Yeast Nutrition and Fermentation Progression
... Needed to alter composition of the plasma membrane (sterols, fatty acids and proteins) so that it can withstand the perturbing effects of ethanol Both phospholipid and protein content must be adjusted ...
... Needed to alter composition of the plasma membrane (sterols, fatty acids and proteins) so that it can withstand the perturbing effects of ethanol Both phospholipid and protein content must be adjusted ...
doc Final Exam 2003
... e) nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 28. Which molecule would be expected to play a direct role in down-regulating the effects of phospholipase C? ...
... e) nicotinic acetylcholine receptor 28. Which molecule would be expected to play a direct role in down-regulating the effects of phospholipase C? ...
Giovanni D`Angelo Institute of Protein Biochemistry
... individual GSLs interact with and modulate specific plasma-membrane receptors, and in this way contribute to cell signalling. Importantly, although GSLs are dispensable for cellular life, they are collectively required for the development of multicellular organisms, and are thus considered to be key ...
... individual GSLs interact with and modulate specific plasma-membrane receptors, and in this way contribute to cell signalling. Importantly, although GSLs are dispensable for cellular life, they are collectively required for the development of multicellular organisms, and are thus considered to be key ...
EphA2 (D4A2) XP® Rabbit mAb
... preference for a subset of ligands: EphA receptors bind to a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored ephrin A ligand, and EphB receptors bind to ephrin B proteins that have a transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain (1,2). Eph receptors and ligands may be involved in many diseases including cancer (3). Bo ...
... preference for a subset of ligands: EphA receptors bind to a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored ephrin A ligand, and EphB receptors bind to ephrin B proteins that have a transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain (1,2). Eph receptors and ligands may be involved in many diseases including cancer (3). Bo ...
Connective Tissue - White Plains Public Schools
... substance existing between cells in an organism. Here they form large complexes, both to other proteoglycans and to fibrous matrix proteins (such as collagen). They are also involved in binding cations, and also regulating the movement of molecules through the ...
... substance existing between cells in an organism. Here they form large complexes, both to other proteoglycans and to fibrous matrix proteins (such as collagen). They are also involved in binding cations, and also regulating the movement of molecules through the ...
Learning Objectives Chapter 10
... Requires a carrier protein in the membrane. The protein undergoes a conformational change that allows molecule to be released on the other side: like enzymes, exhibits saturation kinetics. Example: glucose transporters, which are acted upon by insulin 10. What is a gated channel, examples? Transmemb ...
... Requires a carrier protein in the membrane. The protein undergoes a conformational change that allows molecule to be released on the other side: like enzymes, exhibits saturation kinetics. Example: glucose transporters, which are acted upon by insulin 10. What is a gated channel, examples? Transmemb ...
Slide ()
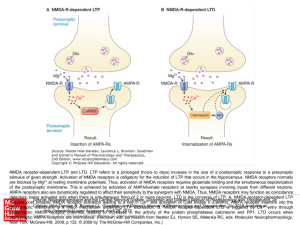
... stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarizatio ...
... stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarizatio ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 5 cellular communication click here
... therefore absolutely requires the expression of receptors on the cell surface – integral membrane proteins that act as first messenger the receptor protein activates a series of signaling events within the cells – e.g. epinephrine binds to receptor and activates an adjacent G-protein in membrane – G ...
... therefore absolutely requires the expression of receptors on the cell surface – integral membrane proteins that act as first messenger the receptor protein activates a series of signaling events within the cells – e.g. epinephrine binds to receptor and activates an adjacent G-protein in membrane – G ...
Lecture slides
... After a receptor notices a change: 1. Cascade message to nucleus 2. Open chromatin & bind transcription factors 3. Recruit RNA polymerase and transcribe 4. Splice mRNA and send to cytoplasm 5. Translate into protein ...
... After a receptor notices a change: 1. Cascade message to nucleus 2. Open chromatin & bind transcription factors 3. Recruit RNA polymerase and transcribe 4. Splice mRNA and send to cytoplasm 5. Translate into protein ...
Biological Molecules continued
... The monomer building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. Most of these amino acids share a common structure. Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These ...
... The monomer building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. Most of these amino acids share a common structure. Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These ...
Towards biome-specific analysis of meta-omics data
... ‘classic’ approaches developed for single genomes. To identify and quantify the biochemical functions and pathways that make up the metabolic wiring of an ecosystem and assess functional shifts upon perturbation, associations between environment, metabolism and species–function relationships, curren ...
... ‘classic’ approaches developed for single genomes. To identify and quantify the biochemical functions and pathways that make up the metabolic wiring of an ecosystem and assess functional shifts upon perturbation, associations between environment, metabolism and species–function relationships, curren ...
Access Slides - Science Signaling
... Rigid Body Model: Straight jacketed receptor Rhodopsin still activates with bridges connecting the cytoplasmic ends of helices 1 & 7, and 3 & 5, and the extracellular ends of helices 3 & 4, and 5 & 6. ...
... Rigid Body Model: Straight jacketed receptor Rhodopsin still activates with bridges connecting the cytoplasmic ends of helices 1 & 7, and 3 & 5, and the extracellular ends of helices 3 & 4, and 5 & 6. ...
Mitogen-activated protein kinases and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
... also, similarly to ERKs, require tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation for their activation. Interest in these kinases was heightened when they were found to phosphorylate c-Jun, a component of the AP-1 transcription factor [6]. JNKs are preferentially activated by cellular stresses, such as ...
... also, similarly to ERKs, require tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation for their activation. Interest in these kinases was heightened when they were found to phosphorylate c-Jun, a component of the AP-1 transcription factor [6]. JNKs are preferentially activated by cellular stresses, such as ...
the brain
... typically amplified, i.e. many more molecules are typically involved at each subsequent step in the pathway. The outcome is an alteration in cellular activity, which can be the result of changes in gene expression within the cell. ...
... typically amplified, i.e. many more molecules are typically involved at each subsequent step in the pathway. The outcome is an alteration in cellular activity, which can be the result of changes in gene expression within the cell. ...
Lecture Exam 1 Study Guide
... - By what two basic methods do cells communicate with each other? - Describe the four types of cell-to-cell communication. - What general types of chemicals carry out local communication? - How is long distance communication carried out in the body? - What is a target cell? Why do some cells respond ...
... - By what two basic methods do cells communicate with each other? - Describe the four types of cell-to-cell communication. - What general types of chemicals carry out local communication? - How is long distance communication carried out in the body? - What is a target cell? Why do some cells respond ...
Effect of ZnO on Pd/ZnO Catalysts in Steam Reforming of Methanol
... Results: • L-proline has two active sites (an amino group and a ...
... Results: • L-proline has two active sites (an amino group and a ...
Chapter 34 HEIN
... Figure 34.5 A single-step oxidation process compared with a multiple process: In the pathway, A, B, and C represent 26 hypothetical pathway intermediates. ...
... Figure 34.5 A single-step oxidation process compared with a multiple process: In the pathway, A, B, and C represent 26 hypothetical pathway intermediates. ...
What is Stem Cell?
... Stem cells refer to all tissue and internal organs of living things that are in their original source. • A stem cell is a “blank” cell • It can divide and produce identical copies – Self Renewal Process • Serves as a built-in repair system for human body ...
... Stem cells refer to all tissue and internal organs of living things that are in their original source. • A stem cell is a “blank” cell • It can divide and produce identical copies – Self Renewal Process • Serves as a built-in repair system for human body ...
Chapters 1, 2, and 3
... Mitochondria are organelles bounded by a double membrane. The inner membrane is folded into cristae. The gel-like material between the cristae is matrix. Mitochondria convert the energy stored in glucose into ATP molecules in a process called cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration and Metabolism ...
... Mitochondria are organelles bounded by a double membrane. The inner membrane is folded into cristae. The gel-like material between the cristae is matrix. Mitochondria convert the energy stored in glucose into ATP molecules in a process called cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration and Metabolism ...