Genetic Mutations
... Alter the coding sequence within a gene Causes permanent change in DNA sequence Involve insertion or removal of 1 or more base pairs Point mutation is a change in single base pair within DNA ...
... Alter the coding sequence within a gene Causes permanent change in DNA sequence Involve insertion or removal of 1 or more base pairs Point mutation is a change in single base pair within DNA ...
Other examples of second site suppressors.
... This is affected by ploidy (diploids bigger than haploids) and by nutrients. Cells in rich media grow bigger before they hit start!! b) Mutants had been isolated which affect cell size in yeast. Most famously an allele of the G1 cyclin CLN3, originally called WHI1-1, later renamed CLN3-1 ...
... This is affected by ploidy (diploids bigger than haploids) and by nutrients. Cells in rich media grow bigger before they hit start!! b) Mutants had been isolated which affect cell size in yeast. Most famously an allele of the G1 cyclin CLN3, originally called WHI1-1, later renamed CLN3-1 ...
- BioMed Central
... A copy of the scripts used by ROSLIN The following script takes a list of accession numbers and uses then to retrieve fasta sequence files for each gene using the emboss software package. The sequences are then blasted against the latest version of the pig genome (7) which was downloaded from the Sa ...
... A copy of the scripts used by ROSLIN The following script takes a list of accession numbers and uses then to retrieve fasta sequence files for each gene using the emboss software package. The sequences are then blasted against the latest version of the pig genome (7) which was downloaded from the Sa ...
CSHL-CBW Lab Module 15 Answers
... Contraction annotations reflect a shared set of genes. These genes represent voltagegated ion channels, which are a group of transmembrane ion channels that activated by changes in electrical potential difference. Even though ion channels are especially critical in neurons and muscle tissue, they ar ...
... Contraction annotations reflect a shared set of genes. These genes represent voltagegated ion channels, which are a group of transmembrane ion channels that activated by changes in electrical potential difference. Even though ion channels are especially critical in neurons and muscle tissue, they ar ...
File
... 1. Use your notes to complete each definition. Purebred - Also called homozygous and consists of gene pairs with genes that are the same. Hybrid - Also called heterozygous and consists of gene pairs that are different. Genotype is the actual gene makeup represented by letters. Phenotype is the physi ...
... 1. Use your notes to complete each definition. Purebred - Also called homozygous and consists of gene pairs with genes that are the same. Hybrid - Also called heterozygous and consists of gene pairs that are different. Genotype is the actual gene makeup represented by letters. Phenotype is the physi ...
What is DNA?
... Any change to your DNA is called a MUTATION Mutations can be caused by: • Environment • Random copying errors Mutations can occur: • During embryonic development (result in change in offspring) • During your lifetime (usually result in cancer) ...
... Any change to your DNA is called a MUTATION Mutations can be caused by: • Environment • Random copying errors Mutations can occur: • During embryonic development (result in change in offspring) • During your lifetime (usually result in cancer) ...
This would be given at the end of the unit
... 11. A strand of DNA formed by the splicing of DNA from two different species is called a. determinant RNA. b. recombinant DNA. c. plasmid DNA. d. restriction RNA. 12. Plasmids a. are circular pieces of bacterial DNA. b. can replicate independently of the organism’s main chromosome. c. are often used ...
... 11. A strand of DNA formed by the splicing of DNA from two different species is called a. determinant RNA. b. recombinant DNA. c. plasmid DNA. d. restriction RNA. 12. Plasmids a. are circular pieces of bacterial DNA. b. can replicate independently of the organism’s main chromosome. c. are often used ...
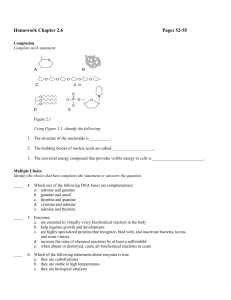
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
20 DetailLectOut 2012
... Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 8th Edition, © Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 8th Edition, © Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Last Universal Common Ancestor
... The number of genomes which must be compared before we are confident we aren’t omitting something. Not all cells might have been freeliving cells such as parasites. Gene losses Genes may have spread so well that they sometimes appear to date back to the time of LUCA, whereas actually , they ar ...
... The number of genomes which must be compared before we are confident we aren’t omitting something. Not all cells might have been freeliving cells such as parasites. Gene losses Genes may have spread so well that they sometimes appear to date back to the time of LUCA, whereas actually , they ar ...
Unit 3 Test
... consistently produce offspring that are similar to themselves? a. Bits of tissue in the parents are incorporated into the offspring, resulting in similar development. b. Hormones from the parents direct the development of the offspring. c. Parents pass their own DNA to their offspring so the same di ...
... consistently produce offspring that are similar to themselves? a. Bits of tissue in the parents are incorporated into the offspring, resulting in similar development. b. Hormones from the parents direct the development of the offspring. c. Parents pass their own DNA to their offspring so the same di ...
Name three amino acids that are typically found at the
... Q19 (1 point). DNA from a newly discovered organism contains 17% C (cytosine) and 33% A (adenine). How many percent G (guanine) does the DNA contain? Answer: 17% (identical to C, since C is complementary to G). ...
... Q19 (1 point). DNA from a newly discovered organism contains 17% C (cytosine) and 33% A (adenine). How many percent G (guanine) does the DNA contain? Answer: 17% (identical to C, since C is complementary to G). ...
Linked Genes and Crossing Over
... 1. Linked genes are genes that are inherited together because they are on the same chromosome. *** Do not get this confused with sex-linked genes which are genes that are only carried on a single sex chromosome. 2. Thomas Hunt Morgan discovered that the expected 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in a dihybri ...
... 1. Linked genes are genes that are inherited together because they are on the same chromosome. *** Do not get this confused with sex-linked genes which are genes that are only carried on a single sex chromosome. 2. Thomas Hunt Morgan discovered that the expected 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in a dihybri ...
The Central Dogma Activity (Student Sheet)
... The objective of this lesson is to explore and then demonstrate the principle of The Central Dogma. By the end of the activity, you should be able to identify and explain the relationship between DNA and protein by describing the three processes involved in the Central Dogma as well as explain the p ...
... The objective of this lesson is to explore and then demonstrate the principle of The Central Dogma. By the end of the activity, you should be able to identify and explain the relationship between DNA and protein by describing the three processes involved in the Central Dogma as well as explain the p ...
Oct 11 - University of San Diego
... Single gene may affect multiple traits Single gene products may affect many cells or cell types in different ways Ex: Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease ...
... Single gene may affect multiple traits Single gene products may affect many cells or cell types in different ways Ex: Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease ...
DNA Fingerprinting
... to complete the Vocabulary Matching. See how fast you can complete it! After you finish, cover up the answers and ...
... to complete the Vocabulary Matching. See how fast you can complete it! After you finish, cover up the answers and ...
The relationship between genes and traits is often complex
... due 12/3/07 (only if needed) Bonus #2 posted Year End Topics: •mtDNA •Mapping •Probability •Evolution and the Origin of Humans ...
... due 12/3/07 (only if needed) Bonus #2 posted Year End Topics: •mtDNA •Mapping •Probability •Evolution and the Origin of Humans ...
Nucleic Acids
... • The addition of a phosphate group creates a nucleoside monophosphate or nucleotide. ...
... • The addition of a phosphate group creates a nucleoside monophosphate or nucleotide. ...
MCA Test Prep Answers Part 1
... c) Chromosomes are segments of genes and code for a specific protein. d) Genes are segments of chromosomes and code for a specific protein ...
... c) Chromosomes are segments of genes and code for a specific protein. d) Genes are segments of chromosomes and code for a specific protein ...
LAB EXERCISE: Genetic Transformation
... In this lab you will perform a procedure known as genetic transformation. Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and inv ...
... In this lab you will perform a procedure known as genetic transformation. Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and inv ...
Lesson 2 Transformation Laboratory
... In this lab you will perform a procedure known as genetic transformation. Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and inv ...
... In this lab you will perform a procedure known as genetic transformation. Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (codes for) a protein. This protein gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes, and inv ...
Inheritance and the Structure of DNA
... • 2 main enzymes involved DNA Helicase and DNA Polymerase ...
... • 2 main enzymes involved DNA Helicase and DNA Polymerase ...