Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein ab140735 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein images 15% SDS-PAGE analysis of ab140735 ...
... Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein images 15% SDS-PAGE analysis of ab140735 ...
Measurement of Protein Molecular Weight using MALDI MS
... To calculate the molecular weight of the protein, the measured m/z value of charge state, n, is multiplied by n and then n protons (n * 1.0079) are subtracted to give the measured molecular weight. ...
... To calculate the molecular weight of the protein, the measured m/z value of charge state, n, is multiplied by n and then n protons (n * 1.0079) are subtracted to give the measured molecular weight. ...
Additional file 1 - Most up-regulated genes with known function
... is one of the four major Ser/Thr phosphatases, and it is implicated in the negative control of cell growth and division. The ligand binding of this receptor leads to the activation of multiple downstream signaling molecules, including JAK1, JAK3, STAT1, and STAT3. PTPs are known to be signaling mole ...
... is one of the four major Ser/Thr phosphatases, and it is implicated in the negative control of cell growth and division. The ligand binding of this receptor leads to the activation of multiple downstream signaling molecules, including JAK1, JAK3, STAT1, and STAT3. PTPs are known to be signaling mole ...
Chapter 3 - Proteins
... determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or greatest order) when it is completely stretched out like a string and when it is properly folded up. Explain. • (True/False) Loops of polypeptide that protrude from the surfac ...
... determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or greatest order) when it is completely stretched out like a string and when it is properly folded up. Explain. • (True/False) Loops of polypeptide that protrude from the surfac ...
2.4 review
... Topic 2.4 Protein Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts ...
... Topic 2.4 Protein Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts ...
Most Proteins Don`t Exist!
... for determining the amino acid sequence (primary structure) of a protein. Knowing the amino acid sequence of a protein and its three dimensional structure allows us to understand how it works. I remember an apocryphal tale in which Perutz predicted how long it would be before an undergraduate degree ...
... for determining the amino acid sequence (primary structure) of a protein. Knowing the amino acid sequence of a protein and its three dimensional structure allows us to understand how it works. I remember an apocryphal tale in which Perutz predicted how long it would be before an undergraduate degree ...
Supplementary Information (doc 34K)
... Samples were lysed in 1ml 50mM Tris-HCL buffer (pH 7.0) (Oxoid) by sonication in ice bath. Cell lysis process were conducted by 10s of sonication with 10s rest for 15 times until the cell suspension was clear. Cell suspensions were then centrifuged at 16,000g for 25mins at 4 ºC. The supernatant (wit ...
... Samples were lysed in 1ml 50mM Tris-HCL buffer (pH 7.0) (Oxoid) by sonication in ice bath. Cell lysis process were conducted by 10s of sonication with 10s rest for 15 times until the cell suspension was clear. Cell suspensions were then centrifuged at 16,000g for 25mins at 4 ºC. The supernatant (wit ...
FCS-FS-8. Students will discuss why proteins are important in food
... dairy by incorporating air, mechanical agitation or by a sudden release in pressure (aerosol can) ...
... dairy by incorporating air, mechanical agitation or by a sudden release in pressure (aerosol can) ...
Kay Hofmann - Tresch Group
... Allows the detection of minor components Minor proteins are not overwhelmed by peptids from major components ...
... Allows the detection of minor components Minor proteins are not overwhelmed by peptids from major components ...
http://gslc. genetics. utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/
... http:// gslc. genetics. utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/ Defme the following terms: Transcription, Translation, Codon Complete the "Build a Protein" Activity You will need to record the sequence of bases in the mRNA as well as the sequence of amino acids on a separate piece of paper that I will col ...
... http:// gslc. genetics. utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/ Defme the following terms: Transcription, Translation, Codon Complete the "Build a Protein" Activity You will need to record the sequence of bases in the mRNA as well as the sequence of amino acids on a separate piece of paper that I will col ...
No Slide Title
... sequence but each has at least 8 nonpolar amino acids -The binding pocket is a large hydrophobic pocket lined by methionines -methionines can accommodate sequences of different size and shape ...
... sequence but each has at least 8 nonpolar amino acids -The binding pocket is a large hydrophobic pocket lined by methionines -methionines can accommodate sequences of different size and shape ...
Protein Structure
... • Speed up chemical reactions (Enzymes) • Transport things through the body (Hemoglobin) • Transport things through the cell membrane (Channel Proteins) • Defend the body against infections (Antibodies) • Growth, Maintenance, and Repair • Some Hormones (such as Insulin) ...
... • Speed up chemical reactions (Enzymes) • Transport things through the body (Hemoglobin) • Transport things through the cell membrane (Channel Proteins) • Defend the body against infections (Antibodies) • Growth, Maintenance, and Repair • Some Hormones (such as Insulin) ...
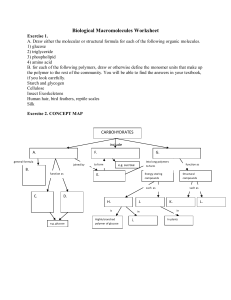
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... 1. What are the building block unit of proteins? How do these building blocks differ from each other? 2. List three structural differences and one functional difference between DNA and RNA. 3. The most abundant protein in your body is collagen which is a type of _________________ protein. 4. _______ ...
... 1. What are the building block unit of proteins? How do these building blocks differ from each other? 2. List three structural differences and one functional difference between DNA and RNA. 3. The most abundant protein in your body is collagen which is a type of _________________ protein. 4. _______ ...
BB 450/500 Lecture 5 Highlights
... 9. Porin is a membrane protein. Proteins embedded in membranes often have external amino acids that are hydrophobic so they can interact with the non-polar portions of membranes. Porin, in addition, has a hole in the center that allows water to pass through it. The amino acids in porin are arranged ...
... 9. Porin is a membrane protein. Proteins embedded in membranes often have external amino acids that are hydrophobic so they can interact with the non-polar portions of membranes. Porin, in addition, has a hole in the center that allows water to pass through it. The amino acids in porin are arranged ...
Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
... Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino acids, and proteins. DNA is a specific nucleic acid that directs protein making in all living things Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and ...
... Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino acids, and proteins. DNA is a specific nucleic acid that directs protein making in all living things Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and ...
Chemistry 100 Name
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
Worksheet 16
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
2. Intro to Proteins
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
In general, animal proteins are considered complete proteins. A complete... essential amino acids. Vegetable (plant-based) proteins are considered incomplete proteins...
... what protein sources you eat. A vegetarian can acquire the recommended amount of protein with a method known as complimentary protein, where you combine certain foods that will create a complete protein. For more information email: [email protected] ...
... what protein sources you eat. A vegetarian can acquire the recommended amount of protein with a method known as complimentary protein, where you combine certain foods that will create a complete protein. For more information email: [email protected] ...
Protein purification
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the characterization of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate.The methods used in protein purification can roughly be divided into analytical and preparative methods. The distinction is not exact, but the deciding factor is the amount of protein that can practically be purified with that method. Analytical methods aim to detect and identify a protein in a mixture, whereas preparative methods aim to produce large quantities of the protein for other purposes, such as structural biology or industrial use. In general, the preparative methods can be used in analytical applications, but not the other way around.