non covalent interactions
... recognition. In the case of superoxide dismutase, for example, the substrate superoxide is a negatively charged molecule, that can interact with the enzyme only through the lines indicating the presence of a positive potential .. Modulation of the activity pH range of an enzyme The serine proteases ...
... recognition. In the case of superoxide dismutase, for example, the substrate superoxide is a negatively charged molecule, that can interact with the enzyme only through the lines indicating the presence of a positive potential .. Modulation of the activity pH range of an enzyme The serine proteases ...
Full Article
... Accumulating evidence suggests that ROS are not only injurious byproducts of cellular metabolism but also essential participants, in cell signaling and regulation [3]. Nitric oxide (NO) functions as a signaling molecule mediating vasodilatation when produced in low concentrations by the constitutive ...
... Accumulating evidence suggests that ROS are not only injurious byproducts of cellular metabolism but also essential participants, in cell signaling and regulation [3]. Nitric oxide (NO) functions as a signaling molecule mediating vasodilatation when produced in low concentrations by the constitutive ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Magnetic behaviour of the complexes has been depicted in Figure 1. The magnetic and electronic properties of the complexes have been explained by assuming eight coordination around manganese(III) ion. However these properties are not so easy to be explained for eight coordinate complexes. Trigonal d ...
... Magnetic behaviour of the complexes has been depicted in Figure 1. The magnetic and electronic properties of the complexes have been explained by assuming eight coordination around manganese(III) ion. However these properties are not so easy to be explained for eight coordinate complexes. Trigonal d ...
IN SILICO EVALUATION OF SELECTED TRITERPENE GLYCOSIDES AS A HUMAN... TOPOISOMERASE II ALPHA (α) INHIBITOR
... conversion, drawing of polymers, organometalics and Markush structures. QSAR property study of saponins ...
... conversion, drawing of polymers, organometalics and Markush structures. QSAR property study of saponins ...
9.3 student Fill in notes
... In the second stage, pyruvate either passes through the _________________ or undergoes ___________________ – Fermentation recycles __________ but does not produce _____________. ...
... In the second stage, pyruvate either passes through the _________________ or undergoes ___________________ – Fermentation recycles __________ but does not produce _____________. ...
Lecture 27
... decarboxylation reactions. Most aminotransferases accept only -ketoglutarate or oxaloacetate as the -keto acid substrate in the second stage of the reaction (reverse reaction). The amino groups of most amino acids are therefore incorporated in the formation of glutamate or aspartate. Glu and Asp a ...
... decarboxylation reactions. Most aminotransferases accept only -ketoglutarate or oxaloacetate as the -keto acid substrate in the second stage of the reaction (reverse reaction). The amino groups of most amino acids are therefore incorporated in the formation of glutamate or aspartate. Glu and Asp a ...
Chapter_02_4E - Ironbark (xtelco)
... Key Points • The oxidative system involves the breakdown of substrates in the presence of oxygen • Oxidation of carbohydrate involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, resulting in the formation of H2O, CO2, and 38-39 molecules of ATP • Fat oxidation involves β-oxidation ...
... Key Points • The oxidative system involves the breakdown of substrates in the presence of oxygen • Oxidation of carbohydrate involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, resulting in the formation of H2O, CO2, and 38-39 molecules of ATP • Fat oxidation involves β-oxidation ...
Chapter 2 part 3
... 2.7 Proteins • Proteins have important functions in cells. – Proteins form the antibodies of the immune system that defend the body from disease. – Proteins such as insulin are hormones that regulate cellular function. – Contractile proteins such as actin and myosin allow parts of cells to move and ...
... 2.7 Proteins • Proteins have important functions in cells. – Proteins form the antibodies of the immune system that defend the body from disease. – Proteins such as insulin are hormones that regulate cellular function. – Contractile proteins such as actin and myosin allow parts of cells to move and ...
optical absorption spectra of clay minerals
... have historically been concerned either state, (3) the spectra are inherently simple, with characterizing the chemical composition of thus facilitating theoretical deciphering and band primary and secondary minerals (i.e. clays and clay assignment. minerals) and attempting to relate variation in ele ...
... have historically been concerned either state, (3) the spectra are inherently simple, with characterizing the chemical composition of thus facilitating theoretical deciphering and band primary and secondary minerals (i.e. clays and clay assignment. minerals) and attempting to relate variation in ele ...
No Slide Title
... 4) What are the reactants of cellular respiration? 5) What are the products of cellular respiration? 6) What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? 7) What is the energy content of ATP relative to that of glucose? 8) What produces the “high energy” nature of ATP? 9) What happens when a molecule bec ...
... 4) What are the reactants of cellular respiration? 5) What are the products of cellular respiration? 6) What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? 7) What is the energy content of ATP relative to that of glucose? 8) What produces the “high energy” nature of ATP? 9) What happens when a molecule bec ...
function finders
... and one binds to DNA. -- P53 has several anti-cancer properties: it can activate DNA repair proteins when DNA has been damaged; it can suspend cell division, allowing time for damaged DNA to be repaired; it can initiate cell suicide (apoptosis) if cells are too badly damaged to be repaired. -- Damag ...
... and one binds to DNA. -- P53 has several anti-cancer properties: it can activate DNA repair proteins when DNA has been damaged; it can suspend cell division, allowing time for damaged DNA to be repaired; it can initiate cell suicide (apoptosis) if cells are too badly damaged to be repaired. -- Damag ...
Anaerobic Fermentation
... even human muscle cells. Examples: Yogurt and some cheeses The burn of tired muscles is from the build up of lactic acid. *Chemical equation (sort of): C 6H12 O6 Lactic Acid + 2ATP ...
... even human muscle cells. Examples: Yogurt and some cheeses The burn of tired muscles is from the build up of lactic acid. *Chemical equation (sort of): C 6H12 O6 Lactic Acid + 2ATP ...
nomenclature of inorganic chemistry
... The coordination number of the central atom in a compound is the number of atoms which are directly linked to the central atom. The attached atoms may be charged or uncharged or part of an ion or molecule. In some types of coordination compounds, the two atoms of a multiple bond in an attached ...
... The coordination number of the central atom in a compound is the number of atoms which are directly linked to the central atom. The attached atoms may be charged or uncharged or part of an ion or molecule. In some types of coordination compounds, the two atoms of a multiple bond in an attached ...
Altering protein specificity: techniques and applications
... led to the double mutant H254R/H257L, which had a specificity constant that was 20-fold higher than wild type toward dementon S. It is noteworthy that each of these three mutants retained only one of the two native Co2+ ions in their active sites, although the precise importance of this observation i ...
... led to the double mutant H254R/H257L, which had a specificity constant that was 20-fold higher than wild type toward dementon S. It is noteworthy that each of these three mutants retained only one of the two native Co2+ ions in their active sites, although the precise importance of this observation i ...
Anaerobic Pathways Lesson Plan
... enables intense exercises and does not cause acidosis because it is deprotonated o lactate thought to be the cause of muscle stiffness and soreness, but lactate levels in muscles return to normal within an hour after exercise o Reducing pyruvate to lactate consumes a proton (counters acidosis) o Aci ...
... enables intense exercises and does not cause acidosis because it is deprotonated o lactate thought to be the cause of muscle stiffness and soreness, but lactate levels in muscles return to normal within an hour after exercise o Reducing pyruvate to lactate consumes a proton (counters acidosis) o Aci ...
Review
... • Carbon atoms are always central atoms. • Generally structures are compact and symmetrical. ...
... • Carbon atoms are always central atoms. • Generally structures are compact and symmetrical. ...
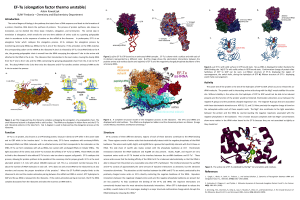
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable)
... The active site of the protein is the site of the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, which occurs to release the aatRNA molecule. The protein and its interacting amino acids along with the Mg2+ metal stabilize this active site. Without stability in the active site the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP would not be ab ...
... The active site of the protein is the site of the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP, which occurs to release the aatRNA molecule. The protein and its interacting amino acids along with the Mg2+ metal stabilize this active site. Without stability in the active site the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP would not be ab ...
Amino Acids 2 Questions
... 2. Gel‐filtration chromatography separates a mixture of proteins on the basis of: A) size B) charge C) affinity for ligands in the column matrix D) density 3. What is the purpose of treating a protein with 2‐mercaptoethanol? A) To hydrolyze the protein into its amino acids. B) To derivatize a ...
... 2. Gel‐filtration chromatography separates a mixture of proteins on the basis of: A) size B) charge C) affinity for ligands in the column matrix D) density 3. What is the purpose of treating a protein with 2‐mercaptoethanol? A) To hydrolyze the protein into its amino acids. B) To derivatize a ...
Degradation of Amino Acids
... because NH4+ glutamate other AA by transamination. (iii) GDH is the major AA oxidative pathway and the major source of NH4+ Also provides directionality to transamination/GDH. In vivo, [GLU] , NAD+ & removal of NH4+ drive deamination of glutamate. With excess NH4+ (bacterial metabolism in inte ...
... because NH4+ glutamate other AA by transamination. (iii) GDH is the major AA oxidative pathway and the major source of NH4+ Also provides directionality to transamination/GDH. In vivo, [GLU] , NAD+ & removal of NH4+ drive deamination of glutamate. With excess NH4+ (bacterial metabolism in inte ...
NO - Blue Devil Chem
... 1. 3Co2+ + 2Al → 3Co + 2Al3+ 2. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 3. 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 4. 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 → 2H2O + Mg(NO3)2 5. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O • Double replacement reactions are never oxidation reduction reactions since none of the atoms change oxidation numbers. ...
... 1. 3Co2+ + 2Al → 3Co + 2Al3+ 2. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 3. 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 4. 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 → 2H2O + Mg(NO3)2 5. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O • Double replacement reactions are never oxidation reduction reactions since none of the atoms change oxidation numbers. ...
Carbon Compounds
... The Chemistry of Carbon Carbon atoms have four valence electrons, allowing them to form strong covalent bonds with many other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen. Living organisms are made up of molecules that consist of carbon and these other elements. ...
... The Chemistry of Carbon Carbon atoms have four valence electrons, allowing them to form strong covalent bonds with many other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen. Living organisms are made up of molecules that consist of carbon and these other elements. ...
StructureQualityValidation_23Mar2009
... angles of an amino acid in a protein. • Due to steric hindrance from amino acid side chains, only certain angles are allowed in a folded protein. • A plot between the dihedral angles of individual amino acids in a protein can serve to indicate how well the structure has been determined. • Any deviat ...
... angles of an amino acid in a protein. • Due to steric hindrance from amino acid side chains, only certain angles are allowed in a folded protein. • A plot between the dihedral angles of individual amino acids in a protein can serve to indicate how well the structure has been determined. • Any deviat ...
Archaea
... hypothesized currently, which are not exclusive. One is that protons are generated on the outside of the membrane in step 5, which would build the proton motive force, in turn allowing ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. The other is that step four drives uptake of Na+ ions, and releasing those back acr ...
... hypothesized currently, which are not exclusive. One is that protons are generated on the outside of the membrane in step 5, which would build the proton motive force, in turn allowing ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. The other is that step four drives uptake of Na+ ions, and releasing those back acr ...
Structure, function, and evolution of phosphoglycerate mutases
... part containing 14 residues of the enzyme has a large degree of ¯exibility and its presence was not observed in any of the structures reported to date, except for the recent complex structure with 3PGA substrate where a part of this tail was located (Crowhurst et al., 1999). Based on the later studi ...
... part containing 14 residues of the enzyme has a large degree of ¯exibility and its presence was not observed in any of the structures reported to date, except for the recent complex structure with 3PGA substrate where a part of this tail was located (Crowhurst et al., 1999). Based on the later studi ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.