Crash Course in Biochemistry
... • Some proteins bind (stick) to each other in a highly specific way – See hemoglobin • The final complex is functional • Individual pieces are not – Toxic truncated peptides ...
... • Some proteins bind (stick) to each other in a highly specific way – See hemoglobin • The final complex is functional • Individual pieces are not – Toxic truncated peptides ...
Discovery of Complement
... Complement Plays a Key Role in Both Innate and Adaptive Immunity - The complement system is the major effector of the humoral branch of the immune system. - Although the discovery of complement and most early studies were linked to the activity of complement following Ab binding, a major role for t ...
... Complement Plays a Key Role in Both Innate and Adaptive Immunity - The complement system is the major effector of the humoral branch of the immune system. - Although the discovery of complement and most early studies were linked to the activity of complement following Ab binding, a major role for t ...
115 things you should know for the living environment regents exam
... 50. Organs and systems in the human body help maintain homeostasis. 51. Enzymes in the digestive system are responsible for the hydrolysis (breaking down) of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. 52. The circulatory system is responsible for moving plasma and cells to all regions of the body through ...
... 50. Organs and systems in the human body help maintain homeostasis. 51. Enzymes in the digestive system are responsible for the hydrolysis (breaking down) of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. 52. The circulatory system is responsible for moving plasma and cells to all regions of the body through ...
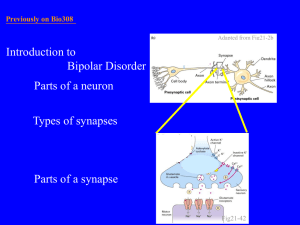
chemical signaling
... may trigger an increase in calcium in the cytosol • Pathways leading to the release of calcium involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as second messengers ...
... may trigger an increase in calcium in the cytosol • Pathways leading to the release of calcium involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as second messengers ...
“ Signal Transduction”?
... Molecules for targeted therapies (1) Small molecules: target the ATP binding site or other regions in protein kinase domain, e.g. Gleevec (to BCR-Abl) (2) Monoclonal Abs: target receptors, cytokines, other surface proteins, e.g. Herceptin (to Her), Erbitux (to EGFR) (3) Others: Decoy receptors (sol ...
... Molecules for targeted therapies (1) Small molecules: target the ATP binding site or other regions in protein kinase domain, e.g. Gleevec (to BCR-Abl) (2) Monoclonal Abs: target receptors, cytokines, other surface proteins, e.g. Herceptin (to Her), Erbitux (to EGFR) (3) Others: Decoy receptors (sol ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • The complement system is a biochemical cascade that helps clear pathogens from an organism • It is part of the innate immune system • The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, normally circulating as inactive zymogens • When these proteins are stimulated by o ...
... • The complement system is a biochemical cascade that helps clear pathogens from an organism • It is part of the innate immune system • The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, normally circulating as inactive zymogens • When these proteins are stimulated by o ...
RED &WHITE BLOOD CELLS
... Major function is to transport oxygen to the tissues . And disposal of carbon dioxide and protons formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
... Major function is to transport oxygen to the tissues . And disposal of carbon dioxide and protons formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
A mutant defective in enzyme
... (c) Argininosuccinase in mitochondria. (d) Ornithine transcarbamoylase in mitochondria. (e) Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase in mitochondria. 二、問答題(54 %) 1. Muscle protein responds to conditions such as starvation, trauma, burns and septicemia, by undergoing massive degradation. Of the amino acids rel ...
... (c) Argininosuccinase in mitochondria. (d) Ornithine transcarbamoylase in mitochondria. (e) Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase in mitochondria. 二、問答題(54 %) 1. Muscle protein responds to conditions such as starvation, trauma, burns and septicemia, by undergoing massive degradation. Of the amino acids rel ...
Homework Exercise 6 1(a). Name the “building blocks” of a protein
... 3. Are proteins that control all of the reactions taking place in a cell. ...
... 3. Are proteins that control all of the reactions taking place in a cell. ...
113 things you should know for the living environment regents exam
... 53. White blood cells fight pathogens in the body. 54. Antibodies are proteins produced by white blood cells in the human body that attach to invading pathogens and clump them together: antigen-antibody complex. 55. When a person gets an organ transplant, the cells of the implanted organ are recogni ...
... 53. White blood cells fight pathogens in the body. 54. Antibodies are proteins produced by white blood cells in the human body that attach to invading pathogens and clump them together: antigen-antibody complex. 55. When a person gets an organ transplant, the cells of the implanted organ are recogni ...
Chapter 4
... sodium-potassium pump. The pump changes shape, transporting the three sodium ions across the cell membrane and releasing them outside the cell. Two potassium ions outside the cell bind to the pump. The two potassium ions are transported across the cell membrane and are released inside the cell. ...
... sodium-potassium pump. The pump changes shape, transporting the three sodium ions across the cell membrane and releasing them outside the cell. Two potassium ions outside the cell bind to the pump. The two potassium ions are transported across the cell membrane and are released inside the cell. ...
Cell Communication per Parrott
... – One signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another molecule, etc., etc. (relays) – These act as relay molecules – Often the message is transferred using protein kinases, which transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to proteins ...
... – One signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another molecule, etc., etc. (relays) – These act as relay molecules – Often the message is transferred using protein kinases, which transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to proteins ...
Special topics in electrical and systems engineering
... • There are specialized receptors on the cell surface • Receptors transduce signals (binding of their ligand) into the cytosol (the inside of the cell) • Signaling cascades originate in the initial binding event • Complicated networks of multistep phosphorylation reactions • Eventually they control ...
... • There are specialized receptors on the cell surface • Receptors transduce signals (binding of their ligand) into the cytosol (the inside of the cell) • Signaling cascades originate in the initial binding event • Complicated networks of multistep phosphorylation reactions • Eventually they control ...
课件三
... • 43,409 articles in Medline that mention G proteins. • 1. Basic facts about G proteins – Each G-protein consists of 3 sub-units: Ga, Gb, and Gg. – These sub-units can be together or separated. – Each G-protein has a binding site that can be occupied by either GDP or GTP. – A G-protein is said to be ...
... • 43,409 articles in Medline that mention G proteins. • 1. Basic facts about G proteins – Each G-protein consists of 3 sub-units: Ga, Gb, and Gg. – These sub-units can be together or separated. – Each G-protein has a binding site that can be occupied by either GDP or GTP. – A G-protein is said to be ...
Problem Set 3 Answer Key, Spring 2003 1) The following
... b) tyrosine residue(s) in the (phosphorylation lip) near the catalytic site that become phosphorylated upon ligand binding and receptor dimerization allowing full kinase function c) tyrosine residues elsewhere that are phosphorylated by the kinase domain and promote binding of other proteins B) What ...
... b) tyrosine residue(s) in the (phosphorylation lip) near the catalytic site that become phosphorylated upon ligand binding and receptor dimerization allowing full kinase function c) tyrosine residues elsewhere that are phosphorylated by the kinase domain and promote binding of other proteins B) What ...
Student CSE paper
... Proteolysis is the breakdown or degradation of proteins and is an important cellular event involving tightly regulated removal of unwanted proteins and retention of those that are essential. The ubiquitin/proteasome pathway plays an important role in the intracellular quality control process by degr ...
... Proteolysis is the breakdown or degradation of proteins and is an important cellular event involving tightly regulated removal of unwanted proteins and retention of those that are essential. The ubiquitin/proteasome pathway plays an important role in the intracellular quality control process by degr ...
Document
... Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate ...
... Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate ...
BIOL 201: Cell Biology and Metabolism
... apart, whereas Beta/Gamma stick together. The 2 complexes move away. GAlpha finds an Effector Protein (Adenylyl Cyclase for epinephrine). Interacts with this protein and modifies it so that there is a change in its activity The Effector Protein will carry out the appropriate downstream event that ar ...
... apart, whereas Beta/Gamma stick together. The 2 complexes move away. GAlpha finds an Effector Protein (Adenylyl Cyclase for epinephrine). Interacts with this protein and modifies it so that there is a change in its activity The Effector Protein will carry out the appropriate downstream event that ar ...
Citric acid Cycle:
... a. Which way will this reaction go in standard condition, forward or backward? b. How does this reaction proceeds in forward direction? c. Calculate the G for this reaction in forward direction if concentration of oxaloacetate is 1x 10-8 M, malate 0.2 mM, and NAD+/NADH ratio in rat liver mitochondr ...
... a. Which way will this reaction go in standard condition, forward or backward? b. How does this reaction proceeds in forward direction? c. Calculate the G for this reaction in forward direction if concentration of oxaloacetate is 1x 10-8 M, malate 0.2 mM, and NAD+/NADH ratio in rat liver mitochondr ...
Lecture 22 - Introduction to Metabolism: Regulation Key Concepts
... Epinephrine binding to β2 adrenergic receptors in liver cells also activates Gsα signaling, however, epinephrine binding to α1 adrenergic receptors in muscle cells activates phospholipase C signaling. cAMP activation of protein kinase A (PKA) activity leads to the phosphorylation of downstream targe ...
... Epinephrine binding to β2 adrenergic receptors in liver cells also activates Gsα signaling, however, epinephrine binding to α1 adrenergic receptors in muscle cells activates phospholipase C signaling. cAMP activation of protein kinase A (PKA) activity leads to the phosphorylation of downstream targe ...