
THE INTERPLAY OF COORDINATION CHEMISTRY AND SOLVATION IN DESIGNING SELECTIVE SENSORS FOR TOXIC METALS AND OTHER IONIC TARGETS
... significant challenges. Solvent extraction from water into a less polar organic phase via the formation of complexes with distinct optical or electrochemical properties presents an opportunity for addressing selectivity issues, by combining the unique coordination properties for each species (via li ...
... significant challenges. Solvent extraction from water into a less polar organic phase via the formation of complexes with distinct optical or electrochemical properties presents an opportunity for addressing selectivity issues, by combining the unique coordination properties for each species (via li ...
HL Periodicity
... As the d-block fills, there are electrons available for other functions (create colors). The atomic radii are curious, also. Based on electron config. ...
... As the d-block fills, there are electrons available for other functions (create colors). The atomic radii are curious, also. Based on electron config. ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
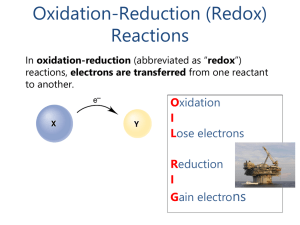
... Oxidation Number (or Oxidation State): actual or hypothetical charge of an atom in a compound if it existed as a monatomic ion ...
... Oxidation Number (or Oxidation State): actual or hypothetical charge of an atom in a compound if it existed as a monatomic ion ...
protein - CSU, Chico
... In order for the body to build a protein, it must have ALL the EAAs. If just one essential amino acid is missing, protein cannot be synthesized, and all the other amino acids are deaminated. ...
... In order for the body to build a protein, it must have ALL the EAAs. If just one essential amino acid is missing, protein cannot be synthesized, and all the other amino acids are deaminated. ...
Atomic Mass
... electrons is not always equal. • Slight attraction between slightly charged regions of a nearby molecules. • A combination of ionic and covalent bonds TED - Gecko Talk ...
... electrons is not always equal. • Slight attraction between slightly charged regions of a nearby molecules. • A combination of ionic and covalent bonds TED - Gecko Talk ...
Station #1: Chemistry
... d. A chemical reaction the releases more energy than it absorbs. e. Increases a reaction by lowering the activation energy. f. A chemical reaction that absorbs more energy that it releases. ...
... d. A chemical reaction the releases more energy than it absorbs. e. Increases a reaction by lowering the activation energy. f. A chemical reaction that absorbs more energy that it releases. ...
chapter 5 Macromolecules
... monomers, a peptide bond forms Peptide bond is a covalent bond that links amino acids together to create proteins. Polypeptide = bonding together of numerous amino acids Proteins are composed of polypeptides in various bond structures ...
... monomers, a peptide bond forms Peptide bond is a covalent bond that links amino acids together to create proteins. Polypeptide = bonding together of numerous amino acids Proteins are composed of polypeptides in various bond structures ...
Chapter 11: Membrane transport
... Net movements of molecules from one site from high concentration to low concentration is diffusion Passive diffusion is unassisted Its facilitated diffusion if a protein allows diffusion across a membrane barrier Channels (with selective permeability) allow diffusion of ions down their concentration ...
... Net movements of molecules from one site from high concentration to low concentration is diffusion Passive diffusion is unassisted Its facilitated diffusion if a protein allows diffusion across a membrane barrier Channels (with selective permeability) allow diffusion of ions down their concentration ...
Lipids, Carbohydrates, and Proteins!
... Ex: chlorine Compound: material that contains only ONE type of MOLECULE. Ex: sodium chloride Remember: elements contain one type of atom Pure compounds contain one type of molecule ...
... Ex: chlorine Compound: material that contains only ONE type of MOLECULE. Ex: sodium chloride Remember: elements contain one type of atom Pure compounds contain one type of molecule ...
Proteins2[1]
... into two or more clusters known as domains • Domains are functional units that look like globular proteins • Domains are parts of protein subunits ...
... into two or more clusters known as domains • Domains are functional units that look like globular proteins • Domains are parts of protein subunits ...
The substances on the left side of a chemical equation are called
... Chemical Bonding is the joining of atoms to form new substances. The properties of these new substances are different from the properties of the original elements. Not all the electrons in an atom are used to make chemical bonds. Valence Electrons that determines how atom will react. (bond) ...
... Chemical Bonding is the joining of atoms to form new substances. The properties of these new substances are different from the properties of the original elements. Not all the electrons in an atom are used to make chemical bonds. Valence Electrons that determines how atom will react. (bond) ...
How Did Life Begin? And What is Life?
... In support of the reverse citric acid cycle: • At hydrothermal vents, there is a constant ...
... In support of the reverse citric acid cycle: • At hydrothermal vents, there is a constant ...
Developing Metals
... which would never occur. Ten outer electrons could either represent a nickel atom (4s23d8) or a Cu+/Zn2+ ion (4s03d10). ...
... which would never occur. Ten outer electrons could either represent a nickel atom (4s23d8) or a Cu+/Zn2+ ion (4s03d10). ...
41. Testing for enzymes
... It may be useful to discuss how to decide which reaction is fastest. Teachers should be sensitive to the needs of vegetarian students. Manganese dioxide, copper oxide and calcium carbonate can also be tested as catalysts to illustrate biological and chemical catalysts. Cooked liver (well done) can a ...
... It may be useful to discuss how to decide which reaction is fastest. Teachers should be sensitive to the needs of vegetarian students. Manganese dioxide, copper oxide and calcium carbonate can also be tested as catalysts to illustrate biological and chemical catalysts. Cooked liver (well done) can a ...
Chem212,Quiz5,99
... • (1) the molecular geometry (octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar, etc.) • (2) d-electron configuration (sketch the d-orbital splitting, label the orbitals, and fill in the correct number of electrons) • (3) expected ligand field splitting (strong or weak-field case) • (4) expected spin type (hig ...
... • (1) the molecular geometry (octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar, etc.) • (2) d-electron configuration (sketch the d-orbital splitting, label the orbitals, and fill in the correct number of electrons) • (3) expected ligand field splitting (strong or weak-field case) • (4) expected spin type (hig ...
Chapter 5 – Homework
... 3. Identify the two “types” of monosaccharides and discuss how they differ in structure. 1 ½ pts total ½ pt each – Aldose and Ketose ½ pt – in the position of the carbonyl group. 4. Both carbohydrates and lipids are built of C,H,O. Discuss how you can tell them apart by just looking at their formula ...
... 3. Identify the two “types” of monosaccharides and discuss how they differ in structure. 1 ½ pts total ½ pt each – Aldose and Ketose ½ pt – in the position of the carbonyl group. 4. Both carbohydrates and lipids are built of C,H,O. Discuss how you can tell them apart by just looking at their formula ...
Michael Carney - University of Wisconsin
... state, NNN and NNP ligands coordinate in a mer fashion and the metal complexes possess distorted square pyramidal structures and high spin (S = 2) electronic configurations. Compounds with NNS coordination environments display a variety of solid state structures, ranging from those with unbound sulf ...
... state, NNN and NNP ligands coordinate in a mer fashion and the metal complexes possess distorted square pyramidal structures and high spin (S = 2) electronic configurations. Compounds with NNS coordination environments display a variety of solid state structures, ranging from those with unbound sulf ...
Essential Question: What is biochemistry
... C, H, N, O, P, and S are the most important elements for organisms. Na, K, and Fe are also important. Atoms of elements are almost never found alone, thus they combine to form larger substances called molecules Exs. O2 , F2 or to form compounds Exs. H2O, C6H12O6 . The attraction that hold to atoms t ...
... C, H, N, O, P, and S are the most important elements for organisms. Na, K, and Fe are also important. Atoms of elements are almost never found alone, thus they combine to form larger substances called molecules Exs. O2 , F2 or to form compounds Exs. H2O, C6H12O6 . The attraction that hold to atoms t ...
Chapter 2
... Primary structure Sequence of amino acids In large part determines other protein features ...
... Primary structure Sequence of amino acids In large part determines other protein features ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.









![Proteins2[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008291804_1-fc4b593e0423ea377f021b9f7071accd-300x300.png)












