Signal Transduction Pathways • Signal Transduction
... –the two α subunits move together to surround one insulin molecule, the kinase domains also draw closer together –the two β subunits forced together, the kinase domain catalyze the phosphoryl groups from ATP to tyrosine residues in the activation loops -- conformational ...
... –the two α subunits move together to surround one insulin molecule, the kinase domains also draw closer together –the two β subunits forced together, the kinase domain catalyze the phosphoryl groups from ATP to tyrosine residues in the activation loops -- conformational ...
Document
... Localizations are inferred from manual curation or Gene Ontology annotation in InnateDB either directly based on cellular compartment annotation or indirectly via functional annotation e.g. proteins annotated with term transcription factor activity will be placed in nucleus. ...
... Localizations are inferred from manual curation or Gene Ontology annotation in InnateDB either directly based on cellular compartment annotation or indirectly via functional annotation e.g. proteins annotated with term transcription factor activity will be placed in nucleus. ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... ECM consists of a mixture of proteins, polysaccharides, and in some cases, minerals The matrix serves two general functions: ...
... ECM consists of a mixture of proteins, polysaccharides, and in some cases, minerals The matrix serves two general functions: ...
New twists on embryonic patterning
... inhibitory component of the Wnt pathway Mao et al. (2001a) thus providing a direct physical link to intracellular protein complexes that mediate canonical Wnt signaling through the β-catenin pathway. Dkk-1 does not act as a direct Wnt antagonist, but rather exerts its inhibitory effect by binding to ...
... inhibitory component of the Wnt pathway Mao et al. (2001a) thus providing a direct physical link to intracellular protein complexes that mediate canonical Wnt signaling through the β-catenin pathway. Dkk-1 does not act as a direct Wnt antagonist, but rather exerts its inhibitory effect by binding to ...
Enzymes
... Are necessary for normal activity of enzymes ;are derived from vitamins; transport small molecules needed by enzymes. ...
... Are necessary for normal activity of enzymes ;are derived from vitamins; transport small molecules needed by enzymes. ...
Biochemistry Objectives 42
... Rate-determining enzyme and regulation mechanism: tyrosine hydroxylase; activated by acetylcholine and Gs induced cAMP increase, inhibited by catecholamine feedback inhibition. c. Acetylcholine and catecholamine release: acetylcholine causes target cell depolarization, increased Ca2+ influx, and sub ...
... Rate-determining enzyme and regulation mechanism: tyrosine hydroxylase; activated by acetylcholine and Gs induced cAMP increase, inhibited by catecholamine feedback inhibition. c. Acetylcholine and catecholamine release: acetylcholine causes target cell depolarization, increased Ca2+ influx, and sub ...
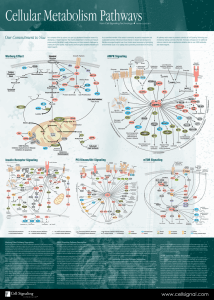
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... and is partially inhibited by rapamycin. mTORC1 integrates multiple signals reflecting the availability of growth factors, nutrients, or energy to promote either cellular growth when conditions are favorable or catabolic processes during stress or when conditions are unfavorable. Growth factors and ...
... and is partially inhibited by rapamycin. mTORC1 integrates multiple signals reflecting the availability of growth factors, nutrients, or energy to promote either cellular growth when conditions are favorable or catabolic processes during stress or when conditions are unfavorable. Growth factors and ...
Protein Structure:
... construction of a vast array of macromolecules from a limited number of monomer building blocks is a recurring theme in biochemistry. Does protein function depend on the linear sequence of amino acids? The function of a protein is directly dependent on its threedimensional structure (Figure 3.1). Re ...
... construction of a vast array of macromolecules from a limited number of monomer building blocks is a recurring theme in biochemistry. Does protein function depend on the linear sequence of amino acids? The function of a protein is directly dependent on its threedimensional structure (Figure 3.1). Re ...
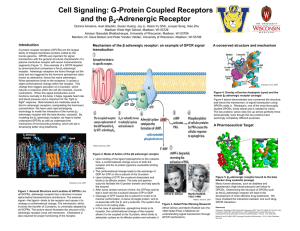
Adrenergic Receptor
... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of integral membrane proteins coded by the human genome. GPCRs are important for signal transduction with the general structural characteristic of a plasma membrane receptor with seven transmembrane segments (Figure 1). One example of a GPCR ...
... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of integral membrane proteins coded by the human genome. GPCRs are important for signal transduction with the general structural characteristic of a plasma membrane receptor with seven transmembrane segments (Figure 1). One example of a GPCR ...
Biology: Exploring Life Resource Pro
... A protein is a polymer made from a set of 20 kinds of monomers called amino acids. An amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side group. The side group is different for each amino acid and causes its particular chemical properties. Pro ...
... A protein is a polymer made from a set of 20 kinds of monomers called amino acids. An amino acid has a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side group. The side group is different for each amino acid and causes its particular chemical properties. Pro ...
Natural killer cell receptor signaling
... also been defined. The CD244 (2B4) and NTB-A [13] receptors contain TxYxxV/I motifs in their cytoplasmic domains, which permit association with the cytoplasmic SLAM-associated protein (SAP) adaptor protein (also called SH2 domain-containing protein 1A; SH2D1A; reviewed in [14]). Upon activation, CD2 ...
... also been defined. The CD244 (2B4) and NTB-A [13] receptors contain TxYxxV/I motifs in their cytoplasmic domains, which permit association with the cytoplasmic SLAM-associated protein (SAP) adaptor protein (also called SH2 domain-containing protein 1A; SH2D1A; reviewed in [14]). Upon activation, CD2 ...
1 | Page Glossary: Atom: Molecule: Compound: Atomic number
... A substance that minimizes change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution fluid within cells o Interstitial fluid: fluid surrounding most tissues o Intra-‐vascula ...
... A substance that minimizes change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution fluid within cells o Interstitial fluid: fluid surrounding most tissues o Intra-‐vascula ...
Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism in the A10 vascular
... /?-Nerve growth factor (NGF)is a 27 kDa protein, composed of two identical subunits 118 amino acids in length, which promotes the survival of peripheral sensory and sympathetic neurons, and has also been shown to be associated with the cells of the basal forebrain cholinergic system of the central A ...
... /?-Nerve growth factor (NGF)is a 27 kDa protein, composed of two identical subunits 118 amino acids in length, which promotes the survival of peripheral sensory and sympathetic neurons, and has also been shown to be associated with the cells of the basal forebrain cholinergic system of the central A ...
Dectin 1
... 3. SYK- and RAF1-pathways fine-tune NF-kB-induced cytokine responses: p65-P subunits form dimers that cannot bind to DNA. This leads to reduced production of IL-1β, IL-12 and IL-23 – major cytokines for Th differentiation. 4. Dectin 1 also induces CCL17 and CCL22 production (CC-chemokine ligand) whi ...
... 3. SYK- and RAF1-pathways fine-tune NF-kB-induced cytokine responses: p65-P subunits form dimers that cannot bind to DNA. This leads to reduced production of IL-1β, IL-12 and IL-23 – major cytokines for Th differentiation. 4. Dectin 1 also induces CCL17 and CCL22 production (CC-chemokine ligand) whi ...
2009 Dental Biochemistry (Questions)
... C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the other two ketone bodies. D) present only in the liver mitochondrion where it is used for energy production during fasting. E) a precursor in the biosynthesis of N-acetylglutamate. The biosynthesis of the “ATP reservoir” creatine requires the amino ...
... C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the other two ketone bodies. D) present only in the liver mitochondrion where it is used for energy production during fasting. E) a precursor in the biosynthesis of N-acetylglutamate. The biosynthesis of the “ATP reservoir” creatine requires the amino ...
ADAM
... Schematic representation of integrins. Both integrin alpha and beta subunits have a single large extracellular domain, one transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail without known enzymatic activity. Integrins bind to a variety of extracellular ligands including other transmembrane proteins ...
... Schematic representation of integrins. Both integrin alpha and beta subunits have a single large extracellular domain, one transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail without known enzymatic activity. Integrins bind to a variety of extracellular ligands including other transmembrane proteins ...
Basic Medical Sciences
... – Consists of cells specialized for exchanging materials between the cell and its environment – Organized into two general types of structures • Epithelial sheets • Secretory glands ...
... – Consists of cells specialized for exchanging materials between the cell and its environment – Organized into two general types of structures • Epithelial sheets • Secretory glands ...
Effect of glucose on insulin promoter activity.
... formation cause pathological changes. • AGE can directly alter protein function in target tissue. • AGE can alter signal transduction pathways by altering matrix-matrix and matrix-cell interactions. • AGE can alter the levels of soluble signals, such as cytokines, hormones or free radicals, through ...
... formation cause pathological changes. • AGE can directly alter protein function in target tissue. • AGE can alter signal transduction pathways by altering matrix-matrix and matrix-cell interactions. • AGE can alter the levels of soluble signals, such as cytokines, hormones or free radicals, through ...
Functions of Complement
... not have DAF and CD59 2) Red cells and platelets cannot repair damage caused by unregulated complement 3) Patients suffer hemolysis and ...
... not have DAF and CD59 2) Red cells and platelets cannot repair damage caused by unregulated complement 3) Patients suffer hemolysis and ...
Chapt03 Lecture 13ed Pt 4
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Andrew Pocklington
... - ISC and MGS data: SNPs with a greater effect on global gene expression generally predict schizophrenia affected status significantly better than those with a lesser effect Alex Richards ...
... - ISC and MGS data: SNPs with a greater effect on global gene expression generally predict schizophrenia affected status significantly better than those with a lesser effect Alex Richards ...
Untitled
... both their presence & their rate of activity are important to chemical reactions in the body. ...
... both their presence & their rate of activity are important to chemical reactions in the body. ...
Quiz8ch8.doc
... 7. How many molecules of ATP would be produced from 20 molecules of glucose at the end of fermentation? a. 10 b. 20 c. 30 d. 40 e. 100 8. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate acts as an electron acceptor in a process called ___________________. a. hydrolysis b. fermentation c. oxidative phosphorylatio ...
... 7. How many molecules of ATP would be produced from 20 molecules of glucose at the end of fermentation? a. 10 b. 20 c. 30 d. 40 e. 100 8. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate acts as an electron acceptor in a process called ___________________. a. hydrolysis b. fermentation c. oxidative phosphorylatio ...