Exam #1
... Gluconeogenesis pg 548-544. What is the biological purpose of this process? Know which steps are the same,(reversible) and not the same (substrate cycles) as glycolysis—what will determine when it will be a a substrate cycle. What is the key control step involving F2,6P as an allosteric activator/in ...
... Gluconeogenesis pg 548-544. What is the biological purpose of this process? Know which steps are the same,(reversible) and not the same (substrate cycles) as glycolysis—what will determine when it will be a a substrate cycle. What is the key control step involving F2,6P as an allosteric activator/in ...
glutathion-s-Transferase
... PREGNANCY: Studies in animals hav e shown the maternal drug metbolising ability is reduced during later stages of pregnancy.this was due to high levels of steroid harmones in circulation during pregnancy. HARMONAL IMBALANCE: Higher levels of one harmone may inhibit the activity of few enzymes while ...
... PREGNANCY: Studies in animals hav e shown the maternal drug metbolising ability is reduced during later stages of pregnancy.this was due to high levels of steroid harmones in circulation during pregnancy. HARMONAL IMBALANCE: Higher levels of one harmone may inhibit the activity of few enzymes while ...
Signal Transduction
... ATP cAMP + PPi Binding of certain hormones (e.g., epinephrine) to the outer surface of a cell activates Adenylate Cyclase to form cAMP within the cell. Cyclic AMP is thus considered to be a second messenger. ...
... ATP cAMP + PPi Binding of certain hormones (e.g., epinephrine) to the outer surface of a cell activates Adenylate Cyclase to form cAMP within the cell. Cyclic AMP is thus considered to be a second messenger. ...
AP `99 Multiple Choice
... 26. When the equation above is balanced and all (B) The oxidation number of H changes from -1 coefficients are reduced to their lowest wholeto +1. number terms, the coefficient for O2(g) is (C) The (A) 6 (B) ...
... 26. When the equation above is balanced and all (B) The oxidation number of H changes from -1 coefficients are reduced to their lowest wholeto +1. number terms, the coefficient for O2(g) is (C) The (A) 6 (B) ...
Predicted effects of mineral neutralization and bisulfate - CE-CERT
... the addition of dilute acid accelerates the breakdown of hemicellulose through the generation of greater concentrations of hydrogen ions and also improves recovery of hemicellulose sugars for later fermentation to ethanol and other products (3). Although many different acids have been used in dilute ...
... the addition of dilute acid accelerates the breakdown of hemicellulose through the generation of greater concentrations of hydrogen ions and also improves recovery of hemicellulose sugars for later fermentation to ethanol and other products (3). Although many different acids have been used in dilute ...
substrate
... Chemical Events at Active Sites • Active site directly participates in the reaction – covalent bonding can occur between enzyme and substrate – R groups of the enzyme’s amino acids can temporarily add chemical groups to the substrates ...
... Chemical Events at Active Sites • Active site directly participates in the reaction – covalent bonding can occur between enzyme and substrate – R groups of the enzyme’s amino acids can temporarily add chemical groups to the substrates ...
enzymes - UniMAP Portal
... • In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that the sugar was fermented even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. • He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase". • In 1907 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his bioche ...
... • In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that the sugar was fermented even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. • He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase". • In 1907 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his bioche ...
1 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Introduction
... • Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. • In general terms, explain the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration. • Explain where and how the respiratory electron transport chain creates a proton gradien ...
... • Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. • In general terms, explain the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration. • Explain where and how the respiratory electron transport chain creates a proton gradien ...
Nitrogen in Lakes
... Oscillatoria when N is low. Nitrogen fixation is important in lakes. a. In Eutrophic lakes fixation is a major process as first NH4+ then NO3- are used and BGA's begin to bloom as they can fix N2. In Clear Lake CA overy 1/2 of the annual N budget is provided by Fixation b. In Oligotrophic fixation i ...
... Oscillatoria when N is low. Nitrogen fixation is important in lakes. a. In Eutrophic lakes fixation is a major process as first NH4+ then NO3- are used and BGA's begin to bloom as they can fix N2. In Clear Lake CA overy 1/2 of the annual N budget is provided by Fixation b. In Oligotrophic fixation i ...
Metabolism
... established with few H+ in the matrix and many in the intermembrane space. The cristae also contain an ATP synthase complex through which hydrogen ions flow down their gradient from the intermembrane space into the matrix. The flow of three H+ through an ATP synthase complex causes a conformationa ...
... established with few H+ in the matrix and many in the intermembrane space. The cristae also contain an ATP synthase complex through which hydrogen ions flow down their gradient from the intermembrane space into the matrix. The flow of three H+ through an ATP synthase complex causes a conformationa ...
44_Physical-chemical properties and chemical composition of
... Water plays an important role in the thermal regulation of living organisms. Water's high heat capacity coupled with the high water content found in most organisms (between 50% and 95%, depending on species) contributes to the maintenance of an organism's internal temperature. Water is a remarkable ...
... Water plays an important role in the thermal regulation of living organisms. Water's high heat capacity coupled with the high water content found in most organisms (between 50% and 95%, depending on species) contributes to the maintenance of an organism's internal temperature. Water is a remarkable ...
Bio102 Problems
... A. This limits the amount of stroma volume, keeping the concentrations of enzymes and substrates very high. B. This allows faster passive transport of small carbohydrates. C. This allows the organelle to have more copies of photosystems I and II and ATP synthase. D. The larger membrane improves its ...
... A. This limits the amount of stroma volume, keeping the concentrations of enzymes and substrates very high. B. This allows faster passive transport of small carbohydrates. C. This allows the organelle to have more copies of photosystems I and II and ATP synthase. D. The larger membrane improves its ...
Choose the response which best completes each of the following
... mitochondrion (5.) none of the previous 51. The enzyme ATP synthase forms ATP (1.) due to the potential energy of a concentration gradient of hydrogen ions across a membrane (2.) due to substrate-level phosphorylation (3.) from glucose in the absence of oxygen (4.) in the absence of chemiosmosis ...
... mitochondrion (5.) none of the previous 51. The enzyme ATP synthase forms ATP (1.) due to the potential energy of a concentration gradient of hydrogen ions across a membrane (2.) due to substrate-level phosphorylation (3.) from glucose in the absence of oxygen (4.) in the absence of chemiosmosis ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint - Trimble County Schools
... – They can be sold as prescription drugs and used to treat certain diseases – They may also be abused with serious consequences, such as liver damage that can lead to cancer ...
... – They can be sold as prescription drugs and used to treat certain diseases – They may also be abused with serious consequences, such as liver damage that can lead to cancer ...
Chromatographic methods for protein purification
... arginines, lysines and histidines, depending of the pH of the surrounding buffer. Any free Nterminal amine will also contribute with a positive charge below pH 8. Negative charges are principally provided by aspartate and glutamate residues and the C-terminal carboxyl group. Virtually all these resi ...
... arginines, lysines and histidines, depending of the pH of the surrounding buffer. Any free Nterminal amine will also contribute with a positive charge below pH 8. Negative charges are principally provided by aspartate and glutamate residues and the C-terminal carboxyl group. Virtually all these resi ...
Map of the unit: Aspects of Agriculture
... To aid planning, laboratory-based practical work is indicated by (P), activities involving IT skills are indicated by (IT) and those developing study skills by (S). ACTIVITIES ...
... To aid planning, laboratory-based practical work is indicated by (P), activities involving IT skills are indicated by (IT) and those developing study skills by (S). ACTIVITIES ...
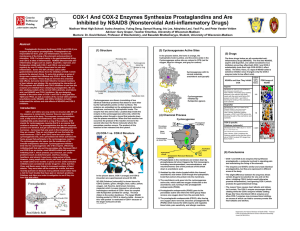
COX-1 And COX-2 Enzymes Synthesize Prostaglandins and Are
... COX-1 and COX-2 are very similar in structure (60- 65% of the sequence is conserved), however they are expressed in different parts of the body. The enzymes convert arachidonic acid, a fatty acid in cell membranes, into prostaglandins, modified fatty acids attached to a ring of five carbons. COX sta ...
... COX-1 and COX-2 are very similar in structure (60- 65% of the sequence is conserved), however they are expressed in different parts of the body. The enzymes convert arachidonic acid, a fatty acid in cell membranes, into prostaglandins, modified fatty acids attached to a ring of five carbons. COX sta ...
Covalent Bonding - whitburnscience
... Many atoms can be found as ions. An ion is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. Atoms gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells and increase their stability. The alkali metals produce a charge of one positive and would be written as X+. So Sodium would be written as Na+. While Magnesiu ...
... Many atoms can be found as ions. An ion is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. Atoms gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells and increase their stability. The alkali metals produce a charge of one positive and would be written as X+. So Sodium would be written as Na+. While Magnesiu ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.