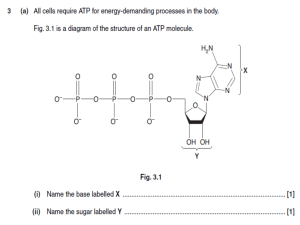
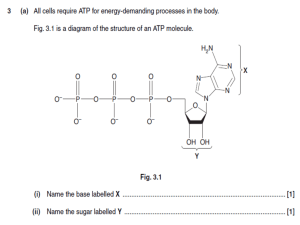
Lecture 2
... The role of neural influences on the vasculature varies greatly from organ to organ. Although all organs receive sympathetic innervation, regulation of blood flow in the cerebral and coronary vascular beds occurs mostly through intrinsic local (metabolic) mechanisms. The circulations in skeletal mus ...
... The role of neural influences on the vasculature varies greatly from organ to organ. Although all organs receive sympathetic innervation, regulation of blood flow in the cerebral and coronary vascular beds occurs mostly through intrinsic local (metabolic) mechanisms. The circulations in skeletal mus ...
Chemistry
... Put a "D-R" next to the double replacement reaction in Box 1-1. Put a "C" next to the reaction in box 1-1 that is a combination reaction. Put a "D" next to the reaction in Box 1-1 that is a decomposition reaction. Put a "S-R" next to the single replacement reaction in Box 1-1. Put an "O" next to the ...
... Put a "D-R" next to the double replacement reaction in Box 1-1. Put a "C" next to the reaction in box 1-1 that is a combination reaction. Put a "D" next to the reaction in Box 1-1 that is a decomposition reaction. Put a "S-R" next to the single replacement reaction in Box 1-1. Put an "O" next to the ...
hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide as part of the
... specifically enabling its production at the right place and at the right time. This would often require the presence of a dedicated enzyme which is able to make the signal. Once the molecule has fulfilled its signaling role, normally it would need to be removed. This would be to stop further signall ...
... specifically enabling its production at the right place and at the right time. This would often require the presence of a dedicated enzyme which is able to make the signal. Once the molecule has fulfilled its signaling role, normally it would need to be removed. This would be to stop further signall ...
Cellular Respiration
... It represents the first steps in the chemical oxidation of glucose by the cell. It produces both ATP and NADH. It converts one glucose molecule to two molecules of pyruvate and carbon dioxide. The first two answers are correct. ...
... It represents the first steps in the chemical oxidation of glucose by the cell. It produces both ATP and NADH. It converts one glucose molecule to two molecules of pyruvate and carbon dioxide. The first two answers are correct. ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
Respiratory System Review
... a) are transported along microscopic tubules b) are exchanged between air and blood c) are produced inside cells d) are exchanged for other gases ...
... a) are transported along microscopic tubules b) are exchanged between air and blood c) are produced inside cells d) are exchanged for other gases ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
... From here, pyruvate is eventually converted back to glucose and returned to muscle cells or stored as glycogen. ...
Respiratory System Notes
... External respiration: In order for carbon dioxide to be released into the alveoli, HCO3must first combine with hydrogen (H+) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) which is quickly split into water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli from the blood stream. Relationship betw ...
... External respiration: In order for carbon dioxide to be released into the alveoli, HCO3must first combine with hydrogen (H+) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) which is quickly split into water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli from the blood stream. Relationship betw ...
Chapter 13, The Respiratory System
... External respiration: In order for carbon dioxide to be released into the alveoli, HCO3must first combine with hydrogen (H+) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) which is quickly split into water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli from the blood stream. Relationship betw ...
... External respiration: In order for carbon dioxide to be released into the alveoli, HCO3must first combine with hydrogen (H+) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) which is quickly split into water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli from the blood stream. Relationship betw ...
Outline
... 5. During carbohydrate starvation or diabetes mellitus, the incomplete break down of fats results in the formation of (keto-acids) which can be deadly because they lower the blood pH resulting in E. Protein Metabolism 1. To be used for energy, amino acids are converted into pyruvic acid or keto-acid ...
... 5. During carbohydrate starvation or diabetes mellitus, the incomplete break down of fats results in the formation of (keto-acids) which can be deadly because they lower the blood pH resulting in E. Protein Metabolism 1. To be used for energy, amino acids are converted into pyruvic acid or keto-acid ...
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals: Gas Exchange
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
oxidation, reduction, redox potential, citric acid cycle, respiratory
... radicals, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical OH. and superoxide O2-. Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) have similar characteristic and function as ROS. The main source of ROS under physiological conditions is respiratory chain. ROS are products of imperfect oxygen reduction. Fenton reaction is ...
... radicals, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical OH. and superoxide O2-. Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) have similar characteristic and function as ROS. The main source of ROS under physiological conditions is respiratory chain. ROS are products of imperfect oxygen reduction. Fenton reaction is ...
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and Animals: Gas Exchange
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
... 3. Describe how air can enter the leaf. If the following are available (microscopes, slides, coverslips, scalpel or blade), prepare thin sections of the upper and lower epidermal surfaces of Rhoeo spathacea. Examine the stomata under the microscope for both the upper and lower epidermis. Which side ...
Powerpoint Slides for Chapter Seven
... losing a carbon in the process. (acetyl CoA) Inside the mitochondria, the two carbon piece left from the sugar is converted to carbon dioxide, water, and lots of ATP (TCA & ETS) ...
... losing a carbon in the process. (acetyl CoA) Inside the mitochondria, the two carbon piece left from the sugar is converted to carbon dioxide, water, and lots of ATP (TCA & ETS) ...
BREATH OF LIFE
... Each cell of your body, including your muscle cells, gets energy from a molecule called ATP, which functions like a rechargeable battery. To recharge the ATP battery cells need to break down sugar. All living cells (plants, bacteria, fungi, animals) can break down sugar without oxygen in a process c ...
... Each cell of your body, including your muscle cells, gets energy from a molecule called ATP, which functions like a rechargeable battery. To recharge the ATP battery cells need to break down sugar. All living cells (plants, bacteria, fungi, animals) can break down sugar without oxygen in a process c ...
Carbon Compounds slideshow Carbon Compounds
... • Molecule – Particle made of two or more __________ joined together. compound Smallest particle of a __________________ ...
... • Molecule – Particle made of two or more __________ joined together. compound Smallest particle of a __________________ ...
Higher Tier, Unit C2: Chemistry
... In the manufacture of iron, haematite (impure iron(lll) oxide), limestone (calcium carbonate), coke (carbon) and hot air are used. (i) What happens to the limestone in the Blast Furnace? ...
... In the manufacture of iron, haematite (impure iron(lll) oxide), limestone (calcium carbonate), coke (carbon) and hot air are used. (i) What happens to the limestone in the Blast Furnace? ...
In organic chemistry, we studied a lot about the essential elements
... Chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids and each chromatid is a complete DNA molecule. The chromatids separate during cell division so that each daughter cell has a copy of each chromosome. The nucleotide bases serve as a sort of genetic alphabet on which the structure of each protein in our ...
... Chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids and each chromatid is a complete DNA molecule. The chromatids separate during cell division so that each daughter cell has a copy of each chromosome. The nucleotide bases serve as a sort of genetic alphabet on which the structure of each protein in our ...
The Respiratory System
... Minute ventilation is the volume of air you breathe in one minute. (VE) You can calculate a person’s minute ventilation by multiplying the volume of air they breathe in one breath, by their respiratory (breathing) rate. VE = TV x f If you breathe 14 times in one minute (respiratory rate) and you bre ...
... Minute ventilation is the volume of air you breathe in one minute. (VE) You can calculate a person’s minute ventilation by multiplying the volume of air they breathe in one breath, by their respiratory (breathing) rate. VE = TV x f If you breathe 14 times in one minute (respiratory rate) and you bre ...
John Ferguson MacDonald John Ferguson MacDonald, who died
... His interest in glutamate led John to examine mechanisms related to glutamate’s potentially noxious action: excessive depolarization and Ca2+ influx via NMDARs result in the death of nerve cells, for example following brain ischemia, when large amounts of glutamate are released from neurons and glia ...
... His interest in glutamate led John to examine mechanisms related to glutamate’s potentially noxious action: excessive depolarization and Ca2+ influx via NMDARs result in the death of nerve cells, for example following brain ischemia, when large amounts of glutamate are released from neurons and glia ...
John Ferguson MacDonald
... His interest in glutamate led John to examine mechanisms related to glutamate’s potentially noxious action: excessive depolarization and Ca2+ influx via NMDARs result in the death of nerve cells, for example following brain ischemia, when large amounts of glutamate are released from neurons and glia ...
... His interest in glutamate led John to examine mechanisms related to glutamate’s potentially noxious action: excessive depolarization and Ca2+ influx via NMDARs result in the death of nerve cells, for example following brain ischemia, when large amounts of glutamate are released from neurons and glia ...
Practice Questions Section 2
... Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following. Pay close attention to the physical states! Also - you must include the charge when writing ions, otherwise your answer is incorrect. Do not balance these equations using fractions for coefficients. sulfur dioxide gas combines with oxygen ...
... Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following. Pay close attention to the physical states! Also - you must include the charge when writing ions, otherwise your answer is incorrect. Do not balance these equations using fractions for coefficients. sulfur dioxide gas combines with oxygen ...
respiratory system notes - Kevan Kruger
... Asthma narrows the airways by causing allergy-induced spasms of surrounding muscles or by clogging the airways with mucus. Bronchitis is an inflammatory response that reduces airflow and is caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollutants, or allergens. Cystic ...
... Asthma narrows the airways by causing allergy-induced spasms of surrounding muscles or by clogging the airways with mucus. Bronchitis is an inflammatory response that reduces airflow and is caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollutants, or allergens. Cystic ...