Pill Bug Investigation
... • If you have been absent, or have missed tasks, check with me. • COE Task on Friday, 3/13 ...
... • If you have been absent, or have missed tasks, check with me. • COE Task on Friday, 3/13 ...
The extracellular matrix (ECM)
... -sulfated glycoamino glycans and a protein core -cover huge areas of extracellular matrix - eg. Aggrecan in cartilage and other connective tissues -contains hyaluronic acid + link protein + core protein ...
... -sulfated glycoamino glycans and a protein core -cover huge areas of extracellular matrix - eg. Aggrecan in cartilage and other connective tissues -contains hyaluronic acid + link protein + core protein ...
dna ppt ques – ANSWERS2
... 2. The mRNA then leaves the ___NUCLEUS_________ and attaches itself to a __RIBOSOME_______________ and passes on the ___MESSAGE__________. 3. The tRNA then attaches to ___MRNA_______ and hooks up the ____AMINO ACIDS___ in the right order. Then it goes back to pick up some __MORE________(like a _TAX ...
... 2. The mRNA then leaves the ___NUCLEUS_________ and attaches itself to a __RIBOSOME_______________ and passes on the ___MESSAGE__________. 3. The tRNA then attaches to ___MRNA_______ and hooks up the ____AMINO ACIDS___ in the right order. Then it goes back to pick up some __MORE________(like a _TAX ...
Chapter 2
... 2) Secondary structure arises when a polypeptide chain twists into a coil (helix) or sheet held in place by hydrogen bonds between different parts of the molecule. The same patterns of secondary structure occur in many different proteins. ...
... 2) Secondary structure arises when a polypeptide chain twists into a coil (helix) or sheet held in place by hydrogen bonds between different parts of the molecule. The same patterns of secondary structure occur in many different proteins. ...
File - Peterson Biology
... 3. tRNA brings correct amino acid (methionine) to the ribosome. Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must ...
... 3. tRNA brings correct amino acid (methionine) to the ribosome. Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must ...
Role of cystinosin in vesicular trafficking and membrane fusion
... laborarory. For this we used the constructs containing fragments of: Cop1, Mad2l2, SNF8 and VPS39 proteins all of which showed good interaction scores in preliminary screen performed by Hybrigenics (constructs obtained form the company). By this mean we were able to confirm interactions of the 5th ...
... laborarory. For this we used the constructs containing fragments of: Cop1, Mad2l2, SNF8 and VPS39 proteins all of which showed good interaction scores in preliminary screen performed by Hybrigenics (constructs obtained form the company). By this mean we were able to confirm interactions of the 5th ...
Thermodynamics of Protein Folding
... • LiCata suggests that unfolded Taq has more surface area, leading to greater relative destabilization of unfolded relative to folded ...
... • LiCata suggests that unfolded Taq has more surface area, leading to greater relative destabilization of unfolded relative to folded ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
... and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet of an animal B. Peptide bonds join amino acids 1. 2 amino acids form a dipeptide 2. Polypeptides are formed from more than 2 amino acids C. Proteins have 4 levels ...
... and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet of an animal B. Peptide bonds join amino acids 1. 2 amino acids form a dipeptide 2. Polypeptides are formed from more than 2 amino acids C. Proteins have 4 levels ...
Gel electrophoresis
... have an overall positive charge and migrate to the cathode (negatively charged electrode) in an electrical field. Proteins even with a variation of one amino acids will have a different overall charge, and thus are electrophoretically distinguishable. ...
... have an overall positive charge and migrate to the cathode (negatively charged electrode) in an electrical field. Proteins even with a variation of one amino acids will have a different overall charge, and thus are electrophoretically distinguishable. ...
Chapter 5 Problem set
... molecules move down their concentration gradient, it is called.______________________ ; this is a key factor in moving substances across cell membranes and through fluid portions of cytoplasm. When the concentration gradient is steep, diffusion is (choose one) ( ) slower ( ) faster. As the gradient ...
... molecules move down their concentration gradient, it is called.______________________ ; this is a key factor in moving substances across cell membranes and through fluid portions of cytoplasm. When the concentration gradient is steep, diffusion is (choose one) ( ) slower ( ) faster. As the gradient ...
Les 6b RNA Transcription and Translation
... mRNA made 5’3’ directionality DNA unzips only at a specific gene sequence for a specific protein Usually only one strand of DNA is read to form a complementary copy of the mRNA ...
... mRNA made 5’3’ directionality DNA unzips only at a specific gene sequence for a specific protein Usually only one strand of DNA is read to form a complementary copy of the mRNA ...
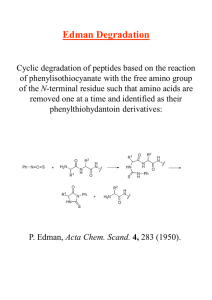
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Organic Notes.graffle
... What are proteins? Proteins are macromolecules (polymers) that are made by adding amino acids (monomers) together. There can be thousands of different proteins found in a single cell. If the 20 different amino acids are put together in various combinations there can be endless numbers of proteins. ...
... What are proteins? Proteins are macromolecules (polymers) that are made by adding amino acids (monomers) together. There can be thousands of different proteins found in a single cell. If the 20 different amino acids are put together in various combinations there can be endless numbers of proteins. ...
protein range - Absolute Organix Lifematrix
... Egg white protein is easily digestible, making it an ideal alternative for people who cannot tolerate milk proteins. Egg whites contain an army of amino acids, including all nine essential aminos and the branched-chain aminos. Research shows that egg white protein has similar effects on stimulating ...
... Egg white protein is easily digestible, making it an ideal alternative for people who cannot tolerate milk proteins. Egg whites contain an army of amino acids, including all nine essential aminos and the branched-chain aminos. Research shows that egg white protein has similar effects on stimulating ...
4 Necessities of Life
... compounds that cannot mix with water. • Phospholipids • molecules that form much of the cell membrane. • Fats and Oils • lipids that store energy • when an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can get energy from these lipids. ...
... compounds that cannot mix with water. • Phospholipids • molecules that form much of the cell membrane. • Fats and Oils • lipids that store energy • when an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can get energy from these lipids. ...
Document
... • A monomer is a molecule that may bind chemically to other molecules to form a polymer. • A polymer is a large molecule (macromolecule) composed of repeating structural units. • Proteins and some carbohydrates are polymers. • Dehydration reactions— smaller molecules bond as water is given off • Hyd ...
... • A monomer is a molecule that may bind chemically to other molecules to form a polymer. • A polymer is a large molecule (macromolecule) composed of repeating structural units. • Proteins and some carbohydrates are polymers. • Dehydration reactions— smaller molecules bond as water is given off • Hyd ...
clarisoy™ protein made clear
... a variety of beverages. Because every formulation is unique, ADM draws on our resources—our people, our products, and our market perspective—to recommend tailored solutions to fit your specific application and nutritional needs. ...
... a variety of beverages. Because every formulation is unique, ADM draws on our resources—our people, our products, and our market perspective—to recommend tailored solutions to fit your specific application and nutritional needs. ...
Biochemistry LTF
... Large carbon molecules = macromolecules - large polymers – composed of repeating units called monomers ...
... Large carbon molecules = macromolecules - large polymers – composed of repeating units called monomers ...
Recombinant Human IL-35-Fc fusion protein (ELISA Std.)
... For research use only. Not for diagnostic use. Not for resale. BioLegend will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. *These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses (see the BioLegend Catalog or our we ...
... For research use only. Not for diagnostic use. Not for resale. BioLegend will not be held responsible for patent infringement or other violations that may occur with the use of our products. *These products may be covered by one or more Limited Use Label Licenses (see the BioLegend Catalog or our we ...
Grooving Down the Helix
... the latter case to be true. When he increased the size of the protein, the rate of motion decreased much more rapidly than it would have for a simple linear motion. Relying on the same technique, the group went on to analyze the diffusion rates of eight different proteins of various sizes. These mol ...
... the latter case to be true. When he increased the size of the protein, the rate of motion decreased much more rapidly than it would have for a simple linear motion. Relying on the same technique, the group went on to analyze the diffusion rates of eight different proteins of various sizes. These mol ...
How does DNA copy itself?
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
Protein adsorption

Adsorption (not to be mistaken for absorption) is the accumulation and adhesion of molecules, atoms, ions, or larger particles to a surface, but without surface penetration occurring. The adsorption of larger biomolecules such as proteins is of high physiological relevance, and as such they adsorb with different mechanisms than their molecular or atomic analogs. Some of the major driving forces behind protein adsorption include: surface energy, intermolecular forces, hydrophobicity, and ionic or electrostatic interaction. By knowing how these factors affect protein adsorption, they can then be manipulated by machining, alloying, and other engineering techniques to select for the most optimal performance in biomedical or physiological applications.