Chemical Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reactants. • Water is the product. ...
... • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reactants. • Water is the product. ...
Formula Equation - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Writing a correct formula is all about looking up the correct symbol, identifying the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
... Writing a correct formula is all about looking up the correct symbol, identifying the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
Definitions
... is a long chain of amino acids folded up to form 3-D shapes. Each protein has a different job. this is a food molecule where large numbers of sugar molecules have been joined together these are elements which are necessary for health. They must be present but are needed in very tiny amounts is a che ...
... is a long chain of amino acids folded up to form 3-D shapes. Each protein has a different job. this is a food molecule where large numbers of sugar molecules have been joined together these are elements which are necessary for health. They must be present but are needed in very tiny amounts is a che ...
Formula Notes `Completed` - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Writing a correct formula is all about looking up the correct symbol, identifying the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
... Writing a correct formula is all about looking up the correct symbol, identifying the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
chapter 19 Respiratory
... 7. The right lung is composed of ____ lobes; the left lung is composed of ____ lobes. • A. superior, middle, and inferior; superior and inferior • B. superior and inferior; superior, middle, and inferior • C. anterior, posterior, and lateral; superior and inferior • D. superior, middle, and inferio ...
... 7. The right lung is composed of ____ lobes; the left lung is composed of ____ lobes. • A. superior, middle, and inferior; superior and inferior • B. superior and inferior; superior, middle, and inferior • C. anterior, posterior, and lateral; superior and inferior • D. superior, middle, and inferio ...
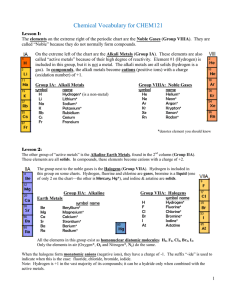
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not have a charge like polyatomic ions, but are neutral. Since more than one combination is possible, the ...
... Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not have a charge like polyatomic ions, but are neutral. Since more than one combination is possible, the ...
Old Exam 1 Questions KEY
... the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products (increase the reaction rate) is to a. add more of the enzyme. b. heat the solution to 90°C. – denatures the enzyme c. add more substrate. d. add an allosteric inhibitor. 79. If an enzyme is added to a solution where the substrates and produ ...
... the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products (increase the reaction rate) is to a. add more of the enzyme. b. heat the solution to 90°C. – denatures the enzyme c. add more substrate. d. add an allosteric inhibitor. 79. If an enzyme is added to a solution where the substrates and produ ...
Nitrogen Metabolism - Oregon State University
... Gene Expression of Enzyme Reduced by Arginine, Increased by Citrulline Enzyme Defects Lead to Citrullinemia - Accumulation of Ammonia Treated with Low Protein Diet, Arginine Supplementation ...
... Gene Expression of Enzyme Reduced by Arginine, Increased by Citrulline Enzyme Defects Lead to Citrullinemia - Accumulation of Ammonia Treated with Low Protein Diet, Arginine Supplementation ...
Honors Chapter 11 Reactions
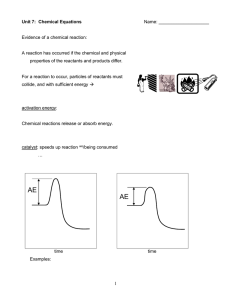
... represents identities and relative amounts of reactants and products in the chemical reaction uses symbols and formulas ...
... represents identities and relative amounts of reactants and products in the chemical reaction uses symbols and formulas ...
+ CuO Cu + O
... 2- The substance which loses an electron or more during a chemical reaction. (…………………………………………) 3- The substance which takes oxygen away or gives hydrogen during a chemical reaction. (………………………………………..) 4- A chemical process in which an atom loses an electron or more. ...
... 2- The substance which loses an electron or more during a chemical reaction. (…………………………………………) 3- The substance which takes oxygen away or gives hydrogen during a chemical reaction. (………………………………………..) 4- A chemical process in which an atom loses an electron or more. ...
Preventive Effect of Modified Citrus Pectin against Aluminium
... Aluminium (Al) is a powerful neurotoxin and has been associated with various cognitive disorders. Al causes extensive damage to the nervous system by accelerating oxidative damage to biomolecules like lipid, protein and nucleic acids. Natural antioxidants, which alleviate the oxidative stress or ind ...
... Aluminium (Al) is a powerful neurotoxin and has been associated with various cognitive disorders. Al causes extensive damage to the nervous system by accelerating oxidative damage to biomolecules like lipid, protein and nucleic acids. Natural antioxidants, which alleviate the oxidative stress or ind ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... 108. Acid levels rise and the pH decreases. 109. Kidneys retain bicarbonate and excrete H+. 110. Respiratory alkalosis is a deficit of carbon dioxide and occurs as a result of hyperventilation. 111. With each exhalation, more carbonic acid is eliminated from the lungs as CO 2. The reaction proceeds ...
... 108. Acid levels rise and the pH decreases. 109. Kidneys retain bicarbonate and excrete H+. 110. Respiratory alkalosis is a deficit of carbon dioxide and occurs as a result of hyperventilation. 111. With each exhalation, more carbonic acid is eliminated from the lungs as CO 2. The reaction proceeds ...
practice final examination
... ii) Calculate the molar concentration of ammonium ion in a 0.333 M solution of ammonium phosphate. ...
... ii) Calculate the molar concentration of ammonium ion in a 0.333 M solution of ammonium phosphate. ...
Unit 3: Chapter 6
... f. Factors that Effect Enzyme Activity i. ___________________ - Enzymes have an ___________ temperature at which they work (__________________) - As temperature increases, enzyme activity increases for the most part - If temp is too high, protein becomes _______________ (change in _________) and n ...
... f. Factors that Effect Enzyme Activity i. ___________________ - Enzymes have an ___________ temperature at which they work (__________________) - As temperature increases, enzyme activity increases for the most part - If temp is too high, protein becomes _______________ (change in _________) and n ...
Stoichiometry
... Two compounds are involved with the cation of one compound EXCHANGING with the cation of another compound. AX + BZ AZ + BX These reactions proceed if one of the ff. is satisfied: 1. An insoluble/slightly soluble product is formed (PRECIPITATE formation) 2. A weakly ionized species is produced. The ...
... Two compounds are involved with the cation of one compound EXCHANGING with the cation of another compound. AX + BZ AZ + BX These reactions proceed if one of the ff. is satisfied: 1. An insoluble/slightly soluble product is formed (PRECIPITATE formation) 2. A weakly ionized species is produced. The ...
Introductory Chemistry Test Review
... 24. Which substance is the limiting reactant when 14.00 g of calcium oxide reacts with 10.00 g of carbon to produce 16.00 g of calcium carbide and 7.00 g of carbon dioxide according to the following balanced chemical equation? CaO(s) + 3 C(s) ...
... 24. Which substance is the limiting reactant when 14.00 g of calcium oxide reacts with 10.00 g of carbon to produce 16.00 g of calcium carbide and 7.00 g of carbon dioxide according to the following balanced chemical equation? CaO(s) + 3 C(s) ...
Breathing and Holding Your Breath
... Why your muscles and other parts of your body need oxygen All parts of your body need energy to do their work. For example, muscles need energy to contract, and all parts of your body need energy to synthesize needed molecules. Your body gets the energy it needs by combining food molecules with oxyg ...
... Why your muscles and other parts of your body need oxygen All parts of your body need energy to do their work. For example, muscles need energy to contract, and all parts of your body need energy to synthesize needed molecules. Your body gets the energy it needs by combining food molecules with oxyg ...
students - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... ___Al + ___CH3OH ___Al(CH3O)3 + ___H2 ** ___C2H2(g) + ___O2(g) ___CO2(g) + ___H2O(l) ** ___C3H8 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O ** ___C5H12 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O ...
... ___Al + ___CH3OH ___Al(CH3O)3 + ___H2 ** ___C2H2(g) + ___O2(g) ___CO2(g) + ___H2O(l) ** ___C3H8 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O ** ___C5H12 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O ...
Gas Exchange - Mrs. Feigenbaum`s Science Classes
... Gases move from high to low concentration. As O2 is used up inside organism, more diffuses in. When excess CO2 is formed inside, it diffuses out. More gases can diffuse if the respiratory surface is greater (meaning: a greater surface area) Small organisms (protists, hydra) can exchange gases direct ...
... Gases move from high to low concentration. As O2 is used up inside organism, more diffuses in. When excess CO2 is formed inside, it diffuses out. More gases can diffuse if the respiratory surface is greater (meaning: a greater surface area) Small organisms (protists, hydra) can exchange gases direct ...
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven
... 10. Repeat – A trick of the trade, when you are forced to attack an element that is in 3 or more compounds – find where it is uncombined. You can find a factor to make it any amount you want, even if that factor is a fraction! – We want to make the O on the left equal 5, therefore we will multiply i ...
... 10. Repeat – A trick of the trade, when you are forced to attack an element that is in 3 or more compounds – find where it is uncombined. You can find a factor to make it any amount you want, even if that factor is a fraction! – We want to make the O on the left equal 5, therefore we will multiply i ...
The G-Proteins - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Activates Protein kinase C (PKC) which translocates from the cytosol to the membrane Activated PKC phosphorylates other proteins and alters their function state. ...
... Activates Protein kinase C (PKC) which translocates from the cytosol to the membrane Activated PKC phosphorylates other proteins and alters their function state. ...
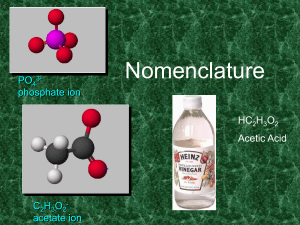
8B31A38F-1279-3B00-CDA90244BEA11A7B
... 2. Add prefixes to indicate # of atoms. Omit mono- prefix on the FIRST element. Mono- is OPTIONAL on the SECOND element (in this class, it’s NOT optional!). 3. Change the ending of the second element to -ide. ...
... 2. Add prefixes to indicate # of atoms. Omit mono- prefix on the FIRST element. Mono- is OPTIONAL on the SECOND element (in this class, it’s NOT optional!). 3. Change the ending of the second element to -ide. ...
Macromolecules Unit Study Guide
... 4. What is a variable in an experiment and why is it important to have them? A variable is something that changed (independent variable), or something that is not changed (controlled variable) in an experiment. It is important to have them because they help to validate the experiment. 5. What is a c ...
... 4. What is a variable in an experiment and why is it important to have them? A variable is something that changed (independent variable), or something that is not changed (controlled variable) in an experiment. It is important to have them because they help to validate the experiment. 5. What is a c ...
Lecture 2
... The role of neural influences on the vasculature varies greatly from organ to organ. Although all organs receive sympathetic innervation, regulation of blood flow in the cerebral and coronary vascular beds occurs mostly through intrinsic local (metabolic) mechanisms. The circulations in skeletal mus ...
... The role of neural influences on the vasculature varies greatly from organ to organ. Although all organs receive sympathetic innervation, regulation of blood flow in the cerebral and coronary vascular beds occurs mostly through intrinsic local (metabolic) mechanisms. The circulations in skeletal mus ...