
Gene expression clustering using gene ontology and biological
... There are many proximity metrics such as L1 and L2 norms, Mahalanobis distance, correlation, etc. ...
... There are many proximity metrics such as L1 and L2 norms, Mahalanobis distance, correlation, etc. ...
DNA Packaging
... Higher-order DNA compaction in a eukaryotic chromosome. This model shows the levels of organization that could provide the observed degree of DNA compaction in the chromosomes of eukaryotes. First the DNA is wrapped around histone octamers, then H1 stimulates formation of the 30 nm filament. Further ...
... Higher-order DNA compaction in a eukaryotic chromosome. This model shows the levels of organization that could provide the observed degree of DNA compaction in the chromosomes of eukaryotes. First the DNA is wrapped around histone octamers, then H1 stimulates formation of the 30 nm filament. Further ...
Algebra 1 - Edublogs
... 2. Which of the following does NOT describe how genetic information is organized in the cell? A. A gene contains the coded information for building a protein B. A nucleus contains chromosomes which are made of genes C. The sequence of bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in protein D. ...
... 2. Which of the following does NOT describe how genetic information is organized in the cell? A. A gene contains the coded information for building a protein B. A nucleus contains chromosomes which are made of genes C. The sequence of bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in protein D. ...
Unit 5 - Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... the same number of chromosomes and has genes identical to those of the parent cell one-half of the number of chromosomes and has genes identical to those of the parent cell the same number of chromosomes, but has genes different from those of the parent cell one-half of the number of chromosomes, bu ...
... the same number of chromosomes and has genes identical to those of the parent cell one-half of the number of chromosomes and has genes identical to those of the parent cell the same number of chromosomes, but has genes different from those of the parent cell one-half of the number of chromosomes, bu ...
Supplementary Material Legends
... methylation levels determined by bisulfite sequencing for selected target transgenes. The quantitative analysis of bisulfite sequencing results [%] was confined to the region of the pNOS sequence in target transgenes that is covered by the pNOS dsRNA arising from the silencer transgene. Total “bisul ...
... methylation levels determined by bisulfite sequencing for selected target transgenes. The quantitative analysis of bisulfite sequencing results [%] was confined to the region of the pNOS sequence in target transgenes that is covered by the pNOS dsRNA arising from the silencer transgene. Total “bisul ...
Evolution of gastrulation - Development
... cell-to-cell signalling may be novel but require little modification of a system in which there is flow of material to the membrane with an external coat. Even the provision of an extracellular matrix would seem to present little difficulty given an endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. There is, perhaps ...
... cell-to-cell signalling may be novel but require little modification of a system in which there is flow of material to the membrane with an external coat. Even the provision of an extracellular matrix would seem to present little difficulty given an endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. There is, perhaps ...
From profiles to function in epigenomics
... epigenomic profiling are still growing in both numbers and complexity. BOX 2 illustrates this complexity of profiles and provides details of the different marks and features profiled to date. These can be divided into the following categories: DNA modifications, which includes C5‑methylcytosine (5 m ...
... epigenomic profiling are still growing in both numbers and complexity. BOX 2 illustrates this complexity of profiles and provides details of the different marks and features profiled to date. These can be divided into the following categories: DNA modifications, which includes C5‑methylcytosine (5 m ...
human embryonic stem cells and their clinical relevance
... from human to human in these culture system still remain. Sato et al reported that activation of Wnt pathway by 6- bromo indirubin 3’- oxime promotes the self renewal of embryonic stem cells in the presence of bFGF, matrigel and a proprietary serum replacement product [8]. Amit et al reported that b ...
... from human to human in these culture system still remain. Sato et al reported that activation of Wnt pathway by 6- bromo indirubin 3’- oxime promotes the self renewal of embryonic stem cells in the presence of bFGF, matrigel and a proprietary serum replacement product [8]. Amit et al reported that b ...
Bio 102 Practice Problems Cell Cycle and Cell Division
... 7. Genetic analysis of cancer cells shows that they are usually aneuploid (have more or fewer chromosomes than normal). In addition to dividing rapidly, they also very often have mutations which affect the checkpoints of the cell cycle. Suppose a cell acquires a mutation so that the checkpoint at th ...
... 7. Genetic analysis of cancer cells shows that they are usually aneuploid (have more or fewer chromosomes than normal). In addition to dividing rapidly, they also very often have mutations which affect the checkpoints of the cell cycle. Suppose a cell acquires a mutation so that the checkpoint at th ...
Plant Transformation - University of Rhode Island
... system, resulting in induction of virulence (vir) genes. Among these genes, virD1 and virD2 form a site-specific nuclease that nicks the T-DNA region at border sequences. In nature, T-DNA resides on the Ti-(tumor inducing) or Ri-(root inducing) plasmid (1), but in the laboratory T-DNA can be “launch ...
... system, resulting in induction of virulence (vir) genes. Among these genes, virD1 and virD2 form a site-specific nuclease that nicks the T-DNA region at border sequences. In nature, T-DNA resides on the Ti-(tumor inducing) or Ri-(root inducing) plasmid (1), but in the laboratory T-DNA can be “launch ...
PowerPoint File
... Genetics Mutants Wild-type – “normal” fully-active gene Null – absence of any activity (e.g. deletion) Hypomorph – reduced function Hypermorph – enhanced activity Neomorph – expressed in cells normally not expressed (transgenic approach) Phenotypic analysis – development, morphology, ...
... Genetics Mutants Wild-type – “normal” fully-active gene Null – absence of any activity (e.g. deletion) Hypomorph – reduced function Hypermorph – enhanced activity Neomorph – expressed in cells normally not expressed (transgenic approach) Phenotypic analysis – development, morphology, ...
A-level Biology B Question paper Unit 2 - Genes and Genetic
... (ii) Explain how the mutation leads to the production of the non-functional enzyme. ...
... (ii) Explain how the mutation leads to the production of the non-functional enzyme. ...
Coordination of Cell Cycle Progression and Mitotic
... histone modifications in regulation of G1/S transcription remains to be clarified in yeast. In human cells it is well established that E2F transcription factors employ Set1 and MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferases during the G1-S transition (Tyagi et al. 2007). Interestingly, the Set1C complex has been inv ...
... histone modifications in regulation of G1/S transcription remains to be clarified in yeast. In human cells it is well established that E2F transcription factors employ Set1 and MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferases during the G1-S transition (Tyagi et al. 2007). Interestingly, the Set1C complex has been inv ...
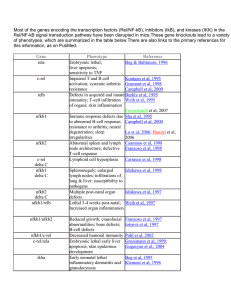
nfkb_gene_knockouts
... Most of the genes encoding the transcription factors (Rel/NF-kB), inhibitors (IkB), and kinases (IKK) in the Rel/NF-kB signal transduction pathway have been disrupted in mice.These gene knockouts lead to a variety of phenotypes, which are summarized in the table below.There are also links to the pri ...
... Most of the genes encoding the transcription factors (Rel/NF-kB), inhibitors (IkB), and kinases (IKK) in the Rel/NF-kB signal transduction pathway have been disrupted in mice.These gene knockouts lead to a variety of phenotypes, which are summarized in the table below.There are also links to the pri ...
CRCT Vocabulary Review Units 1-4
... Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound __________ that have a Organelles specific function to carry out life. ...
... Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound __________ that have a Organelles specific function to carry out life. ...
Biology 50 - BrainMass
... was made between a plant that was true-breeding for red flowers, and another plant truebreeding for yellow flowers. F1 progeny, all having red flowers, were allowed to form seeds, which were then planted to generate F2 progeny. Pollen from all the resulting F2 plants was pooled and used to fertilize ...
... was made between a plant that was true-breeding for red flowers, and another plant truebreeding for yellow flowers. F1 progeny, all having red flowers, were allowed to form seeds, which were then planted to generate F2 progeny. Pollen from all the resulting F2 plants was pooled and used to fertilize ...
chapter 21 notes
... Embryonic stem cells Early human embryo at blastocyst stage (mammalian equivalent of blastula) ...
... Embryonic stem cells Early human embryo at blastocyst stage (mammalian equivalent of blastula) ...
H3 Turnover - [c] crabrock.net
... Chip-Seq • H3.3 bound to DNA in almost all the same places in embryonic neurons and cultured neurons. ...
... Chip-Seq • H3.3 bound to DNA in almost all the same places in embryonic neurons and cultured neurons. ...
Terms to know - Northern Highlands
... homologous chromosomes, diploid, haploid, crossing-over, tetrad, gametes, zygote, somatic cell, fertilization 25. Know the stages of the Cell Cycle, including parts of Interphase. Describe what is occurring in each phase of the cell cycle. 26. Know some cells/tissues that do cell division frequently ...
... homologous chromosomes, diploid, haploid, crossing-over, tetrad, gametes, zygote, somatic cell, fertilization 25. Know the stages of the Cell Cycle, including parts of Interphase. Describe what is occurring in each phase of the cell cycle. 26. Know some cells/tissues that do cell division frequently ...
Cell Processes Energy Ch 2 (teacher)
... 1. The first stage of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm. 2. In the first stage of respiration a great deal of energy is required from the sun. 3. ATP can be made from fermentation or cellular respiration. ...
... 1. The first stage of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm. 2. In the first stage of respiration a great deal of energy is required from the sun. 3. ATP can be made from fermentation or cellular respiration. ...
Cells and DNA Table of Contents
... What is a cell? Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hered ...
... What is a cell? Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hered ...
lec-4 - ucsf biochemistry website
... introduced into flies these often were not expressed, but just as described for enhancer trapping, if these elements are mobilized by 2-3 expression, they will move to new sites and at some of these sites they will trap enhancers. A cross to a UAS-GFP line (responder/reporter) will reveal cases in ...
... introduced into flies these often were not expressed, but just as described for enhancer trapping, if these elements are mobilized by 2-3 expression, they will move to new sites and at some of these sites they will trap enhancers. A cross to a UAS-GFP line (responder/reporter) will reveal cases in ...
Proposal - people.vcu.edu
... One important type of cellular adhesive is known as the desmosome (Garrod & Chigdey, 2008). The desmosome is primarily found in the epidermis and it consists of proteins that help to form its structural component, the desmosome-intermediate filament complex (DFIC). Without proper function of the des ...
... One important type of cellular adhesive is known as the desmosome (Garrod & Chigdey, 2008). The desmosome is primarily found in the epidermis and it consists of proteins that help to form its structural component, the desmosome-intermediate filament complex (DFIC). Without proper function of the des ...
















![H3 Turnover - [c] crabrock.net](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006486995_1-d3c1e811108ce44a4ea294ab9a5bd59a-300x300.png)





