Lecture 5 - Fermentation and CHO feeder
... lactate dehydrogenase (ie. muscle cells) -Pyruvate is converted to ethanol via ethanol dehydrogenase (ie. yeast) Anaerobic pyruvate utilization = Fermentation Both pathways use the NADH (produced in glycolysis): Overall: Glucose → 2 lactate + 2 ATP Biochemistry 3300 ...
... lactate dehydrogenase (ie. muscle cells) -Pyruvate is converted to ethanol via ethanol dehydrogenase (ie. yeast) Anaerobic pyruvate utilization = Fermentation Both pathways use the NADH (produced in glycolysis): Overall: Glucose → 2 lactate + 2 ATP Biochemistry 3300 ...
Chapter 18 Glycolysis
... • Coupled reactions convert some some, but not all all, of the metabolic energy of glucose into ATP • Under U d cellular ll l conditions, diti approximately i t l 50% of the energy of released from glycolysis ...
... • Coupled reactions convert some some, but not all all, of the metabolic energy of glucose into ATP • Under U d cellular ll l conditions, diti approximately i t l 50% of the energy of released from glycolysis ...
Agnieszka Kozieł Aerobic metabolism of human endothelial cells
... variety of specialised functions, which disturbances are implicated in the development of many cardiovascular diseases. In endothelial cells, the ATP synthesis occurs in a major part via a glycolytic pathway. The relatively slight dependence of endothelial cells on mitochondrial oxidative phosphoryl ...
... variety of specialised functions, which disturbances are implicated in the development of many cardiovascular diseases. In endothelial cells, the ATP synthesis occurs in a major part via a glycolytic pathway. The relatively slight dependence of endothelial cells on mitochondrial oxidative phosphoryl ...
Direction of Krebs cycle Which way does the citric acid cycle turn
... et al., 2011). The citric acid cycle is indeed regulated at several steps (LaNoue et al., 1970), (LaNoue et al., 1983), (Bukato et al., 1995), (Gibala et al., 2000), (Pagliarini and Dixon, 2006), (McKenna, 2007); furthermore, different intermediates of the cycle exert different regulation depending ...
... et al., 2011). The citric acid cycle is indeed regulated at several steps (LaNoue et al., 1970), (LaNoue et al., 1983), (Bukato et al., 1995), (Gibala et al., 2000), (Pagliarini and Dixon, 2006), (McKenna, 2007); furthermore, different intermediates of the cycle exert different regulation depending ...
University of Groningen Lactococcus lactis systems biology Eckhardt
... Lactococcus lactis as an industrial work horse The lactic acid bacteria (LAB) form a collection of Gram-positive, acid-tolerant, nonsporulating rod-shaped or coccoid bacteria with low G+C content grouped for a common characteristic: the production of lactic acid, an important metabolic end-product ...
... Lactococcus lactis as an industrial work horse The lactic acid bacteria (LAB) form a collection of Gram-positive, acid-tolerant, nonsporulating rod-shaped or coccoid bacteria with low G+C content grouped for a common characteristic: the production of lactic acid, an important metabolic end-product ...
High Resolution Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis of Proteins*
... After this time no labeled E. coli proteins could be detected. Sample ...
... After this time no labeled E. coli proteins could be detected. Sample ...
Full-Text PDF
... the observed sex bias with a predilection for women, incomplete penetrance, and variability in the time to onset of disease. Genome wide association studies located two single nucleotide polymorphisms downstream of cerebellin 2 (CBLN2) that were associated with a two-fold increased risk of PAH [12]. ...
... the observed sex bias with a predilection for women, incomplete penetrance, and variability in the time to onset of disease. Genome wide association studies located two single nucleotide polymorphisms downstream of cerebellin 2 (CBLN2) that were associated with a two-fold increased risk of PAH [12]. ...
Time-resolved biophysical methods in the study of protein folding
... Because the formation of partially ordered states with regions of native-like structure is thought to be an essential step in protein folding, detecting native tertiary contacts in transient folding populations has been a major goal of folding research. Near-UV CD, which primarily monitors the aroma ...
... Because the formation of partially ordered states with regions of native-like structure is thought to be an essential step in protein folding, detecting native tertiary contacts in transient folding populations has been a major goal of folding research. Near-UV CD, which primarily monitors the aroma ...
Glutamine and cancer: cell biology, physiology
... glutamine in culture (8). Glutamine catabolism begins with its conversion to glutamate in reactions that either donate the amide nitrogen to biosynthetic pathways or release it as ammonia. The latter reactions are catalyzed by the glutaminases (GLSs), of which several isozymes are encoded by human g ...
... glutamine in culture (8). Glutamine catabolism begins with its conversion to glutamate in reactions that either donate the amide nitrogen to biosynthetic pathways or release it as ammonia. The latter reactions are catalyzed by the glutaminases (GLSs), of which several isozymes are encoded by human g ...
Proteome analysis of tobacco BY-2 cell culture - ETH E
... distinguish plant cells from those of other eukaryotes. The origin and evolution of plastids has been an important subject in biological sciences. Plastids represent the endosymbiotic remnants of a free-living cyanobacterial progenitor, which lost the vast majority of its ancestral cyanobacterial ge ...
... distinguish plant cells from those of other eukaryotes. The origin and evolution of plastids has been an important subject in biological sciences. Plastids represent the endosymbiotic remnants of a free-living cyanobacterial progenitor, which lost the vast majority of its ancestral cyanobacterial ge ...
Compartmentation of the Metabolism of Lactose
... Subcellular compartmentation of pools of metabolic intermediates is known to be a widespread phenomenon (Moses, 1966), and it is probable that compartmentation plays a role in the control of biochemical reactions in vivo. Most evidence for metabolic compartmentation so far obtained has come from stu ...
... Subcellular compartmentation of pools of metabolic intermediates is known to be a widespread phenomenon (Moses, 1966), and it is probable that compartmentation plays a role in the control of biochemical reactions in vivo. Most evidence for metabolic compartmentation so far obtained has come from stu ...
Biological significance of structural differences between two highly
... in called Uev1D30, would provide insight into whether these subtle differences might come together in three dimensions to constitute a sufficiently distinct surface. The structure of Uev1D30 was solved by molecular replacement using a poly-alanine model of Mms2 (PDB accession number: 1J74). The densi ...
... in called Uev1D30, would provide insight into whether these subtle differences might come together in three dimensions to constitute a sufficiently distinct surface. The structure of Uev1D30 was solved by molecular replacement using a poly-alanine model of Mms2 (PDB accession number: 1J74). The densi ...
Targeting apicoplasts in malaria parasites
... All rights reserved: reproduction in whole or in part not permitted ...
... All rights reserved: reproduction in whole or in part not permitted ...
... independent (oneappeared twice) and two were full-length, extending of chloride ion transport in a variety of tissues causing death beyond the 5' translational start site. Due to errors introduced during by compromising the function of secretory epithelia of the the 60 amplification cycles required ...
1 High resolution metabolomics with acyl
... Thioester compounds containing coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) are key metabolites in intermediary metabolism. The most prominent of which is acetyl-CoA whose levels regulate critical cellular processes such as energy metabolism, protein acetylation, lipid synthesis and catabolism, and even autophagy (1-4). O ...
... Thioester compounds containing coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) are key metabolites in intermediary metabolism. The most prominent of which is acetyl-CoA whose levels regulate critical cellular processes such as energy metabolism, protein acetylation, lipid synthesis and catabolism, and even autophagy (1-4). O ...
Identification of the Amino Terminus of Neuronal Ca2
... saline (as above plus 1.8 mM C aC l2 ) supplemented with 100 mg /ml penicillin, 100 I U/ml streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD), and 2.5 mM sodium pyruvate. Whole-cell recordings from oocytes were made in the two-electrode voltage-clamp configuration with a chloride-free solution conta ...
... saline (as above plus 1.8 mM C aC l2 ) supplemented with 100 mg /ml penicillin, 100 I U/ml streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD), and 2.5 mM sodium pyruvate. Whole-cell recordings from oocytes were made in the two-electrode voltage-clamp configuration with a chloride-free solution conta ...
metabolism during adventitious root primordium initiation
... inhibitory effect under conditions of endogenous carbohydrate sufficiency (Lovell, Cobb and Moore, 1971; Lovell, Illsley and Moore, 1972; Moore, Cobb and Lovell, 1972). Enhanced starch metabolism in cuttings probably results from the direct or indirect effects of basipetally transported IAA. Auxin t ...
... inhibitory effect under conditions of endogenous carbohydrate sufficiency (Lovell, Cobb and Moore, 1971; Lovell, Illsley and Moore, 1972; Moore, Cobb and Lovell, 1972). Enhanced starch metabolism in cuttings probably results from the direct or indirect effects of basipetally transported IAA. Auxin t ...
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE
... accounts for both the diversity and the unity of living things. D. Describe the structure and function of macromolecules and recognize the role of carbon in the molecular diversity of life. E. Explain the effects of water’s polarity. F. Recognize that cells are the basic structure of all living thin ...
... accounts for both the diversity and the unity of living things. D. Describe the structure and function of macromolecules and recognize the role of carbon in the molecular diversity of life. E. Explain the effects of water’s polarity. F. Recognize that cells are the basic structure of all living thin ...
Student notes in ppt
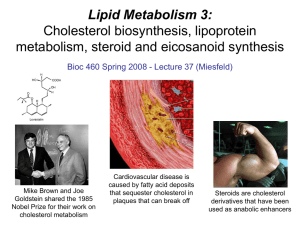
... response that triggers the local accumulation of inflammatory cells that degrade LDL particles causing the cholesterol to be released and taken up by a type of macrophage cell called a foam cell. The site of inflammation grows as more LDL particles attach to the plaque, eventually resulting in smoot ...
... response that triggers the local accumulation of inflammatory cells that degrade LDL particles causing the cholesterol to be released and taken up by a type of macrophage cell called a foam cell. The site of inflammation grows as more LDL particles attach to the plaque, eventually resulting in smoot ...
Single and Competitive Protein Sorption at Soft Polymeric Interfaces
... structure on a silicon surface. Moreover, the adsorption of lysozyme onto the shell of the microgel changed the phase of the AFM signal indicating a change in the mechanical properties. For the measurements in liquid it was shown that the microgels can be attached via electrostatic interactions with ...
... structure on a silicon surface. Moreover, the adsorption of lysozyme onto the shell of the microgel changed the phase of the AFM signal indicating a change in the mechanical properties. For the measurements in liquid it was shown that the microgels can be attached via electrostatic interactions with ...
VAAM-Jahrestagung 2015 1.–4. März in Marburg/Lahn
... More and more human SNPs are analyzed for their potential association with diseases, risk factors and predispositions. Our LightSNiP assays are preestablished, probe-based tests using a melting curve to detect sequence variations. These assays are developed on the Roche LightCycler® 480 system, but ...
... More and more human SNPs are analyzed for their potential association with diseases, risk factors and predispositions. Our LightSNiP assays are preestablished, probe-based tests using a melting curve to detect sequence variations. These assays are developed on the Roche LightCycler® 480 system, but ...
Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in gram
... TnrA/GlnR site upstream of orthologous genes in at least two genomes. Another 11 operons lacked the conserved TnrA-binding site, but their products were involved in nitrogen assimilation (Fig. 3). In all genomes analyzed, the conserved TnrAbinding site was observed upstream of the nrgAB operon. In B ...
... TnrA/GlnR site upstream of orthologous genes in at least two genomes. Another 11 operons lacked the conserved TnrA-binding site, but their products were involved in nitrogen assimilation (Fig. 3). In all genomes analyzed, the conserved TnrAbinding site was observed upstream of the nrgAB operon. In B ...