Nervous System
... Spinal Cord It is a two-way conduction pathway to the brain & a major reflex center 42-45 cm long, cylindrical in shape, lies within the vertebral canal. Extends from foramen magnum to L2 vertebra Continuous above with medulla oblongata Caudal tapering end is called conus medullaris Has 2 enlargeme ...
... Spinal Cord It is a two-way conduction pathway to the brain & a major reflex center 42-45 cm long, cylindrical in shape, lies within the vertebral canal. Extends from foramen magnum to L2 vertebra Continuous above with medulla oblongata Caudal tapering end is called conus medullaris Has 2 enlargeme ...
Chp.6 Nervous System
... Made up of sensory and motor nerve fibers that connect the peripheral (outer) parts of the body to the central nervous system It has both sensory and motor nerves and carries messages to and from central nervous system ...
... Made up of sensory and motor nerve fibers that connect the peripheral (outer) parts of the body to the central nervous system It has both sensory and motor nerves and carries messages to and from central nervous system ...
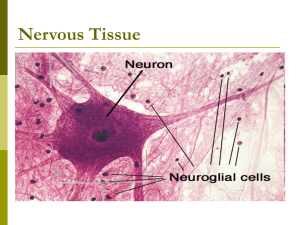
Nervous Tissue
... sensory (afferent) neurons carry info to CNS Interneurons in CNS interpret info and stimulate motor neurons motor (efferent) neurons carry info to effectors ...
... sensory (afferent) neurons carry info to CNS Interneurons in CNS interpret info and stimulate motor neurons motor (efferent) neurons carry info to effectors ...
pia mater
... ventricular system and surrounding the CNS, is formed primarily by the choroid plexuses, with a smaller contribution made by the ependyma lining the ventricles. ...
... ventricular system and surrounding the CNS, is formed primarily by the choroid plexuses, with a smaller contribution made by the ependyma lining the ventricles. ...
SBI4U - 9.3
... • Corpus callosum allows both hemispheres to communicate • Each hemisphere can be further subdivided into 4 lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal ...
... • Corpus callosum allows both hemispheres to communicate • Each hemisphere can be further subdivided into 4 lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal ...
DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Found between the brainstem and cerebrum. Thalamus: Gray matter; switching station for sensory input. Each sense, except smell, channels its nerves through the thalamus. Hypothalamus: Below thalamus, controls hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, & body temperature. FUNCTIONS OF THE BRAIN ...
... Found between the brainstem and cerebrum. Thalamus: Gray matter; switching station for sensory input. Each sense, except smell, channels its nerves through the thalamus. Hypothalamus: Below thalamus, controls hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, & body temperature. FUNCTIONS OF THE BRAIN ...
SKELETAL SYSTEM
... A neuron consists of three main parts: 1.Cell Body: contains the nucleus, or control center of the cell. Regulates the production of proteins within the cell 2.Dendrites: receive information from other neurons or sensory receptors and transmit impulses toward cell body. 3.Axons: transmit impulses aw ...
... A neuron consists of three main parts: 1.Cell Body: contains the nucleus, or control center of the cell. Regulates the production of proteins within the cell 2.Dendrites: receive information from other neurons or sensory receptors and transmit impulses toward cell body. 3.Axons: transmit impulses aw ...
Nervous System Guided Notes
... ___________________________________________________________________________________ The _______________________________________________________ of the nervous system ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________________________________________________________ The _______________________________________________________ of the nervous system ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ ...
The Brain and the Senses
... nerves and sends responses to the motor nerves. • Peripheral Nervous System a. Sensory nerves – 5 senses, picks up stimuli and sends to CNS. b. Motor nerves – voluntary or involuntary, carries out response sent by CNS. ...
... nerves and sends responses to the motor nerves. • Peripheral Nervous System a. Sensory nerves – 5 senses, picks up stimuli and sends to CNS. b. Motor nerves – voluntary or involuntary, carries out response sent by CNS. ...
Nervous System
... Nervous System Structures Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves Function Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment ...
... Nervous System Structures Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves Function Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment ...
Central Nervous System
... Functional Anatomy of Brain • 4 major regions –Cerebral hemispheres –Diencephalon –Brain stem –Cerebellum ...
... Functional Anatomy of Brain • 4 major regions –Cerebral hemispheres –Diencephalon –Brain stem –Cerebellum ...
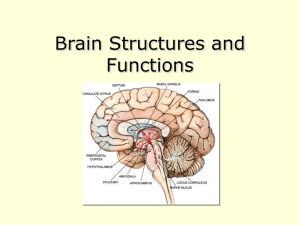
Brain Structures and Functions
... frontal lobe (reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving); parietal lobe (movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli); occipital lobe (visual processing); and temporal lobe (perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech). • Divid ...
... frontal lobe (reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving); parietal lobe (movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli); occipital lobe (visual processing); and temporal lobe (perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech). • Divid ...
The Nervous System
... the pricking of the rose thorns signal travels to the spinal cord along sensory neurons synapse with interneurons within the CNS Interneurons stimulate motor neurons travels along their axons to the muscle Muscle contracts to withdraw the hand ...
... the pricking of the rose thorns signal travels to the spinal cord along sensory neurons synapse with interneurons within the CNS Interneurons stimulate motor neurons travels along their axons to the muscle Muscle contracts to withdraw the hand ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... What are the four major subdivisions of the brain? What comprises gray matter? White matter? What are the four visible lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is a gyrus? What is a sulcus? Which part of the brain has these features? What brain region provides abundant afferents to the cerebral cortex and ...
... What are the four major subdivisions of the brain? What comprises gray matter? White matter? What are the four visible lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is a gyrus? What is a sulcus? Which part of the brain has these features? What brain region provides abundant afferents to the cerebral cortex and ...
Excretory System - École St. Joseph School
... _______ then passes the messages on to neighboring dendrites at a synapse. ...
... _______ then passes the messages on to neighboring dendrites at a synapse. ...
The Central Nervous System
... • Plans and initiates voluntary activity by providing input to cortical motor areas – Procedural memory ...
... • Plans and initiates voluntary activity by providing input to cortical motor areas – Procedural memory ...
anatomy test ch 7 nerves
... 1. The substance released at axonal endings is called a ______________. 2. __________________ is the site of regulation of water balance and body temperature. 3. __________________ is responsible for the regulation of posture and coordination of skeletal muscle movements. 4. Increased peristalsis in ...
... 1. The substance released at axonal endings is called a ______________. 2. __________________ is the site of regulation of water balance and body temperature. 3. __________________ is responsible for the regulation of posture and coordination of skeletal muscle movements. 4. Increased peristalsis in ...
Nervous System: Spine
... Gray Matter of Spinal Cord • central canal • butterfly or “H” shape • dorsal (posterior) horns • ventral (anterior) horns ...
... Gray Matter of Spinal Cord • central canal • butterfly or “H” shape • dorsal (posterior) horns • ventral (anterior) horns ...
the nervous system - Elgin Local Schools
... 4. Right vs. Left Hemisphere - Hemispheres are separate brains which “talk” to each other through commissural fibers a. Corpus callosum b. Anterior and posterior commissures Left brain (hemisphere) ...
... 4. Right vs. Left Hemisphere - Hemispheres are separate brains which “talk” to each other through commissural fibers a. Corpus callosum b. Anterior and posterior commissures Left brain (hemisphere) ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System can be broken into two parts: • The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of the brain and the spinal cord • The PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of all the nerves that aren’t part of the brain or spinal cord ...
... The Nervous System can be broken into two parts: • The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of the brain and the spinal cord • The PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of all the nerves that aren’t part of the brain or spinal cord ...
brain-1 - KarrinsBrAinUniT
... Central nervous system(CNS) – Brain and Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system(PNS) – links CNS with body’s sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
... Central nervous system(CNS) – Brain and Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system(PNS) – links CNS with body’s sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.