Reaction Mechanism
... between the metal and entering group is thought to be concurrent – Interchange mechanism. MLaX + Y → Y…MXa…X → MLaY + X leaving transition leaving group state group In I mechanism, there is no intermediate but various transition states are possible. ◆Dissociative interchange (Id) in which bond break ...
... between the metal and entering group is thought to be concurrent – Interchange mechanism. MLaX + Y → Y…MXa…X → MLaY + X leaving transition leaving group state group In I mechanism, there is no intermediate but various transition states are possible. ◆Dissociative interchange (Id) in which bond break ...
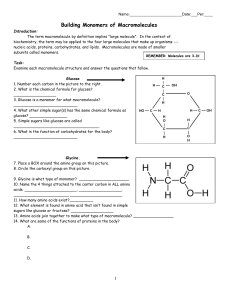
3.2.1 What are Action Molecules?
... Enzyme: An enzyme is a protein in the human body that is used as a catalyst to stimulate a specific chemical reaction. Substrate: A substrate is a molecule that an enzyme bonds with in a reaction. Importance of Enzymes: Enzymes control the speed of chemical reaction in the body. They allow these ...
... Enzyme: An enzyme is a protein in the human body that is used as a catalyst to stimulate a specific chemical reaction. Substrate: A substrate is a molecule that an enzyme bonds with in a reaction. Importance of Enzymes: Enzymes control the speed of chemical reaction in the body. They allow these ...
Unit 04 Enzymes and respiration Review
... 4. Enzymes are a type of _______________________. The characteristics of enzymes are that they can __________________________________, are a ______________________ fit to their substrate referred to as the __________________________ complex, they can be altered by ___________ or _____________, and a ...
... 4. Enzymes are a type of _______________________. The characteristics of enzymes are that they can __________________________________, are a ______________________ fit to their substrate referred to as the __________________________ complex, they can be altered by ___________ or _____________, and a ...
Regulatory Strategies
... – Subunits can interact even in different conformations – Change induced by binding of substrate to one subunits can increase or decrease substrate binding to other subunits • positive or negative homotropic effects ...
... – Subunits can interact even in different conformations – Change induced by binding of substrate to one subunits can increase or decrease substrate binding to other subunits • positive or negative homotropic effects ...
protein review 2 - Ms. Hart WHS Science
... structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances ...
... structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances ...
MMP-10 catalytic domain, human, recombinant
... > 10U/μg. Activity described as U=100 pmol/min at 25°C using a colorimetric assay with thiopeptide Ac-Pro-Leu-Gly-[2mercapto-4-methyl-pentanoyl]-Leu-Gly-OC2H5 (Biomol) as substrate. USAGE Enzyme kinetic studies, cleavage of target substrates and screening of inhibitors. SUPPLIED AS 0.2mg/ml in Tris ...
... > 10U/μg. Activity described as U=100 pmol/min at 25°C using a colorimetric assay with thiopeptide Ac-Pro-Leu-Gly-[2mercapto-4-methyl-pentanoyl]-Leu-Gly-OC2H5 (Biomol) as substrate. USAGE Enzyme kinetic studies, cleavage of target substrates and screening of inhibitors. SUPPLIED AS 0.2mg/ml in Tris ...
S1 Genetics
... Why do changes of one amino acid for another destroy the function of a protein? 1. If the protein is an enzyme, the amino acid that carries out the reaction may be changed 2. The altered amino acid may have been involved in pairing with another amino acid to maintain the shape of the protein. ...
... Why do changes of one amino acid for another destroy the function of a protein? 1. If the protein is an enzyme, the amino acid that carries out the reaction may be changed 2. The altered amino acid may have been involved in pairing with another amino acid to maintain the shape of the protein. ...
Enzyme - Northwest ISD Moodle
... •Protease ________ ___________ •Sucrase ________ ___________ •Lipase ________ ___________ ...
... •Protease ________ ___________ •Sucrase ________ ___________ •Lipase ________ ___________ ...
Metabolism PPT File
... • Plays an important role during extreme physical exercise. • When not enough oxygen getting to muscle cells that need it. • anaerobic respiration supplies the extra energy needed. • But.... What results is a build up of lactic acid in your muscles = pain & fatigue. ...
... • Plays an important role during extreme physical exercise. • When not enough oxygen getting to muscle cells that need it. • anaerobic respiration supplies the extra energy needed. • But.... What results is a build up of lactic acid in your muscles = pain & fatigue. ...
Electorphoretic Separation of Proteins
... The three-dimensional structure of a protein is due to the type and sequence of its constituent amino acids. Since the amino acid sequence of each protein is unique, it follows that different proteins assume different shapes. Thus, there is a remarkable diversity of three-dimensional protein forms. ...
... The three-dimensional structure of a protein is due to the type and sequence of its constituent amino acids. Since the amino acid sequence of each protein is unique, it follows that different proteins assume different shapes. Thus, there is a remarkable diversity of three-dimensional protein forms. ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... For example the atoms in Na, He, N2 and S8 have oxidation numbers of 0. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. For example, the oxidation number of Na+ is +1; the oxidation number of S2- is -2 and of Al3+ is +3. 3. The usual oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (when ...
... For example the atoms in Na, He, N2 and S8 have oxidation numbers of 0. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. For example, the oxidation number of Na+ is +1; the oxidation number of S2- is -2 and of Al3+ is +3. 3. The usual oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (when ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... For example the atoms in Na, He, N2 and S8 have oxidation numbers of 0. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. For example, the oxidation number of Na+ is +1; the oxidation number of S2- is -2 and of Al3+ is +3. 3. The usual oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (when ...
... For example the atoms in Na, He, N2 and S8 have oxidation numbers of 0. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion. For example, the oxidation number of Na+ is +1; the oxidation number of S2- is -2 and of Al3+ is +3. 3. The usual oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (when ...
COMPLEX IONS AND AMPHOTERISM
... ion will form the deep blue water-soluble ion [Cu(NH3)4]2+, and Mn2+ will precipitate as the hydroxide Mn(OH)2. By centrifuging and decanting, the solution and precipitate can be separated and the ions present in each part can be identified by tests based on your investigation of the chemistries of ...
... ion will form the deep blue water-soluble ion [Cu(NH3)4]2+, and Mn2+ will precipitate as the hydroxide Mn(OH)2. By centrifuging and decanting, the solution and precipitate can be separated and the ions present in each part can be identified by tests based on your investigation of the chemistries of ...
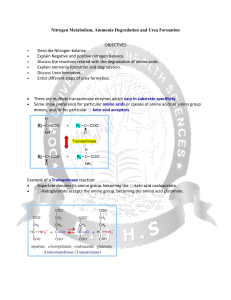
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... Normal concentration: 25-40 mol/l (0.4-0.7 mg/l) Ammonia must be removed from the organism ...
... Normal concentration: 25-40 mol/l (0.4-0.7 mg/l) Ammonia must be removed from the organism ...
Group 2 Elements
... The presence of certain metal ions can be identified by noting the characteristic flame colour that results from burning. The colours for group 2 metal ions are: ...
... The presence of certain metal ions can be identified by noting the characteristic flame colour that results from burning. The colours for group 2 metal ions are: ...
58 - American Chemical Society
... isolated and structurally characterized the anions [Rh13HS-n[Rh14H(C0)25]3-,4 and (CO)z4]" (n = 2, 31,'s' [Rh14(C0)2~]4-,3 [Rh15(C0)27]3-.3We now wish to report the synthesis and X-ray characterization of the new [Rh2z(CO)37]4-anion. This anion was first observed as a minor byproduct in the synthesi ...
... isolated and structurally characterized the anions [Rh13HS-n[Rh14H(C0)25]3-,4 and (CO)z4]" (n = 2, 31,'s' [Rh14(C0)2~]4-,3 [Rh15(C0)27]3-.3We now wish to report the synthesis and X-ray characterization of the new [Rh2z(CO)37]4-anion. This anion was first observed as a minor byproduct in the synthesi ...
Chapter 7: Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... For example, the ions Na+, Ca2+, and Clhave oxidation numbers of +1, +2, and -1, ...
... For example, the ions Na+, Ca2+, and Clhave oxidation numbers of +1, +2, and -1, ...
Alternative G-19
... 1) Mutate the coding DNA sequence of your protein (from step 3) in 5 separate ways: silent, missense, neutral, nonsense, and frameshift. Include (and label) the coding DNA, template DNA, RNA, and Amino acid sequences that changed. You MUST include the full amino acid sequences from [start] to [stop] ...
... 1) Mutate the coding DNA sequence of your protein (from step 3) in 5 separate ways: silent, missense, neutral, nonsense, and frameshift. Include (and label) the coding DNA, template DNA, RNA, and Amino acid sequences that changed. You MUST include the full amino acid sequences from [start] to [stop] ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.