* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes
Survey
Document related concepts
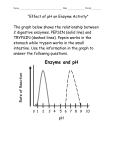
Transcript
SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class made by Pyeongsug Kim Revised: 02/13/10 1. Why can pepsin(an enzyme) digest proteins not carbohydrate or lipid in stomach? How can pepsin be active in stomach but not in mouth or small intestine? An enzyme including pepsin reacts only with specific substrates. Stomach is acidic, the pH which pepsin has optimum activity. 2. Match the term. active site the part of an enzyme that actually interacts with the reactants. enzyme Lowers the activation energy of a reaction. Are biological catalysts that increase rate of chemical reactions by lowering energy enzyme required for a reaction to proceed. enzyme Reactions will not occur at a rate that supports survival without these Series of reactions, each catalyzed by a different enzyme; The product of one metabolic pathway reaction is the substrate for the next. Inborn error of metabolism This is a genetic defect may lead to loss of function of that enzyme. Are necessary for normal activity of enzymes; include metal ions such as Ca+2, cofactor Mg+2, Mn+2, Cu+2, and Zn+2 . coenzyme Are necessary for normal activity of enzymes ;are derived from vitamins; transport small molecules needed by enzymes. Inborn error of metabolism In these situation, Intermediate will accumulate; this may lead to disease a. active site g. enzyme b. cofactor c. coenzyme h. Inborn error of metabolism f. metabolic pathway 3. Match the term. End-product inhibition Describes the process by which the end product of a pathway prevents further activity along that pathway. activation energy An enzyme catalyzes a reaction by lowering this Cu2+, Zn2+ This is an example of cofactor NAD/FAD are derived from vitamins and transfer hydrogens/electrons in the cell. saturation The point at which the reaction rate is highest. Specificity The property that an enzyme only reacts with a particular substate. NAD/FAD This is an example of coenzyme, which helps move electrons around. a. NAD/FAD b. Cu2+, Zn2+ c. saturation d. end-product inhibition e. activation energy f. specificity 4. Answer the following question about enzyme inhibitors: competitive and allosteric inhibition. a. Which type works by binding directly to the active site? Competitive b. Which type works by binding outside the active site, but which distorts the active site when it binds o the enzyme?. Allersteric c. In “end-product inhibition,” does the end product act is a competitive or allosteric inhibitor (indicate which one)? allosteric inhibitor e. Some poison or drugs bind to the enzyme's active site and reduces its activity. Which one? Competitive 5. What are two ways that “inborn errors of metabolism” can contribute to disease? SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class made by Pyeongsug Kim 1) End product of that pathway cannot be synthesized; may lead to disease Revised: 02/13/10 2) Intermediate will accumulate; this may lead to disease 6. a. What is the name of the process that the end product of a pathway prevents further activity along that pathway? Feedback inhibition b. When is the process on(resumes)? In order word when is the pathway inhibited? When end product of a pathway accumulates, it can then inhibit and enzyme that functions earlier in the pathway to prevent more products. c. When does the inhibition process stop? In other word when the pathway resumes? When the end product is depleted, it is not available to inhibit the enzyme, so the pathway resumes. 7. Match the term. Catabolism Anabolism Oxidation The type of reaction or process usually release energy (which can be recaptured by the information of ATP) The type of reaction usually require energy, which is stored in the newly-formed chemical bonds. Cu2+, Zn2+ is the form of this losing electrons is the “currency” of energy in the cell. Energy is stored when ADP is converted to ATP this. Reduction Redox reaction a. Catabolism e. oxidation Refers when an atom or molecule gains electrons. For example, becoming from NAD+/FAD+ into NAD/FAD is this form Refer to the coupled reactions when an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons. b. Anabolism c. Redox reactions (or Oxidation-reduction reactions) f. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) d. Reduction 7. Circle the answer. a. In our body a chemical reaction rate affected by ( substrate concentrations/ enzyme concentrations/ both/ neither). b. (Exergonic/ Endergonic) require input of energy to proceed. (Exergonic/ Endergonic) release energy. c. Endergonic products contain (more/less) free energy than reactants. Exergonic products contain (more/less) free energy than reactants. d. These reactions are (coupled / independent each other) in biologic systems..