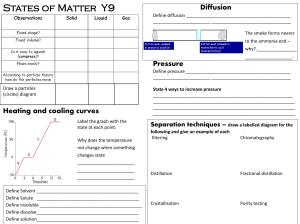
Chapter 15 Review Questions
... them together (i.e. several amino acid chains, folded in tertiary shapes). All this is accomplished with the help of enzymes. 8. RNA contains ribose and DNA contains deoxyribose (one less oxygen on the sugar); DNA stays in the nucleus, RNA travels back and forth between the nucleus and the cytoplasm ...
... them together (i.e. several amino acid chains, folded in tertiary shapes). All this is accomplished with the help of enzymes. 8. RNA contains ribose and DNA contains deoxyribose (one less oxygen on the sugar); DNA stays in the nucleus, RNA travels back and forth between the nucleus and the cytoplasm ...
View document as PDF
... Teaching Points When proteins fold into their tertiary structures, there are often subdivisions within the protein, designated as domains, which are characterized by similar features or motifs. One such motif is the zinc finger, in which a specific domain of the protein is arranged into a “finger-li ...
... Teaching Points When proteins fold into their tertiary structures, there are often subdivisions within the protein, designated as domains, which are characterized by similar features or motifs. One such motif is the zinc finger, in which a specific domain of the protein is arranged into a “finger-li ...
ENZYME
... Core has 3 layers: a/b/a. In general, alkaline phosphatase is a dimer containing nearly identical subunits which each have two molecules of zinc and one molecule of magnesium ion. One molecule of zinc is tightly bound, giving the structure stability and the other is loosely bound which provide ...
... Core has 3 layers: a/b/a. In general, alkaline phosphatase is a dimer containing nearly identical subunits which each have two molecules of zinc and one molecule of magnesium ion. One molecule of zinc is tightly bound, giving the structure stability and the other is loosely bound which provide ...
PPT Oxidation
... There are three other chemical species available in a basic solution besides the ones shown above. They are: ...
... There are three other chemical species available in a basic solution besides the ones shown above. They are: ...
Biochemistry
... Explain the difference between elements and compounds Describe the location and charge of the 3 subatomic particles (protons, neutrons and electrons) Describe what isotopes are and how radioactive isotopes are used in biology Describe the difference between a covalent and an ionic bond and explain w ...
... Explain the difference between elements and compounds Describe the location and charge of the 3 subatomic particles (protons, neutrons and electrons) Describe what isotopes are and how radioactive isotopes are used in biology Describe the difference between a covalent and an ionic bond and explain w ...
ENZYMES
... • Some reactions RELEASE energy ie: 2H2+O2---> 2H2O + heat • Some reactions ABSORB energy ie: 2H2O----> 2H2+O2 (energy is needed - light reactions of photosynthesis) • Energy is stored in the bonds between molecules • Matter and energy must be conserved - some reactions happen slowly, others happen ...
... • Some reactions RELEASE energy ie: 2H2+O2---> 2H2O + heat • Some reactions ABSORB energy ie: 2H2O----> 2H2+O2 (energy is needed - light reactions of photosynthesis) • Energy is stored in the bonds between molecules • Matter and energy must be conserved - some reactions happen slowly, others happen ...
Nucleic Acid Notes
... Folding occurs as protein is synthesized, but physical/chemical environment plays a role DENATURATION: = unraveling/ loss of native confirmation • makes proteins biologically inactive ~ Reason high fevers can be fatal • • does NOT break peptide bonds • so primary structure remains intact • may regai ...
... Folding occurs as protein is synthesized, but physical/chemical environment plays a role DENATURATION: = unraveling/ loss of native confirmation • makes proteins biologically inactive ~ Reason high fevers can be fatal • • does NOT break peptide bonds • so primary structure remains intact • may regai ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... 9. When fluorine forms an ionic bond it tends to a. lose electrons b. gain electrons c. share electrons d. lose protons 10. Copper (II) hydroxide is composed of a. 2 elements, 2 atoms b. 2 elements, 3 atoms c. 3 elements, 4 atoms d. 3 elements, 5 atoms ...
... 9. When fluorine forms an ionic bond it tends to a. lose electrons b. gain electrons c. share electrons d. lose protons 10. Copper (II) hydroxide is composed of a. 2 elements, 2 atoms b. 2 elements, 3 atoms c. 3 elements, 4 atoms d. 3 elements, 5 atoms ...
Multiple Choice:
... RNA Polymerase I is involved in the synthesis of various rRNA subunits, not protein products (that is done by RNA Polymerase II). 26. C Resonance of the double bond between the carbonyl (C=O) and amide (C-N) bonds imparts a partial double bond character to the peptide (or amide) bond. Atoms that are ...
... RNA Polymerase I is involved in the synthesis of various rRNA subunits, not protein products (that is done by RNA Polymerase II). 26. C Resonance of the double bond between the carbonyl (C=O) and amide (C-N) bonds imparts a partial double bond character to the peptide (or amide) bond. Atoms that are ...
Stability of complexes of metal ions in aqueous solution.
... Figure 2. The Be(II) and La(III) aqua ions, Be(II) generated using PM3, the La(III) is from the CSD (Cambridge Structural Database)1, entry number SUDDAW. As shown, the geometry around the La3+ is a tricapped trigonal prism, a common geometry for nine-coordinate species with unidentate ligands. ...
... Figure 2. The Be(II) and La(III) aqua ions, Be(II) generated using PM3, the La(III) is from the CSD (Cambridge Structural Database)1, entry number SUDDAW. As shown, the geometry around the La3+ is a tricapped trigonal prism, a common geometry for nine-coordinate species with unidentate ligands. ...
PROTEINS - Hyndland Secondary School
... protein groups, called prosthetic groups – e.g. myoglobin & haemoglobin bind to a porphyrin (haem) chelating an Iron atom – e.g. Chlorophyll has a similar prosthetic group chelating Mg ...
... protein groups, called prosthetic groups – e.g. myoglobin & haemoglobin bind to a porphyrin (haem) chelating an Iron atom – e.g. Chlorophyll has a similar prosthetic group chelating Mg ...
ROTAFER PLUS ROTAFER PLUS (Capsules) (iron (III) hydroxide
... Rotafer Puls is a complex of iron, zinc and group-B vitamins. Iron is a compound in the form of hydroxide Fe3+ polymaltose complex. The outer multi-core hydroxide Fe3+ centres are surrounded by many noncovalently bound polymaltose molecules, thusly forming a complex with total weight of 50,000 dalto ...
... Rotafer Puls is a complex of iron, zinc and group-B vitamins. Iron is a compound in the form of hydroxide Fe3+ polymaltose complex. The outer multi-core hydroxide Fe3+ centres are surrounded by many noncovalently bound polymaltose molecules, thusly forming a complex with total weight of 50,000 dalto ...
Mapping the Body.indd
... b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? ...
... b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? ...
Molecule Challenge
... 21 of 24) In the picture, chlorine is stealing an electron from sodium. Two part question: a) What type of bond is this? b) Which atom will have the negative charge? ...
... 21 of 24) In the picture, chlorine is stealing an electron from sodium. Two part question: a) What type of bond is this? b) Which atom will have the negative charge? ...
Electron Rule.
... Oxidation State Electron Count. Ligands are viewed as “close-shelled” entities. (No radicals). This is what we did in the earlier examples. We dissect the structure When neutral Lewis base ligands (like NH3) are considered they are viewed as neutral molecules with 2 electrons for donation to the met ...
... Oxidation State Electron Count. Ligands are viewed as “close-shelled” entities. (No radicals). This is what we did in the earlier examples. We dissect the structure When neutral Lewis base ligands (like NH3) are considered they are viewed as neutral molecules with 2 electrons for donation to the met ...
Chemistry and “Magic Numbers” 18
... Oxidation State Electron Count. Ligands are viewed as “close-shelled” entities. (No radicals). This is what we did in the earlier examples. We dissect the structure When neutral Lewis base ligands (like NH3) are considered they are viewed as neutral molecules with 2 electrons for donation to the met ...
... Oxidation State Electron Count. Ligands are viewed as “close-shelled” entities. (No radicals). This is what we did in the earlier examples. We dissect the structure When neutral Lewis base ligands (like NH3) are considered they are viewed as neutral molecules with 2 electrons for donation to the met ...
Molecule Challenge
... 21 of 24) In the picture, chlorine is stealing an electron from sodium. Two part question: a) What type of bond is this? b) Which atom will have the negative charge? ...
... 21 of 24) In the picture, chlorine is stealing an electron from sodium. Two part question: a) What type of bond is this? b) Which atom will have the negative charge? ...
File
... 4. An enzyme is a protein that changes the rate (catalyzes) a chemical reaction. a. Without enzymes, chemical reactions necessary for life would not occur at a rate sufficient for sustaining life b. Enzymes are protein (organic) catalysts. Substrate = The reactant molecules to which an enzyme binds ...
... 4. An enzyme is a protein that changes the rate (catalyzes) a chemical reaction. a. Without enzymes, chemical reactions necessary for life would not occur at a rate sufficient for sustaining life b. Enzymes are protein (organic) catalysts. Substrate = The reactant molecules to which an enzyme binds ...
4.1_Proteins_Amino_Acids_2011
... (A) Each amino acid contributes three bonds (red) to the backbone of the chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is ...
... (A) Each amino acid contributes three bonds (red) to the backbone of the chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is ...
Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept
... intermembrane space while passing electrons between them b) proton gradient - so that hydrogen ions will diffuse through the ATP synthase channels down their concentration gradient c) c) ATP synthase complex – as hydrogen ions pass through the synthases, the production of ATP from ADP and Pi is cata ...
... intermembrane space while passing electrons between them b) proton gradient - so that hydrogen ions will diffuse through the ATP synthase channels down their concentration gradient c) c) ATP synthase complex – as hydrogen ions pass through the synthases, the production of ATP from ADP and Pi is cata ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.