CCP4 - Software for Protein Structure Solution
... facilities by Pharma industry – 100s of crystals – Speed critical ...
... facilities by Pharma industry – 100s of crystals – Speed critical ...
Ch. 2 H. Bio Notes
... Reactant bonds are broken, atoms are rearranged, and new bonds form to make ...
... Reactant bonds are broken, atoms are rearranged, and new bonds form to make ...
File - Ms. Perez`s Science
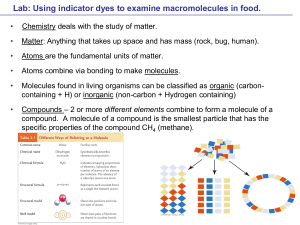
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space Element: matter in its simplest form Compound: two or more elements combined in simple whole number ratios of atoms Atom: the smallest form of an element that still displays its particular properties Consists of a nucleus of positively charged prot ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space Element: matter in its simplest form Compound: two or more elements combined in simple whole number ratios of atoms Atom: the smallest form of an element that still displays its particular properties Consists of a nucleus of positively charged prot ...
Do Now: Wednesday, March 19
... are joined together The string of amino acids forms a polypeptide (another word for a ...
... are joined together The string of amino acids forms a polypeptide (another word for a ...
Why should we take care of our bodies?
... Animal fats are usually saturated fats These line up together very well which is why they are solid at room temperature This makes it easy to clog blood vessels and organs They are SOLID at room temperature ...
... Animal fats are usually saturated fats These line up together very well which is why they are solid at room temperature This makes it easy to clog blood vessels and organs They are SOLID at room temperature ...
Versatile Bioassays Using Surface Plasmon Resonance
... Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) spectroscopy from a planar gold film is an important technique for studying biomolecular interactions on solid-liquid interface. Noble metal nanoparticles, i.e. gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), have strong interactions with light to generate localized SPR (LSPR) that leads ...
... Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) spectroscopy from a planar gold film is an important technique for studying biomolecular interactions on solid-liquid interface. Noble metal nanoparticles, i.e. gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), have strong interactions with light to generate localized SPR (LSPR) that leads ...
Biopolymers
... Three-dimensional structure of B-DNA. The sugar–phosphate backbone winds around the outside of the helix, and the bases occupy the interior. Stacking of the base pairs creates two grooves of unequal width, the major and the minor grooves. In DNA the two strands are wound around each other, joined b ...
... Three-dimensional structure of B-DNA. The sugar–phosphate backbone winds around the outside of the helix, and the bases occupy the interior. Stacking of the base pairs creates two grooves of unequal width, the major and the minor grooves. In DNA the two strands are wound around each other, joined b ...
Structure of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats
... Fats are a sub-group of compounds known as lipids that are found in the body and have the general property of being hydrophobic (meaning they are insoluble in water). Fats are also known as triglycerides, molecules made from the combination of one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids, as depi ...
... Fats are a sub-group of compounds known as lipids that are found in the body and have the general property of being hydrophobic (meaning they are insoluble in water). Fats are also known as triglycerides, molecules made from the combination of one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids, as depi ...
Structure and Function of Salivary Proteins Outline Basic salivary
... 1 H-chain 2 L-chain 3 J-chain 4 secretory component ...
... 1 H-chain 2 L-chain 3 J-chain 4 secretory component ...
Gene Section RPS27 (ribosomal protein S27) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... binding domain on MDM2. Once bound, MDM2 is stimulated to ubiquinate and degrade the RPS27 or p53, whichever it is bound to. When RPS27 levels are elevated, it can out-compete p53 for MDM2 binding and subsequent degradation, thus stabilizing p53 levels. This would be an appropriate cellular response ...
... binding domain on MDM2. Once bound, MDM2 is stimulated to ubiquinate and degrade the RPS27 or p53, whichever it is bound to. When RPS27 levels are elevated, it can out-compete p53 for MDM2 binding and subsequent degradation, thus stabilizing p53 levels. This would be an appropriate cellular response ...
Document
... ribosomes, RNA polymerase and other needed materials. It resulted in a protein made of only phenylalanine. Further research determined the rest of the code. ...
... ribosomes, RNA polymerase and other needed materials. It resulted in a protein made of only phenylalanine. Further research determined the rest of the code. ...
Institute of Biotechnology and Antibiotics
... • the improvement of antibiotic biosynthesis processes, • the study of mechanisms of transmitting antibiotic-resistant genes in bacteria, • development of new preparations for diagnosis based on monoclonal antibodies. ...
... • the improvement of antibiotic biosynthesis processes, • the study of mechanisms of transmitting antibiotic-resistant genes in bacteria, • development of new preparations for diagnosis based on monoclonal antibodies. ...
chapter 7 cell membrane
... Controls traffic into & out of the cell selectively permeable allowing some substances to cross more easily than others ...
... Controls traffic into & out of the cell selectively permeable allowing some substances to cross more easily than others ...
ws: Enzymes as Catalyst review
... 5. What happens to Catalase when it is exposed to high temperatures? 6. What happens to Lactase when it is exposed to high temperatures? Comprehensive Question: 7. What do these two graphs tell you about enzymes, their environments, and their function? In your answer be sure to explain how temperatu ...
... 5. What happens to Catalase when it is exposed to high temperatures? 6. What happens to Lactase when it is exposed to high temperatures? Comprehensive Question: 7. What do these two graphs tell you about enzymes, their environments, and their function? In your answer be sure to explain how temperatu ...
Cysteine-mutated FXYD proteins enhance the anti
... • accounting for 17.3 million deaths per year • a number that is expected to grow to >23.6 million by 2030 http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ ...
... • accounting for 17.3 million deaths per year • a number that is expected to grow to >23.6 million by 2030 http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ ...
PartFourSumm_ThemesInRegulation.doc
... different contacts with RNA polymerase at different operons and activate transcription by different mechanisms, affecting the affinity of the polymerase for the promoter in one case and the rate of closed to open complex in the other. b. Another example is the repressor from bacteriophage , which i ...
... different contacts with RNA polymerase at different operons and activate transcription by different mechanisms, affecting the affinity of the polymerase for the promoter in one case and the rate of closed to open complex in the other. b. Another example is the repressor from bacteriophage , which i ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
... simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. Unlike some other indicators, Benedict’s solution does not work at room temperature - it must be heated first Details: ...
... simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. Unlike some other indicators, Benedict’s solution does not work at room temperature - it must be heated first Details: ...
PART I. TUTORIAL QUESTIONS (30 marks total)
... Disadvantage: (1) The presence of GFP may present steric hindrance which may interfere with the function of the tagged protein or with the interactions that the tagged protein might be involved in. Also acceptable: usually requires overexpression of the protein of interest. Overexpression may have n ...
... Disadvantage: (1) The presence of GFP may present steric hindrance which may interfere with the function of the tagged protein or with the interactions that the tagged protein might be involved in. Also acceptable: usually requires overexpression of the protein of interest. Overexpression may have n ...
Power Point 1 - G. Holmes Braddock
... compounds with the rings containing nitrogen and carbon. Adenine and guanine are purines, which contain a pair of fused rings; cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines, which contain a single ring. The acidic character of nucleotides is due to the presence of phosphate, which dissociates at the ...
... compounds with the rings containing nitrogen and carbon. Adenine and guanine are purines, which contain a pair of fused rings; cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines, which contain a single ring. The acidic character of nucleotides is due to the presence of phosphate, which dissociates at the ...
A Glance on Genetics
... • Those structure that are not made of proteins are produced by enzymes (which are proteins) • A human contains proteins of the order of 100,000 different proteins • Proteins are of variable length and shape • Proteins are mixed polymers of 20 different amino acids (or residues) ...
... • Those structure that are not made of proteins are produced by enzymes (which are proteins) • A human contains proteins of the order of 100,000 different proteins • Proteins are of variable length and shape • Proteins are mixed polymers of 20 different amino acids (or residues) ...
Protein adsorption

Adsorption (not to be mistaken for absorption) is the accumulation and adhesion of molecules, atoms, ions, or larger particles to a surface, but without surface penetration occurring. The adsorption of larger biomolecules such as proteins is of high physiological relevance, and as such they adsorb with different mechanisms than their molecular or atomic analogs. Some of the major driving forces behind protein adsorption include: surface energy, intermolecular forces, hydrophobicity, and ionic or electrostatic interaction. By knowing how these factors affect protein adsorption, they can then be manipulated by machining, alloying, and other engineering techniques to select for the most optimal performance in biomedical or physiological applications.