences and are antiparallel to each other. e. The two strands have identical sequences and a ...
... other. b. The two strands have complementary sequences and are parallel to each other. c. The two strands have identical sequences and are antiparallel to each other. d. The two strands have complementary sequences and are antiparallel to each other. e. The two strands have identical sequences and a ...
Chapter 11
... nucleotides in a continuous fashion; this new daughter strand is called the leading strand. 2 Priming the Leading Strand ...
... nucleotides in a continuous fashion; this new daughter strand is called the leading strand. 2 Priming the Leading Strand ...
Week 4 Pre-Lecture Slides
... • Which of these changes for your DNA is most likely to destroy function of the protein? • Why are prenatal doctors much more likely to test for small chromosomal breakages than for point mutations of 5-20 bases? • Which is more likely to be mutagenic: – A cosmic ray that only changes A’s to U’s in ...
... • Which of these changes for your DNA is most likely to destroy function of the protein? • Why are prenatal doctors much more likely to test for small chromosomal breakages than for point mutations of 5-20 bases? • Which is more likely to be mutagenic: – A cosmic ray that only changes A’s to U’s in ...
Section 12-1
... a. Showed that the percentages of the bases A and T are approximately equal and C and T are approximately equal b. Therefore, in DNA, A pairs with T; C pairs with G C. Rosalind Franklin (1952) used X-ray diffraction to study the structure of DNA D. Watson and Crick (1953) made a model of DNA (fig 12 ...
... a. Showed that the percentages of the bases A and T are approximately equal and C and T are approximately equal b. Therefore, in DNA, A pairs with T; C pairs with G C. Rosalind Franklin (1952) used X-ray diffraction to study the structure of DNA D. Watson and Crick (1953) made a model of DNA (fig 12 ...
DNA Transcription and Translation Project
... DNA Transcription and Translation Activity This assignment is due on the day of the Transcription/Translation test. No late work will be accepted. All organisms use proteins to grow and function. These proteins are made up of thousands of amino acids which were created through the processes of DNA t ...
... DNA Transcription and Translation Activity This assignment is due on the day of the Transcription/Translation test. No late work will be accepted. All organisms use proteins to grow and function. These proteins are made up of thousands of amino acids which were created through the processes of DNA t ...
5о end of mRNA 1 2 1 1 2 3 Protein Ribosome RNA
... – Given a diagram of replicating DNA, locate likely sites of action for each enzyme involved in replication – Assign descriptive terms appropriately to replication on the leading or lagging strands of a particular replication fork ...
... – Given a diagram of replicating DNA, locate likely sites of action for each enzyme involved in replication – Assign descriptive terms appropriately to replication on the leading or lagging strands of a particular replication fork ...
For teachers: Get four colours of beads or rubber bands. You can
... 1. Read letters left to right in sets of three 2. Each three-letter code corresponds to an amino acid, such as “Leu” (see key) 3. T = U in the key* ...
... 1. Read letters left to right in sets of three 2. Each three-letter code corresponds to an amino acid, such as “Leu” (see key) 3. T = U in the key* ...
specific location on chromosome, consisting of a segment of DNA
... contains ribose sugar (not deoxyribose), it is single stranded, and it contains uracil (not thymine) to pair with adenine 3. PROTEIN: large, complex polymer essential to all life. Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and usually sulfur; provides structure for tissues and organs and helps ...
... contains ribose sugar (not deoxyribose), it is single stranded, and it contains uracil (not thymine) to pair with adenine 3. PROTEIN: large, complex polymer essential to all life. Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and usually sulfur; provides structure for tissues and organs and helps ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.