Biology-transition-b..
... understanding of AS‐Level. http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/biology-4401/past-papers-and-markschemes/old-past-papers-and-mark-schemes The cells in animals and plants all need oxygen to be able to release energy for the jobs they do. They all produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. Cand ...
... understanding of AS‐Level. http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/biology-4401/past-papers-and-markschemes/old-past-papers-and-mark-schemes The cells in animals and plants all need oxygen to be able to release energy for the jobs they do. They all produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. Cand ...
clin sys MENU v 8
... ELITech Clinical Systems offers a broad and growing menu of liquid-stable reagents backed by more than 25 years of experience in assay development and reagent manufacturing. ELITech reagents are: ...
... ELITech Clinical Systems offers a broad and growing menu of liquid-stable reagents backed by more than 25 years of experience in assay development and reagent manufacturing. ELITech reagents are: ...
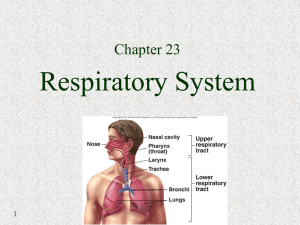
Chapter 23
... capillary cell walls. In this case, the released proton remains in blood plasma, thus blood pH goes down. Without much ventilation (hyhpoventilation) blood pH goes down. While by hyperventilation, blood pH goes up. ...
... capillary cell walls. In this case, the released proton remains in blood plasma, thus blood pH goes down. Without much ventilation (hyhpoventilation) blood pH goes down. While by hyperventilation, blood pH goes up. ...
Document
... Further downward positive regulation of ERF1: ERF1 a secondary transcription factor then binds with the GCC box present in the promoter of other genes (PDF1.2,Hls1 and ChiB). The product of above mentioned genes acts as metabolic protein and control the various responses in plant body. For examp ...
... Further downward positive regulation of ERF1: ERF1 a secondary transcription factor then binds with the GCC box present in the promoter of other genes (PDF1.2,Hls1 and ChiB). The product of above mentioned genes acts as metabolic protein and control the various responses in plant body. For examp ...
Isolation and expression of an allergen
... sequence of 12 amino acids ( VYCDTCRAGFET ). In addition, certain cysteine residues are highly conserved both within the group of allergens and in SN20 (Fig. 2), suggesting that these proteins are likely to share a similar secondary structure and may display a common function. Despite extensive rese ...
... sequence of 12 amino acids ( VYCDTCRAGFET ). In addition, certain cysteine residues are highly conserved both within the group of allergens and in SN20 (Fig. 2), suggesting that these proteins are likely to share a similar secondary structure and may display a common function. Despite extensive rese ...
Thermodynamic considerations of carbon dioxide evolution in
... CO,) and the CO, transfer from lung capillacy blood - > COZa__.). It is not clear to lung alveoli (CO,,,. whether the last two steps are both rate-limiting, or whether the carbonic anhydrase reaction (as was suggested by Roughton C51) is the only step that is removed from equilibrium. Inhibition of ...
... CO,) and the CO, transfer from lung capillacy blood - > COZa__.). It is not clear to lung alveoli (CO,,,. whether the last two steps are both rate-limiting, or whether the carbonic anhydrase reaction (as was suggested by Roughton C51) is the only step that is removed from equilibrium. Inhibition of ...
Respiratory System Part 2
... Carbon dioxide transport in the blood Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, ...
... Carbon dioxide transport in the blood Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, ...
2018 Specimen Paper 2 - Cambridge International Examinations
... 12 20 cm3 of ethyne, C2H2, are reacted with 500 cm3 of oxygen. The equation for the reaction is 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) ...
... 12 20 cm3 of ethyne, C2H2, are reacted with 500 cm3 of oxygen. The equation for the reaction is 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) ...
Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases
... nNOS are both activated by an elevation in intracellular Ca 21 , followed by the subsequent binding of Ca 21 / CaM. In contrast, iNOS contains irreversibly bound CaM, and is hence largely independent of Ca 21 , although a 2-fold greater activity is observed in the presence of 2.5 mM Ca 21 compared t ...
... nNOS are both activated by an elevation in intracellular Ca 21 , followed by the subsequent binding of Ca 21 / CaM. In contrast, iNOS contains irreversibly bound CaM, and is hence largely independent of Ca 21 , although a 2-fold greater activity is observed in the presence of 2.5 mM Ca 21 compared t ...
Breathing On Mars-Laura Wunderl
... device that is implanted inside a human body for respiratory support. The artificial lung oxygenates the blood and removes the excess carbon dioxide from the blood (Nolan, et al., 2011). These are intentional outcomes in hopes of saving the lives of those who need respiratory aids or new lungs. One ...
... device that is implanted inside a human body for respiratory support. The artificial lung oxygenates the blood and removes the excess carbon dioxide from the blood (Nolan, et al., 2011). These are intentional outcomes in hopes of saving the lives of those who need respiratory aids or new lungs. One ...
Respiratory System: Oxygen Delivery System The primary function
... tubes. The bronchial tubes lead directly into the lungs where they divide into many smaller tubes which connect to tiny sacs called alveoli. The average adult's lungs contain about 600 million of these spongy, air-filled sacs that are surrounded by capillaries. The inhaled oxygen passes into the alv ...
... tubes. The bronchial tubes lead directly into the lungs where they divide into many smaller tubes which connect to tiny sacs called alveoli. The average adult's lungs contain about 600 million of these spongy, air-filled sacs that are surrounded by capillaries. The inhaled oxygen passes into the alv ...
2402_Ch23.ppt
... • Carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions (70%) in combination with blood proteins (23%) and in solution with plasma (7%) • Hemoglobin that has released oxygen binds more readily to carbon dioxide than hemoglobin that has oxygen bound to it (Haldane effect) • In tissue capillaries, carbon ...
... • Carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions (70%) in combination with blood proteins (23%) and in solution with plasma (7%) • Hemoglobin that has released oxygen binds more readily to carbon dioxide than hemoglobin that has oxygen bound to it (Haldane effect) • In tissue capillaries, carbon ...
chapter3_Sections 1
... cholesterol more than any other fat, and directly alter the function of arteries and veins • Eating as little as 2 grams a day of hydrogenated vegetable oils increases risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), heart attack, and diabetes ...
... cholesterol more than any other fat, and directly alter the function of arteries and veins • Eating as little as 2 grams a day of hydrogenated vegetable oils increases risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), heart attack, and diabetes ...
Bio Respiration 2009 Yingxin
... O All organism can metabolize glucose anaerobically using glycolysis (in cytoplasm) O Energy yield very low O Produces much more toxic waste products O Yeast and plants: alcoholic fermentation O Animals: production of lactic acid O Plants & Yeast C6H12O6 C2H5OH (Ethanol) + CO2 + small amount of ener ...
... O All organism can metabolize glucose anaerobically using glycolysis (in cytoplasm) O Energy yield very low O Produces much more toxic waste products O Yeast and plants: alcoholic fermentation O Animals: production of lactic acid O Plants & Yeast C6H12O6 C2H5OH (Ethanol) + CO2 + small amount of ener ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... as peptide bonds. Use your textbook to make a sketch of a dipeptide (2 amino acids linked with a peptide bond) molecule. (p59) ...
... as peptide bonds. Use your textbook to make a sketch of a dipeptide (2 amino acids linked with a peptide bond) molecule. (p59) ...
Overview of Body Systems Test Name: Date: ______ Match the
... C) Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates wastes D) Nourishes a developing fetus and embryo ...
... C) Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates wastes D) Nourishes a developing fetus and embryo ...
3. What are macromolecules?
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
Unit 1 – Life on Earth
... is the term given to the process of cell division. • Cells must divide for GROWTH and REPAIR purposes in the body. • There are 6 key stages in this process which ends in 2 daughter cells being IDENTICAL to the parent cell. • They are genetically identical to prevent loss of information (sometimes wr ...
... is the term given to the process of cell division. • Cells must divide for GROWTH and REPAIR purposes in the body. • There are 6 key stages in this process which ends in 2 daughter cells being IDENTICAL to the parent cell. • They are genetically identical to prevent loss of information (sometimes wr ...
Genetics Protein Project
... Human myoglobin has 153 amino acid residues in a highly folded and compact structure with eight separate and distinct alpha helical secondary structures. ...
... Human myoglobin has 153 amino acid residues in a highly folded and compact structure with eight separate and distinct alpha helical secondary structures. ...
... that uses Arg in the synthesis of muscle creatin. Arg is considered an important modulator of immunological and physiological processes. The degradation of Arg produces ornithine, a precursor of polyamines that are key to cell division, DNA synthesis, and cell cycle regulation. Arg participates in t ...
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS 06 AUGUST
... The steep concentration gradient results in diffusion of oxygen from the air in the alveoli to the blood capillaries. Oxygen dissolves in the moisture lining each alveolus and diffuses through the thin wall of the alveolus and the thin wall of the capillary into the blood. The blood becomes oxygenat ...
... The steep concentration gradient results in diffusion of oxygen from the air in the alveoli to the blood capillaries. Oxygen dissolves in the moisture lining each alveolus and diffuses through the thin wall of the alveolus and the thin wall of the capillary into the blood. The blood becomes oxygenat ...
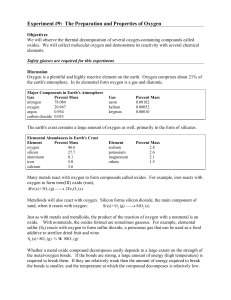
Experiment # 9 Properties of Oxygen
... Your apparatus will consist of a collecting trough that is connected by rubber tubing to a generator bottle with a thistle tube. The reaction will take place in the generator bottle and then the oxygen gas will move through the tubing into the collecting trough where the collection bottles will be. ...
... Your apparatus will consist of a collecting trough that is connected by rubber tubing to a generator bottle with a thistle tube. The reaction will take place in the generator bottle and then the oxygen gas will move through the tubing into the collecting trough where the collection bottles will be. ...
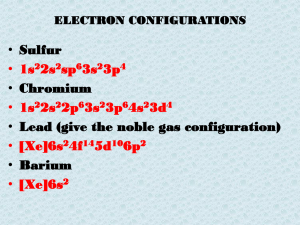
Writing formulas and naming ionic bonds
... Al(ClO3)3 Lead(II) sulfide Pb3S2 Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 ...
... Al(ClO3)3 Lead(II) sulfide Pb3S2 Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 ...