Role of aerobic glycolysis in genetically engineered mouse models of cancer Abstract
... energy in the form of ATP were worked out long ago. As shown in Figure 1, these start with a series of chemical conversions to pyruvate (producing two ATPs) followed either by oxidation in the mitochondrion (producing 30 ATPs) or the conversion of pyruvate to lactate. The steps from glucose to lact ...
... energy in the form of ATP were worked out long ago. As shown in Figure 1, these start with a series of chemical conversions to pyruvate (producing two ATPs) followed either by oxidation in the mitochondrion (producing 30 ATPs) or the conversion of pyruvate to lactate. The steps from glucose to lact ...
Exercise Physiology Study Guide-Test 1 History of Exercise
... o Breakdown of glucose, may be anaerobic or aerobic o Requires 12 enzymatic reaction to breakdown glucose and glycogen into ATP o When it occurs in glycolytic system is anaerobic o Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of the muscle cell o Glycogenesis-process by which glycogen is synthesized from glucos ...
... o Breakdown of glucose, may be anaerobic or aerobic o Requires 12 enzymatic reaction to breakdown glucose and glycogen into ATP o When it occurs in glycolytic system is anaerobic o Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of the muscle cell o Glycogenesis-process by which glycogen is synthesized from glucos ...
Cellular Respiration
... In the absence of oxygen, a cell will use fermentation to produce ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Lactic Acid Fermentation converts glucose into lactic acid. This type of fermentation occurs in human muscle cells during strenuous exercise when breathing cannot supply the cells with enough ox ...
... In the absence of oxygen, a cell will use fermentation to produce ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. Lactic Acid Fermentation converts glucose into lactic acid. This type of fermentation occurs in human muscle cells during strenuous exercise when breathing cannot supply the cells with enough ox ...
Anaerobic Glucose and Serine Metabolism in Staphy
... at 12000 g for 15 min on a Sorvall RC-5 Superspeed centrifuge, washed twice with 02-free 67 mM-Na+/K-lphosphate buffer pH 6.8 (referred to as phosphate buffer) and resuspended to the required concentration in the same buffer. Bacterial suspensions used in anaerobic experiments were held under 0,-fre ...
... at 12000 g for 15 min on a Sorvall RC-5 Superspeed centrifuge, washed twice with 02-free 67 mM-Na+/K-lphosphate buffer pH 6.8 (referred to as phosphate buffer) and resuspended to the required concentration in the same buffer. Bacterial suspensions used in anaerobic experiments were held under 0,-fre ...
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
... Causes of Hyperglycemia Glucose is an essential nutrient that provides energy for the proper functioning of the body cells. Carbohydrates are broken down in the small intestine and the glucose in digested food is then absorbed by the intestinal cells into the blood stream and is carried by the blood ...
... Causes of Hyperglycemia Glucose is an essential nutrient that provides energy for the proper functioning of the body cells. Carbohydrates are broken down in the small intestine and the glucose in digested food is then absorbed by the intestinal cells into the blood stream and is carried by the blood ...
The Effect of L-Carnitine Treatment on Lactic Acid Levels in Normal
... The blood was collected at the initial, first and second hours during the oral glucose tolerance test. The oral glucose tolerance test was repeated after oral carnitine therapy (3 gr/day) for seven days. According to the ADA criteria ten subjects (7 women / 3 men) had normal glucose tolerance (NGT) ...
... The blood was collected at the initial, first and second hours during the oral glucose tolerance test. The oral glucose tolerance test was repeated after oral carnitine therapy (3 gr/day) for seven days. According to the ADA criteria ten subjects (7 women / 3 men) had normal glucose tolerance (NGT) ...
Quiz SBI 4UI - Waterloo Region District School Board
... 22. What does the NAD Dehy, Cyt b-c1 and Cyt oxidase have in ...
... 22. What does the NAD Dehy, Cyt b-c1 and Cyt oxidase have in ...
Gluconeogensis
... b. Cleaves CO2 & attaches a phosphate to oxaloacetate c. Called a kinase b/c ATP is involved d. Single ATP can’t add phosphate to pyruvate to make PEP b/c it requires more energy than the ATP has i. Doing it this way is more energetically favorable (cutting off the CO2) ii. Jesse asks a question in ...
... b. Cleaves CO2 & attaches a phosphate to oxaloacetate c. Called a kinase b/c ATP is involved d. Single ATP can’t add phosphate to pyruvate to make PEP b/c it requires more energy than the ATP has i. Doing it this way is more energetically favorable (cutting off the CO2) ii. Jesse asks a question in ...
Benfotiamine 150 + Alpha-Lipoic Acid 300
... Aging brings an accumulation of oxidized proteins that interfere with mitochondrial efficiency, and a reduction in mitochondrial mass that leads to imperfect energy homeostasis. Alpha-lipoic acid’s status as a so-called “mitochondrial nutrient” helps to address these aging factors.18, 19 Benfotiamin ...
... Aging brings an accumulation of oxidized proteins that interfere with mitochondrial efficiency, and a reduction in mitochondrial mass that leads to imperfect energy homeostasis. Alpha-lipoic acid’s status as a so-called “mitochondrial nutrient” helps to address these aging factors.18, 19 Benfotiamin ...
A laktóz (lac) operon – egy példa a prokarióta génszabályozásra
... Presence of glucose: stop the operation of the lac operon Catabolite repression: a process when the end product of the reaction stops the reaction. cAMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase enzyme. Under conditions of high glucose content, a glucose breakdown product inhibits the enzyme ad ...
... Presence of glucose: stop the operation of the lac operon Catabolite repression: a process when the end product of the reaction stops the reaction. cAMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase enzyme. Under conditions of high glucose content, a glucose breakdown product inhibits the enzyme ad ...
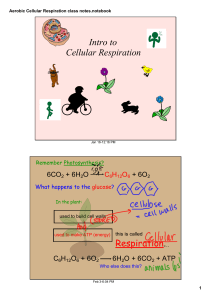
Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook
... Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook ...
... Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook ...
The liver is the largest gland in the body, weighing about 1.4 Kg. It is
... are modified by the liver for excreted by kidneys. Bilirubin metabolism :It is a greenish-yellow pigment, it is formed as end product of Hb. It is fat soluble, very toxic, its secretion is one of important function of the liver. It combines with plasma albumin, called free or unconjugated bilirubin ...
... are modified by the liver for excreted by kidneys. Bilirubin metabolism :It is a greenish-yellow pigment, it is formed as end product of Hb. It is fat soluble, very toxic, its secretion is one of important function of the liver. It combines with plasma albumin, called free or unconjugated bilirubin ...
Q#1,2,5-8 pg. 194
... glycolysis generate 2 ATP per molecule of glucose. Conversely aerobic respiration uses an electron transport chain and produces approximately 36–38 ATP per molecule of glucose. 2. (a) The major difference between fermentation and glycolysis is that the fermentation pathway includes additional reacti ...
... glycolysis generate 2 ATP per molecule of glucose. Conversely aerobic respiration uses an electron transport chain and produces approximately 36–38 ATP per molecule of glucose. 2. (a) The major difference between fermentation and glycolysis is that the fermentation pathway includes additional reacti ...
Key area 2 * Cellular respiration
... • Describe the citric acid cycle. • Understand that respiration is a series of enzyme mediated reactions • Explain the importance of the products of the citric acid cycle ...
... • Describe the citric acid cycle. • Understand that respiration is a series of enzyme mediated reactions • Explain the importance of the products of the citric acid cycle ...
HOW CELLS HARVEST ENERGY
... Occurs on the inner membrane of the mitochondria Uses energy in NADH and FADH2 to make 32 ATP NADH and FADH2 donate e- to ETC As e- is moved thru ETC, the energy in e- is used to actively pump protons across the inner membrane NRG from the e- is now stored in the proton gradient As the protons diff ...
... Occurs on the inner membrane of the mitochondria Uses energy in NADH and FADH2 to make 32 ATP NADH and FADH2 donate e- to ETC As e- is moved thru ETC, the energy in e- is used to actively pump protons across the inner membrane NRG from the e- is now stored in the proton gradient As the protons diff ...
Kevin Ahern's Biochemistry (BB 450/550) at Oregon State University
... ATP energy. Gluconeogenesis, the synthesis of glucose, is an anabolic pathway that involves reduction and requires ATP and ATP.. There are 10 reactions in glycolysis. Students should know structures of fructose and glucose compounds, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, 1,3 BPG, all enzyme names, all molecul ...
... ATP energy. Gluconeogenesis, the synthesis of glucose, is an anabolic pathway that involves reduction and requires ATP and ATP.. There are 10 reactions in glycolysis. Students should know structures of fructose and glucose compounds, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, 1,3 BPG, all enzyme names, all molecul ...
Short Answer Questions: a workshop
... Look at a student’s answer to the question below and summarise it in NO MORE THAN 20 words. Question: The enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) catalyses the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA in the mitochondria. Some children have a deficiency of this enzyme activity. Explain why: these children h ...
... Look at a student’s answer to the question below and summarise it in NO MORE THAN 20 words. Question: The enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) catalyses the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA in the mitochondria. Some children have a deficiency of this enzyme activity. Explain why: these children h ...
Cellular respiration 2
... is the only way to make enough ATP. Cellular respiration releases energy more slowly than fermentation. _____________ Well conditioned athletes must pace themselves during a long race. ...
... is the only way to make enough ATP. Cellular respiration releases energy more slowly than fermentation. _____________ Well conditioned athletes must pace themselves during a long race. ...
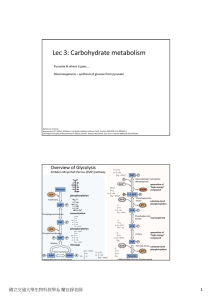
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... However, in the lack of O2 (such as anaerobic microorganisms and intensively exercised muscle), NADH still needs to dump its electron on somewhere in order to regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis to continue. ...
... However, in the lack of O2 (such as anaerobic microorganisms and intensively exercised muscle), NADH still needs to dump its electron on somewhere in order to regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis to continue. ...
AP Biology Cellular Respiration Notes 9.1
... production of ATP by chemiosmosis. 1. Electrons are made available in the Citric Acid cycle. 2. The first protein in the ETC is reduced when it accepts e-‘s 3. The proteins of the ETC are arranged by increasing electronegativity 4. The proteins pull the e- back and forth across the membrane “exergon ...
... production of ATP by chemiosmosis. 1. Electrons are made available in the Citric Acid cycle. 2. The first protein in the ETC is reduced when it accepts e-‘s 3. The proteins of the ETC are arranged by increasing electronegativity 4. The proteins pull the e- back and forth across the membrane “exergon ...
Metabolism: Introduction
... ATP is the energy currency of cells In phototrophs, light energy is transformed into the light energy of ATP In heterotrophs, catabolism produces ATP, which drives activities of cells ATP cycle carries energy from photosynthesis or catabolism to the energy-requiring processes of cells ...
... ATP is the energy currency of cells In phototrophs, light energy is transformed into the light energy of ATP In heterotrophs, catabolism produces ATP, which drives activities of cells ATP cycle carries energy from photosynthesis or catabolism to the energy-requiring processes of cells ...
Dear Notetaker:
... o Can get amino acids from Kreb’s cycle Intermediate is OAA OAA can be used to make glucose o Gluconeogenesis is basically the reverse of glycolysis Can take the end products of glycolysis and use them for gluconeogenesis Have to bypass 3 important steps of glycolysis o Occurs predominantly ...
... o Can get amino acids from Kreb’s cycle Intermediate is OAA OAA can be used to make glucose o Gluconeogenesis is basically the reverse of glycolysis Can take the end products of glycolysis and use them for gluconeogenesis Have to bypass 3 important steps of glycolysis o Occurs predominantly ...
Lecture 08 Notes
... Lecture 8 Notes – How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Questions • How does the ATP molecule store chemical energy needed to run biological processes? • How are enzymes involved in regulating energy metabolism? ...
... Lecture 8 Notes – How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Questions • How does the ATP molecule store chemical energy needed to run biological processes? • How are enzymes involved in regulating energy metabolism? ...
Zygorrhynchus moelleri
... A further sample (IV) was prepared corresponding to the growing cells used in an earlier investigation (Moses, 1957). The latter were grown for 13 hr. only instead of the customary 18 hr., and were subsequently resuspended in a modified growth medium containing glucose and acetate as carbon source, ...
... A further sample (IV) was prepared corresponding to the growing cells used in an earlier investigation (Moses, 1957). The latter were grown for 13 hr. only instead of the customary 18 hr., and were subsequently resuspended in a modified growth medium containing glucose and acetate as carbon source, ...
L02_2002
... Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing a (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of GLYCOGENIN. This attachment step i ...
... Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing a (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of GLYCOGENIN. This attachment step i ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.