Practice problems for chapter 1, 2 and 3 1) A small amount of salt
... C) +3 D) -5 E) -6 30) Horizontal rows of the periodic table are known as __________. A) periods B) groups C) metalloids D) metals E) nonmetals 31) Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________. A) chalcogens B) alkali metals C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 32) When a metal and ...
... C) +3 D) -5 E) -6 30) Horizontal rows of the periodic table are known as __________. A) periods B) groups C) metalloids D) metals E) nonmetals 31) Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________. A) chalcogens B) alkali metals C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 32) When a metal and ...
Cell Respiration State that oxidation involves the loss of electrons
... In the Krebs cycle and glycolysis, pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed from the respiratory substrates. Oxidised NAD is converted into reduced NAD, except in the Krebs cycle, where FAD is reduced instead. Hydrogen atoms or their electrons are transported along a series of carriers in the final stage ...
... In the Krebs cycle and glycolysis, pairs of hydrogen atoms are removed from the respiratory substrates. Oxidised NAD is converted into reduced NAD, except in the Krebs cycle, where FAD is reduced instead. Hydrogen atoms or their electrons are transported along a series of carriers in the final stage ...
CH 115 Exam 2 - UAB General Chemistry Supplemental Instruction
... b. X and Y c. X and Z d. Y and Z e. Z only 15. What volume of 0.400 M HCl(aq) do you need to dissolve 12.0 g of CaCO3(s)? a. Not enough information to answer b. 599 mL c. 300 mL d. 10.9 mL e. 822 mL 16. If you titrate 40.0 mL of NaOH(aq) with 45.0 mL of 0.335 M H2SO4(aq), what is the concentration o ...
... b. X and Y c. X and Z d. Y and Z e. Z only 15. What volume of 0.400 M HCl(aq) do you need to dissolve 12.0 g of CaCO3(s)? a. Not enough information to answer b. 599 mL c. 300 mL d. 10.9 mL e. 822 mL 16. If you titrate 40.0 mL of NaOH(aq) with 45.0 mL of 0.335 M H2SO4(aq), what is the concentration o ...
Biomolecules
... These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many other things. ...
... These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many other things. ...
Metals and the Environment
... New mining techniques can decrease the effects of metal extraction on the environment. In bioleaching, metal ores are dissolved in a solution then mixed with certain bacteria. Depending on the type of bacteria, different metals will be ‘leached’ from the ores into the solution, ready for electrolysi ...
... New mining techniques can decrease the effects of metal extraction on the environment. In bioleaching, metal ores are dissolved in a solution then mixed with certain bacteria. Depending on the type of bacteria, different metals will be ‘leached’ from the ores into the solution, ready for electrolysi ...
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS COMPLEX
... composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands (atoms, ions, or molecules) that are formally donating electrons to the metal center ...
... composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands (atoms, ions, or molecules) that are formally donating electrons to the metal center ...
Comparative Biochemistry
... To give species – specific structural variations of common proteins/enzymes To give the modes of nitrogenous end-product metabolism in the animal kingdom. To identify and give the functional properties of oxygen – binding pigments in vertebrates and invertebrates. To compare the intermediary metabol ...
... To give species – specific structural variations of common proteins/enzymes To give the modes of nitrogenous end-product metabolism in the animal kingdom. To identify and give the functional properties of oxygen – binding pigments in vertebrates and invertebrates. To compare the intermediary metabol ...
Ch 2 PowerPoint Notes
... •A substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction is called a substrate. •Enzymes act only on specific substrates. •An enzyme’s shape determines its activity. Typically, an enzyme is a large protein with one or more deep folds on its surface. These folds form pockets called active site ...
... •A substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction is called a substrate. •Enzymes act only on specific substrates. •An enzyme’s shape determines its activity. Typically, an enzyme is a large protein with one or more deep folds on its surface. These folds form pockets called active site ...
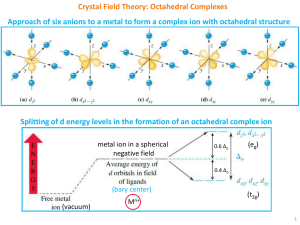
Crystal Field Theory: Octahedral Complexes
... There are only 4 ligands in the tetrahedral complex and hence the ligand field is roughly 2/3 of the octahedral field. The direction of ligand approach in tetrahedral complex does not coincide with the d-orbitals. This reduces the field by a factor of 2/3. Therefore Δt is roughly 2/3 x 2/3 = 4/9 ...
... There are only 4 ligands in the tetrahedral complex and hence the ligand field is roughly 2/3 of the octahedral field. The direction of ligand approach in tetrahedral complex does not coincide with the d-orbitals. This reduces the field by a factor of 2/3. Therefore Δt is roughly 2/3 x 2/3 = 4/9 ...
Cloning and Sequencing of DNA from a Plasmid Library
... for sequencing to the BioResource Center (Cornell University), using T3 and T7 universal primers. Internal primers were designed using WebGenetics software, and each sequence was verified with overlapping sequences on each strand. Sequences were compared to those in the NCBI databases using the Blas ...
... for sequencing to the BioResource Center (Cornell University), using T3 and T7 universal primers. Internal primers were designed using WebGenetics software, and each sequence was verified with overlapping sequences on each strand. Sequences were compared to those in the NCBI databases using the Blas ...
METABOLISM FOUR CLASSES OF BIOMOLECULES (ALL
... is tough and strong. Hair, fingernails, fur, and the outer layers of animal skin are made mostly of keratin. 2. Enzymes make chemical reactions occur quickly. An example of an enzyme is the protein called amylase. Amylase is found in human saliva and helps digest starch. Starch is a carbohydrate mad ...
... is tough and strong. Hair, fingernails, fur, and the outer layers of animal skin are made mostly of keratin. 2. Enzymes make chemical reactions occur quickly. An example of an enzyme is the protein called amylase. Amylase is found in human saliva and helps digest starch. Starch is a carbohydrate mad ...
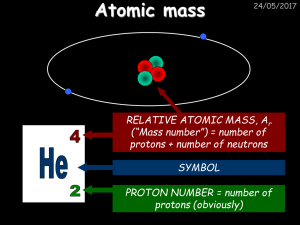
Atomic mass - drseemaljelani
... nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
... nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
Oxygen binding proteins RESP 312
... Oxygen Binding Proteins are Hemoproteins • Oxygen binding proteins (myoglobin and hemoglobin) are hemoproteins • Hemoproteins are a group of specialized proteins that contain heme as a tightly bound prosthetic group. ...
... Oxygen Binding Proteins are Hemoproteins • Oxygen binding proteins (myoglobin and hemoglobin) are hemoproteins • Hemoproteins are a group of specialized proteins that contain heme as a tightly bound prosthetic group. ...
www.theallpapers.com
... The main uses of zinc are preventing steel from rusting and making alloys. (a) The main ore of zinc is zinc blende. Zinc blende consists mainly of zinc sulfide, ZnS. There are two major methods of extracting zinc from its ore. They are the direct reduction of zinc oxide to zinc and by electrolysis. ...
... The main uses of zinc are preventing steel from rusting and making alloys. (a) The main ore of zinc is zinc blende. Zinc blende consists mainly of zinc sulfide, ZnS. There are two major methods of extracting zinc from its ore. They are the direct reduction of zinc oxide to zinc and by electrolysis. ...
www.eastpenn.k12.pa.us
... -Amino acids are compounds with an amino group on one end (NH2)and a carboxyl group on the other end (-COOH) -Covalent bonds called peptide bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide -Multiple polypeptides join to form a protein -In living things, proteins make up cellular structures. Som ...
... -Amino acids are compounds with an amino group on one end (NH2)and a carboxyl group on the other end (-COOH) -Covalent bonds called peptide bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide -Multiple polypeptides join to form a protein -In living things, proteins make up cellular structures. Som ...
Ch. 5 "The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... 8. Describe the unique properties, building block molecules, and biological importance of the three important groups of lipids: fats, phospholipids, and steroids. 9. Identify an ester linkage and describe how it is formed. ----------Proteins------------------10. Describe the characteristics that dis ...
... 8. Describe the unique properties, building block molecules, and biological importance of the three important groups of lipids: fats, phospholipids, and steroids. 9. Identify an ester linkage and describe how it is formed. ----------Proteins------------------10. Describe the characteristics that dis ...
A2 Respiration test
... An experiment was carried out to measure the rate at which a sample of mitochondria used oxygen under different conditions. The mitochondria were placed in a well oxygenated liquid with a water potential equal to the water potential of their contents. At time A, an end-product of glycolysis was add ...
... An experiment was carried out to measure the rate at which a sample of mitochondria used oxygen under different conditions. The mitochondria were placed in a well oxygenated liquid with a water potential equal to the water potential of their contents. At time A, an end-product of glycolysis was add ...
BI ACE_02 .
... In solution, amino acids will ionize The amino group and carboxyl group will do so. The carboxyl group produces Hydrogen ions and acts like an acid, while the amino group removes Hydrogen ions from solution, acting as a base. ...
... In solution, amino acids will ionize The amino group and carboxyl group will do so. The carboxyl group produces Hydrogen ions and acts like an acid, while the amino group removes Hydrogen ions from solution, acting as a base. ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.