pharmaceutical biochemistry
... universal central pathway of anaerob glucose catabolism. It takes place in the cytosol because the plasma membrane generally lacks transporters for phosphorylated sugars and so the intermediates cannot leave this compartment. Glycolysis could be divided to two parts: the breakdown of the sixcarbon g ...
... universal central pathway of anaerob glucose catabolism. It takes place in the cytosol because the plasma membrane generally lacks transporters for phosphorylated sugars and so the intermediates cannot leave this compartment. Glycolysis could be divided to two parts: the breakdown of the sixcarbon g ...
acetyl CoA
... molecule of Coenzyme A, and so converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis. During the transformation process of pyruvate into acetyl CoA , a molecule of CO2 is released and a molecule of NADH is produced. ...
... molecule of Coenzyme A, and so converted to acetyl CoA, which links the cycle to glycolysis. During the transformation process of pyruvate into acetyl CoA , a molecule of CO2 is released and a molecule of NADH is produced. ...
9) Several oxygen saturation curves are shown in the figure below
... B) it is fully oxidized C) it is a β-keto carboxylic acid D) it contains at least one group more oxidized than an aldehyde E) it contains at least one group more reduced than an alkane 21) The committed step of the Urea Cycle, shown below, is catalyzed by Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase. This reactio ...
... B) it is fully oxidized C) it is a β-keto carboxylic acid D) it contains at least one group more oxidized than an aldehyde E) it contains at least one group more reduced than an alkane 21) The committed step of the Urea Cycle, shown below, is catalyzed by Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase. This reactio ...
Isotope fractionations in the biosynthesis of cell components by
... was determined for four different fungi (Rhizopus arrhizus, Mortierella isabellina, Fusarium solani, Aspergillus niger). Carbon isotope ratios of fungi closely followed that of the substrates. Palmitic acid (C16:0), derived from phospholipids, did not display a large carbon isotope fractionation aga ...
... was determined for four different fungi (Rhizopus arrhizus, Mortierella isabellina, Fusarium solani, Aspergillus niger). Carbon isotope ratios of fungi closely followed that of the substrates. Palmitic acid (C16:0), derived from phospholipids, did not display a large carbon isotope fractionation aga ...
Chapter 9: How do cells harvest energy?
... C. proteins are broken into amino acids, which can be broken down further 1. amino group is removed (deamination) 2. amino group may eventually be converted to urea and excreted 2 of 4 ...
... C. proteins are broken into amino acids, which can be broken down further 1. amino group is removed (deamination) 2. amino group may eventually be converted to urea and excreted 2 of 4 ...
Metabolic Integration during the Postprandial, Fasting and Feedback
... Copyright Rocha AJ. This book chapter is open access distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which allows users to download, copy and build upon published articles even for commercial purposes, as long as the author and publisher are properly credited. ...
... Copyright Rocha AJ. This book chapter is open access distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which allows users to download, copy and build upon published articles even for commercial purposes, as long as the author and publisher are properly credited. ...
Regulation of Glucose metabolism
... • Affects adipose tissue and causes a reduction in plasma fatty acids A decrease in triglyceride degradation (inhibits hormone sensitive lipase) An increase in triglyceride synthesis by: Increased glucose uptake which is converted into glycerol 3 phosphate Activation of lipoprotein lipase wh ...
... • Affects adipose tissue and causes a reduction in plasma fatty acids A decrease in triglyceride degradation (inhibits hormone sensitive lipase) An increase in triglyceride synthesis by: Increased glucose uptake which is converted into glycerol 3 phosphate Activation of lipoprotein lipase wh ...
Mol Bio CH 14 Nov 15
... -Other (less well understood) mechanisms function for mRNAs without these sequences ...
... -Other (less well understood) mechanisms function for mRNAs without these sequences ...
SUBJECT OUTLINE Chemistry and Biochemistry BIOB111
... Describe the components that make up the nucleic acids in cells, describe DNA and RNA structure and alterations in ...
... Describe the components that make up the nucleic acids in cells, describe DNA and RNA structure and alterations in ...
Identification, Synthesis and Biological Activity of Galloyl Inhibitors of
... their better docking scores than PLP and NSC107022. All of the β-amino acids entered the active site with amino acid motif with the galloyl group pointing out of the active site and can be seen docked in LMW-PTP IF2 with key interactions in figures 5-11. The screening of primary aromatic amines uti ...
... their better docking scores than PLP and NSC107022. All of the β-amino acids entered the active site with amino acid motif with the galloyl group pointing out of the active site and can be seen docked in LMW-PTP IF2 with key interactions in figures 5-11. The screening of primary aromatic amines uti ...
Lecture 4
... atom, the smallest possible ‘sidechain’, affixed to its Cα-atom. Nonpolar groups have an aversion to water. They tend to cluster together and form contacts among themselves to avoid water. Amino acids having nonpolar sidechains are therefore hydrophobic (H), except for glycine and alanine, the two s ...
... atom, the smallest possible ‘sidechain’, affixed to its Cα-atom. Nonpolar groups have an aversion to water. They tend to cluster together and form contacts among themselves to avoid water. Amino acids having nonpolar sidechains are therefore hydrophobic (H), except for glycine and alanine, the two s ...
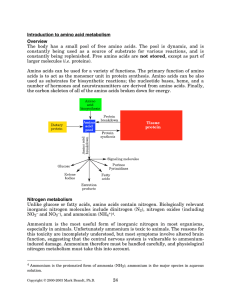
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... to allow the glutamine synthetase reaction to occur. In most plants, and in some microorganisms, a second reaction, catalyzed by glutamate synthase, is therefore used to regenerate the glutamate. In organisms that use this pathway, the net reaction is the conversion of an a-ketoglutarate to glutamat ...
... to allow the glutamine synthetase reaction to occur. In most plants, and in some microorganisms, a second reaction, catalyzed by glutamate synthase, is therefore used to regenerate the glutamate. In organisms that use this pathway, the net reaction is the conversion of an a-ketoglutarate to glutamat ...
09_Lecture
... • Blood is buffered by the bicarbonate buffer system. • Dissolved CO2 produced during cellular respiration travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. • This dissolved CO2 is rapidly equilibrated through carbonic acid into bicarbonate ions. ...
... • Blood is buffered by the bicarbonate buffer system. • Dissolved CO2 produced during cellular respiration travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. • This dissolved CO2 is rapidly equilibrated through carbonic acid into bicarbonate ions. ...
CHEMISTRY (HONOURS) Part
... (c) Explain, with example, denaturation of proteins. (d) Give an-account of nucleic acids. 10. (a) Explain the terms diamagnetic anisotropy. (b) What is meant by 'splitting of a signal' in NMR spectroscopy? How many splittings in the signals are expected for the protons in 1. l-dichloroethane and I- ...
... (c) Explain, with example, denaturation of proteins. (d) Give an-account of nucleic acids. 10. (a) Explain the terms diamagnetic anisotropy. (b) What is meant by 'splitting of a signal' in NMR spectroscopy? How many splittings in the signals are expected for the protons in 1. l-dichloroethane and I- ...
Biology
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with the electrons from other atoms to form ...
... The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with the electrons from other atoms to form ...
Practical Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations Brochure
... More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2174997/ ...
... More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2174997/ ...
Slides
... Linear arrangement of n amino acid residues linked by peptide bonds. Polymers composed of two, three, a few, and many amino acid residues are called as dipeptides, tripeptides, oligopeptides and polypeptides. Proteins are molecules that consist of one or more polypeptide chains. ...
... Linear arrangement of n amino acid residues linked by peptide bonds. Polymers composed of two, three, a few, and many amino acid residues are called as dipeptides, tripeptides, oligopeptides and polypeptides. Proteins are molecules that consist of one or more polypeptide chains. ...
A Supramolecular Peptide Synthesizer
... 10182 – 10228; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 10030 – 10074. ...
... 10182 – 10228; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 10030 – 10074. ...
Life and Cell
... Which of the following deoxyoligonucleotides will hybridize with a DNA containing the sequence (5')AGACTGGTC(3')? A) (5')CTCATTGAG(3') B) (5')GACCAGTCT(3') C) (5')GAGTCAACT(3') D) (5')TCTGACCAG(3') E) (5')TCTGGATCT(3') ...
... Which of the following deoxyoligonucleotides will hybridize with a DNA containing the sequence (5')AGACTGGTC(3')? A) (5')CTCATTGAG(3') B) (5')GACCAGTCT(3') C) (5')GAGTCAACT(3') D) (5')TCTGACCAG(3') E) (5')TCTGGATCT(3') ...
I. CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE, cont
... that are formed from interactions between 2 or more polypeptide chains folded together. Examples include hemoglobin, collagen, chlorophyll ...
... that are formed from interactions between 2 or more polypeptide chains folded together. Examples include hemoglobin, collagen, chlorophyll ...
23.1 The Citric Acid Cycle
... Karen C. Timberlake General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
... Karen C. Timberlake General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake ...
Redox Reactions and Cofactors
... A coenzyme synthesized in plants and animals as a 6,8-dithiooctanoic acid. The role of α-lipoic acid in metabolic reactions is to provide a reactive disulfide that can participate in redox reactions within the enzyme active site. Lipoamide, the naturally occurring form of α-lipoic acid, is a covalen ...
... A coenzyme synthesized in plants and animals as a 6,8-dithiooctanoic acid. The role of α-lipoic acid in metabolic reactions is to provide a reactive disulfide that can participate in redox reactions within the enzyme active site. Lipoamide, the naturally occurring form of α-lipoic acid, is a covalen ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam III - S2014 Name:________________________
... iii) why this regulation is useful to the cell (1 pts). Choice B: The liver cell responds to a number of different hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine. Select any one of these hormones and: i) State under what conditions the hormone would be released (e.g. low blood glucose levels ...
... iii) why this regulation is useful to the cell (1 pts). Choice B: The liver cell responds to a number of different hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine. Select any one of these hormones and: i) State under what conditions the hormone would be released (e.g. low blood glucose levels ...
a method to produce insect resistance in plant by altering amino
... B. tabaci adults (0-1 day old, 30/pot) were released on separate pots containing similar number of mutant and control plants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Number of surviving B. tabaci was counted after one week and percent mortality calculated. Experiment was performed in triplicate. Mortality data was ...
... B. tabaci adults (0-1 day old, 30/pot) were released on separate pots containing similar number of mutant and control plants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Number of surviving B. tabaci was counted after one week and percent mortality calculated. Experiment was performed in triplicate. Mortality data was ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.