3 BondsMolpH
... mean? This means that sulfur wants to form chemical bonds with other atoms in order to gain 2 more electrons, even if the sulfur atoms has to share those two electrons in a covalent bond with another atom. In the course of a chemical reaction where sulfur acquires two new electrons, chemists show th ...
... mean? This means that sulfur wants to form chemical bonds with other atoms in order to gain 2 more electrons, even if the sulfur atoms has to share those two electrons in a covalent bond with another atom. In the course of a chemical reaction where sulfur acquires two new electrons, chemists show th ...
(null): 110.ReactionsIntro
... electrical, radiant, mechanical) b) KE transformed into chem PE 3) Do reduced version of Zn & HCl: one zinc pellet in test tube plus a few ml of HCl. While bubbling discuss where energy is stored and where it goes 4) Return to reaction, have Ss feel test tube (warm!) & decide if reaction followed Op ...
... electrical, radiant, mechanical) b) KE transformed into chem PE 3) Do reduced version of Zn & HCl: one zinc pellet in test tube plus a few ml of HCl. While bubbling discuss where energy is stored and where it goes 4) Return to reaction, have Ss feel test tube (warm!) & decide if reaction followed Op ...
S1-2-02: What is the basic subatomic structure of an atom?
... S1-0-04: What symbols and systems help people use chemicals safely at home, work and for the environment? 4. What are some similarities and differences between WHMIS and HHPS? ...
... S1-0-04: What symbols and systems help people use chemicals safely at home, work and for the environment? 4. What are some similarities and differences between WHMIS and HHPS? ...
Biomolecules are organic molecules built and used inside of cells
... – All have this general structure, with the ______group representing the molecule that makes each AA unique AAs have: • C,H,O, and ____ • An ______ group ...
... – All have this general structure, with the ______group representing the molecule that makes each AA unique AAs have: • C,H,O, and ____ • An ______ group ...
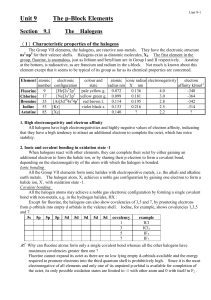
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
Micronutrients and beneficial elements in horticultural crops
... In soilless media and hydroponics, pH monitoring of water and media is relatively easier than in soils. When regular testing is performed, and pH control is adequate, it is possible to prefer the inexpensive, less stable iron chelates. On the other hand, in alkaline soils, where it is difficult to e ...
... In soilless media and hydroponics, pH monitoring of water and media is relatively easier than in soils. When regular testing is performed, and pH control is adequate, it is possible to prefer the inexpensive, less stable iron chelates. On the other hand, in alkaline soils, where it is difficult to e ...
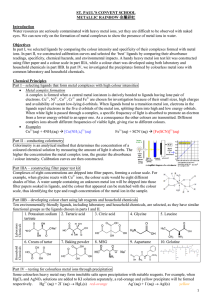
ST. PAUL`S CONVENT SCHOOL METALLIC RAINBOW 金屬彩虹
... In part I, NH3, en, citrate and glycine were chosen for Cu2+ for the conduction of colorimetry; EDTA, oxalate and tartrate for Ni2+; conc. HCl, en and tartrate for Co2+; NaBr, EDTA and leucine for Cr3+; KSCN, rust indicator, en, citrate and glycine for Fe3+. In part II, en and glycine were selec ...
... In part I, NH3, en, citrate and glycine were chosen for Cu2+ for the conduction of colorimetry; EDTA, oxalate and tartrate for Ni2+; conc. HCl, en and tartrate for Co2+; NaBr, EDTA and leucine for Cr3+; KSCN, rust indicator, en, citrate and glycine for Fe3+. In part II, en and glycine were selec ...
Option C - Human biochemistry C.1 Diet-
... • -they contain an amine group (NH2) on the central carbon atom (a), a carboxyl group and different R-groups. • -all amino acids are optically active (not needed, but good to know) ...
... • -they contain an amine group (NH2) on the central carbon atom (a), a carboxyl group and different R-groups. • -all amino acids are optically active (not needed, but good to know) ...
Physical Science/Chemistry Unit Standard Benchmarks Activities
... 1. Recognize that all substances are pg. 124-129 composed of one or more 2. Untamed Science: Organizing Like elements. The periodic table Mendeleev organizes the elements into 3. Songs: Meet the Elements groups with similar properties. 4. Gizmo: Element Builder 5. Lab: Playful Periodic Table ...
... 1. Recognize that all substances are pg. 124-129 composed of one or more 2. Untamed Science: Organizing Like elements. The periodic table Mendeleev organizes the elements into 3. Songs: Meet the Elements groups with similar properties. 4. Gizmo: Element Builder 5. Lab: Playful Periodic Table ...
Final Exam S06 KEY
... b) Using your character tables, deduce which metal orbitals will be used to form the n bonds, and draw pictures of the n bonding interactions between the Pt(I1) and the CNligands. (For your pictures, simply show diagrams that illustrate the n bonding between the d orbitals and ligand orbitals of co ...
... b) Using your character tables, deduce which metal orbitals will be used to form the n bonds, and draw pictures of the n bonding interactions between the Pt(I1) and the CNligands. (For your pictures, simply show diagrams that illustrate the n bonding between the d orbitals and ligand orbitals of co ...
basic chemistry of atoms and molecules
... Protons have a positive electric charge. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines the identity of that element. An atom of carbon always has six protons. If there is any different number of protons in the nucleus, then the atom is not carbon. An atom of nitrogen has seven pr ...
... Protons have a positive electric charge. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines the identity of that element. An atom of carbon always has six protons. If there is any different number of protons in the nucleus, then the atom is not carbon. An atom of nitrogen has seven pr ...
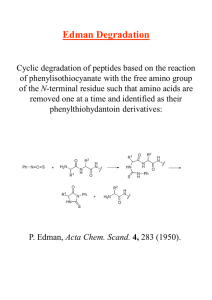
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Hearthburn wonder labs balanced equations copy
... 2) Count the number of atoms on each side of the equation, keeping subscripts and parentheses into account 3) To balance the number of atoms on each side of the equation (LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER!) we will add coefficients to compounds where we need more of a certain element. ...
... 2) Count the number of atoms on each side of the equation, keeping subscripts and parentheses into account 3) To balance the number of atoms on each side of the equation (LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER!) we will add coefficients to compounds where we need more of a certain element. ...
Chapter 11 Review sheet Name
... reaction. If the change is caused by heat supplied to the reaction, the Greek symbol (9) is often written above the "yields" symbol in the equation. A chemical change in which a free element replaces and releases another element in a compound is called a(n) (10) reaction. A chemical change in which ...
... reaction. If the change is caused by heat supplied to the reaction, the Greek symbol (9) is often written above the "yields" symbol in the equation. A chemical change in which a free element replaces and releases another element in a compound is called a(n) (10) reaction. A chemical change in which ...
second exam2
... the maximum possible membrane potential that could be generated by NADH oxidation by oxygen and the maximum amount of ATP that could be generated from this process. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN FOR ANY CREDIT. a) 5 points. Consider the oxidation of NADH by oxygen (this is the reaction run in your body to ...
... the maximum possible membrane potential that could be generated by NADH oxidation by oxygen and the maximum amount of ATP that could be generated from this process. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN FOR ANY CREDIT. a) 5 points. Consider the oxidation of NADH by oxygen (this is the reaction run in your body to ...
2P32 - Pilkington Group
... For [M(H20)6]n+ in order for the metal ion to accommodate six ligands it must have at least a 52 pm radius. Six waters fit exactly around a metal ion with 52 pm radius (not crowded). At 92 pm’s the six waters have moved far enough apart that more waters can fit. If the metal ion is smaller than 52pm ...
... For [M(H20)6]n+ in order for the metal ion to accommodate six ligands it must have at least a 52 pm radius. Six waters fit exactly around a metal ion with 52 pm radius (not crowded). At 92 pm’s the six waters have moved far enough apart that more waters can fit. If the metal ion is smaller than 52pm ...
Click to download. - Life Learning Cloud
... AN ATOM is the smallest particle of an element. They cannot be split into smaller particles in chemical reactions. Iron is made of iron atoms (Fe). Sulphur is made of sulphur atoms (S) A MOLECULE is a small group of atoms joined together. The atoms may be the same (e.g. O2) or different (e.g. H2O). ...
... AN ATOM is the smallest particle of an element. They cannot be split into smaller particles in chemical reactions. Iron is made of iron atoms (Fe). Sulphur is made of sulphur atoms (S) A MOLECULE is a small group of atoms joined together. The atoms may be the same (e.g. O2) or different (e.g. H2O). ...
The dinitrogenase reductase
... • Then the side chain amino group of Gln is further transferred to a-ketoglutarate to form Glu in a reaction catalyzed by glutamate synthase, an enzyme only present in bacteria and plants, not in animals. ...
... • Then the side chain amino group of Gln is further transferred to a-ketoglutarate to form Glu in a reaction catalyzed by glutamate synthase, an enzyme only present in bacteria and plants, not in animals. ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... – Nucleus: consists of protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) of equal mass (atomic number = number of protons = element’s identity) – Electrons (-): low mass, arranged in shells around nucleus (outer shells reactive, high energy, can be attracted to other nuclei) – Isotopes: different forms of same ele ...
... – Nucleus: consists of protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) of equal mass (atomic number = number of protons = element’s identity) – Electrons (-): low mass, arranged in shells around nucleus (outer shells reactive, high energy, can be attracted to other nuclei) – Isotopes: different forms of same ele ...
Fall Exam 4 - Chemistry - University of Kentucky
... Starting with answer "1" on SIDE 1, fill in the circle indicating the one best answer for each of the 60 questions in this examination. Your score is the sum of the appropriate credit for each response. Soon after the examination is finished, an examination key will be posted on Blackboard. Grading ...
... Starting with answer "1" on SIDE 1, fill in the circle indicating the one best answer for each of the 60 questions in this examination. Your score is the sum of the appropriate credit for each response. Soon after the examination is finished, an examination key will be posted on Blackboard. Grading ...
Two-Metal-Ion Catalysis in Adenylyl Cyclase
... tion, binds at site B. Mn2⫹ is an activator of AC, whereas Zn2⫹ is an inhibitor [IC50 ⫽ 15 M (13)]. Although Zn2⫹ does not generally inhibit two-metal-ion– utilizing enzymes (16 –18), it does inhibit several DNA and RNA polymerases (19). In these enzymes and AC, Zn2⫹ may perturb the coordination of ...
... tion, binds at site B. Mn2⫹ is an activator of AC, whereas Zn2⫹ is an inhibitor [IC50 ⫽ 15 M (13)]. Although Zn2⫹ does not generally inhibit two-metal-ion– utilizing enzymes (16 –18), it does inhibit several DNA and RNA polymerases (19). In these enzymes and AC, Zn2⫹ may perturb the coordination of ...
Enzymes are proteins which control biochemical reactions in cells
... o Reaction may not take place in absence of enzymes (each enzyme has a specific catalytic action) o Enzymes catalyse a reaction at max. rate at an optimum state * Induced fit theory o Enzyme's shape changes when substrate binds to active site o Amino acids are moulded into a precise form to perform ...
... o Reaction may not take place in absence of enzymes (each enzyme has a specific catalytic action) o Enzymes catalyse a reaction at max. rate at an optimum state * Induced fit theory o Enzyme's shape changes when substrate binds to active site o Amino acids are moulded into a precise form to perform ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation on Model Titanium Oxide Surfaces
... oxygen pressure. In surface science, for most of these oxidation/ reduction processes the decomposition (dissociation) pathways are studied where the number of moles consumed is equal or less to the number of moles produced. This preference is in part due to what it generally referred to as the pres ...
... oxygen pressure. In surface science, for most of these oxidation/ reduction processes the decomposition (dissociation) pathways are studied where the number of moles consumed is equal or less to the number of moles produced. This preference is in part due to what it generally referred to as the pres ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.