Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation by Acetyl
... Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation by Acetyl-CoA Generated from Glucose Utilization in Isolated Myocytes. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology (1996) 28, 825–833. The regulation of fatty acid oxidation in isolated myocytes was examined by manipulating mitochondrial acetyl-CoA levels produced ...
... Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation by Acetyl-CoA Generated from Glucose Utilization in Isolated Myocytes. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology (1996) 28, 825–833. The regulation of fatty acid oxidation in isolated myocytes was examined by manipulating mitochondrial acetyl-CoA levels produced ...
Document
... 3- The oxidative decarboxylation of a -keto acids derived from leucine, valine & isoleucine (branched chain amino acids catalyzed by a single enzyme complex , branched-chain a -keto acids dehydrogenase complex ...
... 3- The oxidative decarboxylation of a -keto acids derived from leucine, valine & isoleucine (branched chain amino acids catalyzed by a single enzyme complex , branched-chain a -keto acids dehydrogenase complex ...
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except
... 2- The globular proteins is characterized by the following except: a) the axial ratio is less than 10. b) they include albumin and globulin. c) they are less stable than fibrous proteins. d) they include keratin and myosin. e) is a shape of the tertiary structure of the protein. 3- Which of the foll ...
... 2- The globular proteins is characterized by the following except: a) the axial ratio is less than 10. b) they include albumin and globulin. c) they are less stable than fibrous proteins. d) they include keratin and myosin. e) is a shape of the tertiary structure of the protein. 3- Which of the foll ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism - BITS Academic Resource Center
... In addition, 2 ATP is formed by substrate level phosphorylation catalyzed by succinate thiokinase. ...
... In addition, 2 ATP is formed by substrate level phosphorylation catalyzed by succinate thiokinase. ...
Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis – Structure, function, regulation
... 2400 Å2 at the enzymes surface. Substrates appear to access the active site from within this region which is consistent with their localization in plastid membranes (Lee et al., 2008). AOSs belong to an atypical cytochrome P450 subfamily, the CYP74 enzymes. Unlike other P450s, they do not require mo ...
... 2400 Å2 at the enzymes surface. Substrates appear to access the active site from within this region which is consistent with their localization in plastid membranes (Lee et al., 2008). AOSs belong to an atypical cytochrome P450 subfamily, the CYP74 enzymes. Unlike other P450s, they do not require mo ...
Homework Solutions
... Use Figure 21.10 to determine which types of intermolecular forces occur between each amino acid pair. a. isoleucine and valine: London dispersion forces of the nonpolar side chains b. threonine and phenylalanine: London dispersion forces. Since the side chain of phenylalanine has no O or N atom, no ...
... Use Figure 21.10 to determine which types of intermolecular forces occur between each amino acid pair. a. isoleucine and valine: London dispersion forces of the nonpolar side chains b. threonine and phenylalanine: London dispersion forces. Since the side chain of phenylalanine has no O or N atom, no ...
Absorption of Amino Acids from an Amino Acid
... 2. Total absorption was greater from the tryptic hydrolysate than from the amino acid mixture. There was wide variation in the extent to which individual amino acids were absorbed from the amino acid mixture. This was decreased when the tryptic hydrolysate was perfused. Amino acids which were partic ...
... 2. Total absorption was greater from the tryptic hydrolysate than from the amino acid mixture. There was wide variation in the extent to which individual amino acids were absorbed from the amino acid mixture. This was decreased when the tryptic hydrolysate was perfused. Amino acids which were partic ...
chapt08
... 1. The citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of mitochondria. 2. The cycle is sometimes called the Krebs cycle, named for Sir Hans Krebs, who described the fundamentals of the reactions in the 1930s. 3. The cycle begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule, forming ...
... 1. The citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of mitochondria. 2. The cycle is sometimes called the Krebs cycle, named for Sir Hans Krebs, who described the fundamentals of the reactions in the 1930s. 3. The cycle begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule, forming ...
PROTEIN METABOLISM
... cytosol into mitochondria, where it undergoes oxidative deamination catalyzed by Lglutamate dehydrogenase ...
... cytosol into mitochondria, where it undergoes oxidative deamination catalyzed by Lglutamate dehydrogenase ...
The light reaction of photosynthesis does not include
... Which of the following occurs in both photosynthesis and respiration? chemiosmosis glycolysis calvin cycle krebs cycle 2. Which of the following statements is FALSE? glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and an ...
... Which of the following occurs in both photosynthesis and respiration? chemiosmosis glycolysis calvin cycle krebs cycle 2. Which of the following statements is FALSE? glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and an ...
Welcome to Class 14 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Several amino acids are derived from oxaloacetate and from pyruvate! ...
... Several amino acids are derived from oxaloacetate and from pyruvate! ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... The reduced co-reactant can also pass on the electrons, through a series of redox carriers (the ‘terminal respiratory system’; TRS), until, eventually, they combine with O2 deliberately taken into the cell, to form H2O. The citric acid cycle, in which much of the reduction of NAD+ and FAD occurs, is ...
... The reduced co-reactant can also pass on the electrons, through a series of redox carriers (the ‘terminal respiratory system’; TRS), until, eventually, they combine with O2 deliberately taken into the cell, to form H2O. The citric acid cycle, in which much of the reduction of NAD+ and FAD occurs, is ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... electron transport chain, the released energy is used to drive the movement of H+ into the intermembrane space H+ then moves down its concentration gradient through ATP synthase ADP is converted to ATP by ATP synthase ...
... electron transport chain, the released energy is used to drive the movement of H+ into the intermembrane space H+ then moves down its concentration gradient through ATP synthase ADP is converted to ATP by ATP synthase ...
Slayt 1 - Prof.Dr.Orhan CANBOLAT
... to the corresponding nucleotides IMP and GMP. • Inability to utilize PRPP in the salvage pathway leads to PRPP accumulation, which, in conjunction with low levels of IMP and GMP, causes chronic allosteric activation of PRPP glutamyl amidotransferase and excessive purine synthesis. • The excess purin ...
... to the corresponding nucleotides IMP and GMP. • Inability to utilize PRPP in the salvage pathway leads to PRPP accumulation, which, in conjunction with low levels of IMP and GMP, causes chronic allosteric activation of PRPP glutamyl amidotransferase and excessive purine synthesis. • The excess purin ...
1 mg/kg/day - Autism One
... Acetyl-L-Carnitine: 50-100 mg/kg/day L-Carnosine: 200-400 mg twice a day Pycnogenol: 1 mg/kg/day (often higher) MB12 injections: 75 mcg/kg every 1-3 days Folinic acid 400 mcg twice a day Omega-3’s: DHA and EPA ~800 mg/day each Zinc 20-150 mg/day Melatonin: 1-6 mg 30 mins before bedtime ...
... Acetyl-L-Carnitine: 50-100 mg/kg/day L-Carnosine: 200-400 mg twice a day Pycnogenol: 1 mg/kg/day (often higher) MB12 injections: 75 mcg/kg every 1-3 days Folinic acid 400 mcg twice a day Omega-3’s: DHA and EPA ~800 mg/day each Zinc 20-150 mg/day Melatonin: 1-6 mg 30 mins before bedtime ...
Document
... levels of glucose. Having GLUT transporters with a high Km enables sensitivity to these changes even at high blood glucose levels. If β-cells had GLUT transporters with a Km lower or nearly equal to that of fasting blood glucose levels, the transporters would be easily saturated and unable to delive ...
... levels of glucose. Having GLUT transporters with a high Km enables sensitivity to these changes even at high blood glucose levels. If β-cells had GLUT transporters with a Km lower or nearly equal to that of fasting blood glucose levels, the transporters would be easily saturated and unable to delive ...
Cellular respiration - Jocha
... • Reactions are used to synthesize ATP and capture hydrogens (H) •The coenzyme NAD+ capture the H and eand is reduced to NADH • Again, each step requires a specific enzyme ...
... • Reactions are used to synthesize ATP and capture hydrogens (H) •The coenzyme NAD+ capture the H and eand is reduced to NADH • Again, each step requires a specific enzyme ...
Chapter 5
... • Fats made from unsaturated fatty acids are called unsaturated fats or oils, and are liquid at room temperature ...
... • Fats made from unsaturated fatty acids are called unsaturated fats or oils, and are liquid at room temperature ...
ppt-file
... This scheme gives rise to 36 elem. modes producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable tha ...
... This scheme gives rise to 36 elem. modes producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable tha ...
Lecture 3: Introduction to Proteins
... Draw the structure of a typical amino acid, indicating the following features: α-carbon, α-carboxyl group, α-amino group, side chain (“R group”), and ionic forms that predominate at acidic (say, pH 1), neutral (pH 7), and basic (pH 13) pH values. Classify each of the 20 common amino acids found in p ...
... Draw the structure of a typical amino acid, indicating the following features: α-carbon, α-carboxyl group, α-amino group, side chain (“R group”), and ionic forms that predominate at acidic (say, pH 1), neutral (pH 7), and basic (pH 13) pH values. Classify each of the 20 common amino acids found in p ...
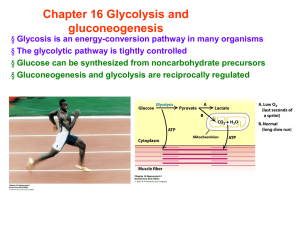
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... for other amino acids are shown in yellow. The nine essential amino acids are shown in boldface. The carbon skeletons come from intermediates of glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway and the citric acid cycle. On the basis of the starting points the 20 amino acids can be group into 6 categories ...
... for other amino acids are shown in yellow. The nine essential amino acids are shown in boldface. The carbon skeletons come from intermediates of glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway and the citric acid cycle. On the basis of the starting points the 20 amino acids can be group into 6 categories ...
LESSON
... A. 1 and 4 B. 2 and 5 C. 3 and 6 D. 2 and 4 E. 3 and 5 30. The tertiary structure of proteins is typified by the: A. association of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds. B. order in which amino acids are joined in a peptide chain. C. bonding of two amino acids to form a dipeptide. D. folding of ...
... A. 1 and 4 B. 2 and 5 C. 3 and 6 D. 2 and 4 E. 3 and 5 30. The tertiary structure of proteins is typified by the: A. association of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds. B. order in which amino acids are joined in a peptide chain. C. bonding of two amino acids to form a dipeptide. D. folding of ...
ch24a_wcr
... transport chain carries out oxidative phosphorylation, which accounts for most of the ATP generated by cellular respiration. ...
... transport chain carries out oxidative phosphorylation, which accounts for most of the ATP generated by cellular respiration. ...
DRUGS for DYSLIPIDEMIAS MED PHARM
... Cholesterol is excreted by conversion to bile acids in liver cells Bile acids are recycled from ileum via enterohepatic circulation to feedback repress 7hydroxylase Sequestering resins bind bile salts (made from bile acids) to reduce recycling Chain of events: reduced recycling lowers liver bile sa ...
... Cholesterol is excreted by conversion to bile acids in liver cells Bile acids are recycled from ileum via enterohepatic circulation to feedback repress 7hydroxylase Sequestering resins bind bile salts (made from bile acids) to reduce recycling Chain of events: reduced recycling lowers liver bile sa ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.