Cells are exposed to DNA damaging agents that can affect their
... do not have any symmetry, especially those of the so-called “molecular machines” where a collection of proteins interact to work in such various processes as DNA repair or RNA splicing. Also, some important molecules in the size range of 100 kDa are multi-domain proteins which are difficult to expre ...
... do not have any symmetry, especially those of the so-called “molecular machines” where a collection of proteins interact to work in such various processes as DNA repair or RNA splicing. Also, some important molecules in the size range of 100 kDa are multi-domain proteins which are difficult to expre ...
Cellular Chemical Reactions
... The four main types of large molecules are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. All of theses large molecules contain Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is that they cannot mix with water. Proteins are needed in the cell for ...
... The four main types of large molecules are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. All of theses large molecules contain Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is that they cannot mix with water. Proteins are needed in the cell for ...
Biochemistry- Ch 11. Carbohydrates
... cleaves the glycosidic bonds to the sialic acid residues, freeing the virus to infect the cell. Inhibitor of this enzyme are showing some promise as anti-influenza agents. ...
... cleaves the glycosidic bonds to the sialic acid residues, freeing the virus to infect the cell. Inhibitor of this enzyme are showing some promise as anti-influenza agents. ...
Molecules of life 2.4 - Madison County Schools
... 3. Tertiary Structure (3’ ) (“Tert” means “third”) a. A variety of bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen) between distant amino acids causes large folds in the protein. These help provide stability to the folded protein. 4. Quaternary Structure (4’ ) “Quarter” means “fourth” a. This is when two or more p ...
... 3. Tertiary Structure (3’ ) (“Tert” means “third”) a. A variety of bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen) between distant amino acids causes large folds in the protein. These help provide stability to the folded protein. 4. Quaternary Structure (4’ ) “Quarter” means “fourth” a. This is when two or more p ...
Class Notes 2
... Peptide units are joined by covalent bonds between Cα atoms. Thus – Peptides can rotate along 2 bonds: • N-Cα and Cα-C ...
... Peptide units are joined by covalent bonds between Cα atoms. Thus – Peptides can rotate along 2 bonds: • N-Cα and Cα-C ...
Protein Digestion
... blood albumin) is a specific sequence of 20 different amino acids. Each amino acid contains at least one atom of nitrogen. ...
... blood albumin) is a specific sequence of 20 different amino acids. Each amino acid contains at least one atom of nitrogen. ...
Bio 1000 Human Biology for Non-Majors
... 2. Develop a model that is consistent with what you have observed. 3. Use the model to make predictions (hypotheses). 4. Test those predictions by experiments or further observations. 5. Modify the theory in the light of your results. 6. Go to step 3. ...
... 2. Develop a model that is consistent with what you have observed. 3. Use the model to make predictions (hypotheses). 4. Test those predictions by experiments or further observations. 5. Modify the theory in the light of your results. 6. Go to step 3. ...
amino acids
... Amino acids • Structure – central carbon – amino group – carboxyl group (acid) – R group (side chain) ...
... Amino acids • Structure – central carbon – amino group – carboxyl group (acid) – R group (side chain) ...
Proteins
... Families of Proteins: different but related functions evolved from a single ancestral protein e.g. trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase (protein choppers) ...
... Families of Proteins: different but related functions evolved from a single ancestral protein e.g. trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase (protein choppers) ...
MolBioIntro
... The ability to move; plants turn toward light, sponges' collar cells' flagella turn round, fungi (exc. the little pot fungi, which have flagellate spores) and bacteria without locomotory apparatuses... huh. The ability to respire, turning nutrients into energy. For life on Earth, this process is gly ...
... The ability to move; plants turn toward light, sponges' collar cells' flagella turn round, fungi (exc. the little pot fungi, which have flagellate spores) and bacteria without locomotory apparatuses... huh. The ability to respire, turning nutrients into energy. For life on Earth, this process is gly ...
Protein Needs for Athletes
... • Animal-derived proteins (milk, eggs, meat and fish) are high quality because they have all of the essential amino acids (EAAs), which are building blocks for proteins in our body. • Some plant-based proteins (soy, quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat) contain all EAAs while most plant-bas ...
... • Animal-derived proteins (milk, eggs, meat and fish) are high quality because they have all of the essential amino acids (EAAs), which are building blocks for proteins in our body. • Some plant-based proteins (soy, quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat) contain all EAAs while most plant-bas ...
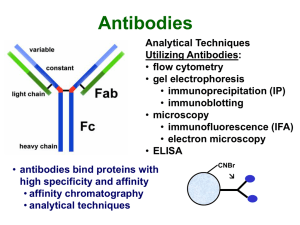
Typical IP Protocol
... isolation of Ag-Ab complexes • analyze by gel electrophoresis • initially based on centrifugation of large supramolecular complexes • [high] and equal amounts • isolation of Ag-Ab complexes • fixed S. aureus • protein A-agarose • protein G-agarose ...
... isolation of Ag-Ab complexes • analyze by gel electrophoresis • initially based on centrifugation of large supramolecular complexes • [high] and equal amounts • isolation of Ag-Ab complexes • fixed S. aureus • protein A-agarose • protein G-agarose ...
protein folding
... each other. Conversely, similarly charged side chains repel each other. In addition, interactions involving hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds all exert an influence on the folding process. This process of trial and error tests many, but not all, possible configurations, s ...
... each other. Conversely, similarly charged side chains repel each other. In addition, interactions involving hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds all exert an influence on the folding process. This process of trial and error tests many, but not all, possible configurations, s ...
Organic Compounds - Ms. Nevel's Biology Website
... electrons, allowing carbon to form covalent bonds with many elements including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen. ...
... electrons, allowing carbon to form covalent bonds with many elements including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen. ...
Fast Categorization of Bacteriophage Protein Families using
... SAM (Sequence Alignment and Modeling) tells us that sequences are related, but there are times when the program is incorrect, and just by looking at a picture, we can tell it’s wrong, or vice versa. Therefore, we need a program to let a Human make the comparison on whether certain proteins are h ...
... SAM (Sequence Alignment and Modeling) tells us that sequences are related, but there are times when the program is incorrect, and just by looking at a picture, we can tell it’s wrong, or vice versa. Therefore, we need a program to let a Human make the comparison on whether certain proteins are h ...
Document
... Carbon compounds A. Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms B. Chemistry of carbon – because of its 4 valence e- , carbon will form 4 strong polar covalent bonds in a wide variety of ways C. Macromolecules 1. polymers: made of 100s-1000s of smaller mol ...
... Carbon compounds A. Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms B. Chemistry of carbon – because of its 4 valence e- , carbon will form 4 strong polar covalent bonds in a wide variety of ways C. Macromolecules 1. polymers: made of 100s-1000s of smaller mol ...
02 Chemistry b - Crestwood Local Schools
... Macromolecules composed of combinations of 20 types of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds ...
... Macromolecules composed of combinations of 20 types of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds ...
Protein-Surface Interactions
... elastin—elasticity to ligaments; adhesion proteins: fibronectin, laminin, vitronectin—glycoproteins that mediate cell attachment (bonded to GAGs) • Enzymes: catalyze rxns by lowering Ea thru stabilized transition state, via release of binding energy e.g., urease—catalyzes hydrolysis of urea ...
... elastin—elasticity to ligaments; adhesion proteins: fibronectin, laminin, vitronectin—glycoproteins that mediate cell attachment (bonded to GAGs) • Enzymes: catalyze rxns by lowering Ea thru stabilized transition state, via release of binding energy e.g., urease—catalyzes hydrolysis of urea ...
Nucleic Acid Notes
... Folding occurs as protein is synthesized, but physical/chemical environment plays a role DENATURATION: = unraveling/ loss of native confirmation • makes proteins biologically inactive ~ Reason high fevers can be fatal • • does NOT break peptide bonds • so primary structure remains intact • may regai ...
... Folding occurs as protein is synthesized, but physical/chemical environment plays a role DENATURATION: = unraveling/ loss of native confirmation • makes proteins biologically inactive ~ Reason high fevers can be fatal • • does NOT break peptide bonds • so primary structure remains intact • may regai ...
Amino acid sequence fingerprints in divergent evolution of
... e-mail: [email protected] Proteins may basically be related by divergent or convergent evolution. In divergent evolution, i.e. the evolution from a common ancestor, there is only a small percentage of residues in the amino acid sequence of a protein, that have to be conserved in order the prot ...
... e-mail: [email protected] Proteins may basically be related by divergent or convergent evolution. In divergent evolution, i.e. the evolution from a common ancestor, there is only a small percentage of residues in the amino acid sequence of a protein, that have to be conserved in order the prot ...
Lect21.RegulProtTurnover
... Cellular proteins have different stabilities. It is the combination of synthesis and degradation rates that determines the level of a protein in a cell, and changes in either rate can serve as means to regulate a protein’s concentration in the cell. ...
... Cellular proteins have different stabilities. It is the combination of synthesis and degradation rates that determines the level of a protein in a cell, and changes in either rate can serve as means to regulate a protein’s concentration in the cell. ...
Cyclol

The cyclol hypothesis is the first structural model of a folded, globular protein. It was developed by Dorothy Wrinch in the late 1930s, and was based on three assumptions. Firstly, the hypothesis assumes that two peptide groups can be crosslinked by a cyclol reaction (Figure 1); these crosslinks are covalent analogs of non-covalent hydrogen bonds between peptide groups. These reactions have been observed in the ergopeptides and other compounds. Secondly, it assumes that, under some conditions, amino acids will naturally make the maximum possible number of cyclol crosslinks, resulting in cyclol molecules (Figure 2) and cyclol fabrics (Figure 3). These cyclol molecules and fabrics have never been observed. Finally, the hypothesis assumes that globular proteins have a tertiary structure corresponding to Platonic solids and semiregular polyhedra formed of cyclol fabrics with no free edges. Such ""closed cyclol"" molecules have not been observed either.Although later data demonstrated that this original model for the structure of globular proteins needed to be amended, several elements of the cyclol model were verified, such as the cyclol reaction itself and the hypothesis that hydrophobic interactions are chiefly responsible for protein folding. The cyclol hypothesis stimulated many scientists to research questions in protein structure and chemistry, and was a precursor of the more accurate models hypothesized for the DNA double helix and protein secondary structure. The proposal and testing of the cyclol model also provides an excellent illustration of empirical falsifiability acting as part of the scientific method.