The Nervous System
... Cerebellum Consists of two hemispheres Involuntary coordination of skeletal-muscle contractions within muscles, tendons, joints, and sensory organs ...
... Cerebellum Consists of two hemispheres Involuntary coordination of skeletal-muscle contractions within muscles, tendons, joints, and sensory organs ...
Central Nervous System
... Q1: If you touched a hot object, what would be the stimulus and response? Q2: When you run, how does your breathing ...
... Q1: If you touched a hot object, what would be the stimulus and response? Q2: When you run, how does your breathing ...
test yourself
... Part of the brain located at the top end of the spinal cord that controls breathing and other involuntary functions. Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Part of the brain between the hypothalamus and the pons that regulates visual, auditory, and rightening reflexes. Soft, white, fatty ma ...
... Part of the brain located at the top end of the spinal cord that controls breathing and other involuntary functions. Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Part of the brain between the hypothalamus and the pons that regulates visual, auditory, and rightening reflexes. Soft, white, fatty ma ...
The Nervous System
... Message travels form the dendrites through the cell body and to the end of the axon. The message causes chemicals, neurotransmitters, to be released from the end of the axon into the space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another ...
... Message travels form the dendrites through the cell body and to the end of the axon. The message causes chemicals, neurotransmitters, to be released from the end of the axon into the space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another ...
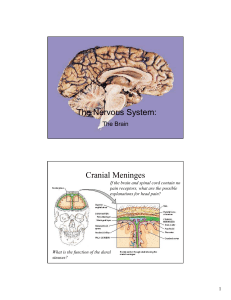
The Nervous System: Cranial Meninges
... Describe the location of the basal nuclei relative to the cerebral cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus. What does this structural feature imply about the function of the basal nuclei? ...
... Describe the location of the basal nuclei relative to the cerebral cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus. What does this structural feature imply about the function of the basal nuclei? ...
Organization of NS and the neuron File
... Divided into left(verbal, logic, mathematical skills) and right(visual/spatial awareness- creativity) hemispheres 2 hemispheres connected by a nerve tract called corpus callosum Surface of cerebrum (outer layer) is known as cerebral cortex. It is made of grey matter and contains many folds [call ...
... Divided into left(verbal, logic, mathematical skills) and right(visual/spatial awareness- creativity) hemispheres 2 hemispheres connected by a nerve tract called corpus callosum Surface of cerebrum (outer layer) is known as cerebral cortex. It is made of grey matter and contains many folds [call ...
Nervous System study guide
... The brain weighs about 3 pounds and is protected by our skull. Nerve cells carry messages to and from the spinal cord and brain, and then back to the rest of your body. The three parts of a nerve, or neuron, are: 1. Axon: attached to the nerve cell that sends messages AWAY from cell body. (Axon=Away ...
... The brain weighs about 3 pounds and is protected by our skull. Nerve cells carry messages to and from the spinal cord and brain, and then back to the rest of your body. The three parts of a nerve, or neuron, are: 1. Axon: attached to the nerve cell that sends messages AWAY from cell body. (Axon=Away ...
BRAINS!!! A Presentation on the Nervous System
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM • System in an animal that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions. • Two main parts • Central Nervous System (CNS)= brain and spinal chord • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)= nerves and ganglia (nerve cells and tissue) outside of the brain ...
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM • System in an animal that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions. • Two main parts • Central Nervous System (CNS)= brain and spinal chord • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)= nerves and ganglia (nerve cells and tissue) outside of the brain ...
9-1_BrainStemNeurons_BujtarZs
... Neurons are individual cells which are able to convey information to other similar cells. Electrical and chemical signals originate in neurons. Nerve contains more cells and make up a conducting zone for transporting signals from neurons. ...
... Neurons are individual cells which are able to convey information to other similar cells. Electrical and chemical signals originate in neurons. Nerve contains more cells and make up a conducting zone for transporting signals from neurons. ...
Dr. Ray L. Winstead
... Control center for drives such as hunger, thirst, and sex. Regulates functions such as body temperature, blood pressure, water balance. Amygdala – controls emotional responses, especially fear. Hippocampus – emotions, consolidation of new memories, navigation, and spatial orientation. 2. Midbrain – ...
... Control center for drives such as hunger, thirst, and sex. Regulates functions such as body temperature, blood pressure, water balance. Amygdala – controls emotional responses, especially fear. Hippocampus – emotions, consolidation of new memories, navigation, and spatial orientation. 2. Midbrain – ...
The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... Objectives • Understand how the nervous system is divided and the types of cells that are found in nervous tissue • Know the anatomy of a neuron and the structural and functional types of neurons • Understand what occurs at the synapse ...
... Objectives • Understand how the nervous system is divided and the types of cells that are found in nervous tissue • Know the anatomy of a neuron and the structural and functional types of neurons • Understand what occurs at the synapse ...
Sp.CBSTH functions
... The peripheral regions of the spinal cord contains neuronal white matter tracts containing sensory and motor neurons. The central region is gray matter that contains nerve cell bodies. ...
... The peripheral regions of the spinal cord contains neuronal white matter tracts containing sensory and motor neurons. The central region is gray matter that contains nerve cell bodies. ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... Forebrain becomes the neocortex. Midbrain becomes the tegmentum and tectum (substantia nigra, inferior/superior colliculi) Hindbrain becomes the cerebellum, pons, medulla, and brain stem. ...
... Forebrain becomes the neocortex. Midbrain becomes the tegmentum and tectum (substantia nigra, inferior/superior colliculi) Hindbrain becomes the cerebellum, pons, medulla, and brain stem. ...
The Nervous System
... • Dendrites receive and carry information toward the cell body • Axon carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Glial cells protect, support and assist neurons • In the PNS, the glial cells are Schwann cells – Schwann cells are wrapped by a myelin sheath ...
... • Dendrites receive and carry information toward the cell body • Axon carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Glial cells protect, support and assist neurons • In the PNS, the glial cells are Schwann cells – Schwann cells are wrapped by a myelin sheath ...
The Nervous System and Control of Movement
... Largest part of the part, containing the nerve centres that control sensory and motor Cerebellum Main function to coordinate muscle movement and control balance Brain Stem Links the cerebrum with the spinal cord Autonomic functions, postural control, muscle tone and eye movements ...
... Largest part of the part, containing the nerve centres that control sensory and motor Cerebellum Main function to coordinate muscle movement and control balance Brain Stem Links the cerebrum with the spinal cord Autonomic functions, postural control, muscle tone and eye movements ...
Central Nervous System - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... images, touch, pressure, pain, temperature (NC) ...
... images, touch, pressure, pain, temperature (NC) ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SPECIAL SENSES
... -Axons have synaptic knobs at distal ends, which secrete neurotransmitters -Neurotransmitter released when nerve impulse reaches end of axon-Neurotransmitter reaching the postsynaptic neuron membrane may trigger nerve impulse ...
... -Axons have synaptic knobs at distal ends, which secrete neurotransmitters -Neurotransmitter released when nerve impulse reaches end of axon-Neurotransmitter reaching the postsynaptic neuron membrane may trigger nerve impulse ...
nervous system
... The nervous system is the control a communication system of the body. main job is to send and receive message The nervous system allows people interact with the world around them. T brain, spinal cord, and nerves make up t nervous system. The cells that make the nervous system are called neuron Thes ...
... The nervous system is the control a communication system of the body. main job is to send and receive message The nervous system allows people interact with the world around them. T brain, spinal cord, and nerves make up t nervous system. The cells that make the nervous system are called neuron Thes ...
central_nervous_system_overview_211
... system, the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, and distinguish the differences between each. Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. ...
... system, the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, and distinguish the differences between each. Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. ...
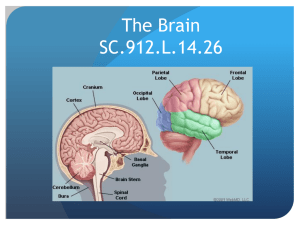
The Brain SC.912.L.14.26
... and spinal cord. The CNS is composed of interneurons that interact with other nerves in body. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the collection of nerves that connects the CNS to all of your organ system. ...
... and spinal cord. The CNS is composed of interneurons that interact with other nerves in body. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the collection of nerves that connects the CNS to all of your organ system. ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.