CT Scan Parameters and Radiation Dose
... radiation dose imparted during an examination. As a general rule of thumb, the radiation dose changes with the square of kVp, and a reduction in kVp from 120 to 100 reduces radiation dose by 33%, while a further reduction to 80 kVp can reduce dose by 65% [12,13]. As a further advantage, particularly ...
... radiation dose imparted during an examination. As a general rule of thumb, the radiation dose changes with the square of kVp, and a reduction in kVp from 120 to 100 reduces radiation dose by 33%, while a further reduction to 80 kVp can reduce dose by 65% [12,13]. As a further advantage, particularly ...
Origin, Characteristics, and Entry of Radon Gas Characteristics: Entry:
... There are natural and manmade conditions that affect the amount of radon gas (Radon-222) entering a structure. • Pathways – soil porosity and type along with cracks, holes, and other openings in foundation materials provide an easier path for radon to enter. Radon gas entry is 15 times greater at pe ...
... There are natural and manmade conditions that affect the amount of radon gas (Radon-222) entering a structure. • Pathways – soil porosity and type along with cracks, holes, and other openings in foundation materials provide an easier path for radon to enter. Radon gas entry is 15 times greater at pe ...
Total Body/Total Skin Irradiation
... imaging doses often unaccounted for Current site-specific scan protocols offered by the manufacturers provide certain dose reduction, but are essentially non-personalized and non-differentiable with no consideration of individual patient being scanned So far, no tool available to help clinicians ...
... imaging doses often unaccounted for Current site-specific scan protocols offered by the manufacturers provide certain dose reduction, but are essentially non-personalized and non-differentiable with no consideration of individual patient being scanned So far, no tool available to help clinicians ...
Chapter 11
... Photons can be absorbed by the patient’s body part’s Photons could pass right thru the patient’s body and enter the film, putting density on the film. These photons are called exit radiation or remnant radiation Photons could hit something in the patient’s body, bounce off, and fly out in a ne ...
... Photons can be absorbed by the patient’s body part’s Photons could pass right thru the patient’s body and enter the film, putting density on the film. These photons are called exit radiation or remnant radiation Photons could hit something in the patient’s body, bounce off, and fly out in a ne ...
Full Text - RSNA Publications Online
... transferred to charged particles from ionizing photon radiation. The unit of kerma is the gray (formerly, rad; 1 Gy = 100 rad), and 1 Gy of kerma is equivalent to 1 J of energy transferred to charged particles per kilogram of irradiated medium. For air, 1 Gy of kerma is equivalent to 115 R of exposu ...
... transferred to charged particles from ionizing photon radiation. The unit of kerma is the gray (formerly, rad; 1 Gy = 100 rad), and 1 Gy of kerma is equivalent to 1 J of energy transferred to charged particles per kilogram of irradiated medium. For air, 1 Gy of kerma is equivalent to 115 R of exposu ...
Radiation Protection and Dose Monitoring in Medical
... small but statistically significant increase in risk of cancer (42); doses between 50-100 mSv are much debated (the effective dose from a single CT can range from less than 1.0 mSv to more than 30 mSv, although most provide between 2-20 mSv). While there is little direct evidence for a link to cance ...
... small but statistically significant increase in risk of cancer (42); doses between 50-100 mSv are much debated (the effective dose from a single CT can range from less than 1.0 mSv to more than 30 mSv, although most provide between 2-20 mSv). While there is little direct evidence for a link to cance ...
Date approved or revised
... M. Gross Exposure Error (e.g., mottle, light or dark, low contrast) ...
... M. Gross Exposure Error (e.g., mottle, light or dark, low contrast) ...
CMPI Exam Format - College of Medical Physics, India
... 6.2 The candidates desiring to take only the written examination will have to pay Rs 2000 /- only, however such candidates will have to pay Rs 3000 /- as oral examination fee while appearing for the oral examination. Candidates can pay the fees in total or in parts as given above. 6.3 Reappearance i ...
... 6.2 The candidates desiring to take only the written examination will have to pay Rs 2000 /- only, however such candidates will have to pay Rs 3000 /- as oral examination fee while appearing for the oral examination. Candidates can pay the fees in total or in parts as given above. 6.3 Reappearance i ...
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF THE RUSSIAN
... individual features of the structure of a healthy body, as well as changes in various diseases of organs. To be able to: independently identify the image of all human organs and indicate their main anatomical structures on radiographs, angiograms, computer x-ray and an MRI, Ultrasound, postglacial. ...
... individual features of the structure of a healthy body, as well as changes in various diseases of organs. To be able to: independently identify the image of all human organs and indicate their main anatomical structures on radiographs, angiograms, computer x-ray and an MRI, Ultrasound, postglacial. ...
ACR–ASTRO Practice Parameter for the Performance of Stereotactic
... Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is an external beam radiation therapy method that very precisely delivers a high dose of radiation to an extracranial target. SBRT is typically a complete course of therapy delivered in 1 to 5 sessions (fractions). Specialized treatment planning results in ...
... Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is an external beam radiation therapy method that very precisely delivers a high dose of radiation to an extracranial target. SBRT is typically a complete course of therapy delivered in 1 to 5 sessions (fractions). Specialized treatment planning results in ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ______ Page#: ____ X
... the arrangement of atoms in crystals. Archeologists sometimes use x-rays to examine an ancient object that might be damaged by attempts to remove its covering material. X-rays can also be used to cause ...
... the arrangement of atoms in crystals. Archeologists sometimes use x-rays to examine an ancient object that might be damaged by attempts to remove its covering material. X-rays can also be used to cause ...
Why Quantitative I-131
... complete dosimetry to protect critical organs. Patient Preparation: This exam should not be performed if the patient has had any iodine medications which will interfere with the study or any iodinated contrast media within the last 6 weeks. TSH level should be evaluated prior to radiopharmaceutical ...
... complete dosimetry to protect critical organs. Patient Preparation: This exam should not be performed if the patient has had any iodine medications which will interfere with the study or any iodinated contrast media within the last 6 weeks. TSH level should be evaluated prior to radiopharmaceutical ...
BasisandPurposeAttachment2009-00806
... 1. The title of the Part is modified by deleting the word “Diagnostic”. Part 6 contains provisions that apply broadly across uses of x-rays and imaging in the healing arts. New equipment has weakened the distinction between diagnostic, therapeutic and combined human uses of x-rays. Not included from ...
... 1. The title of the Part is modified by deleting the word “Diagnostic”. Part 6 contains provisions that apply broadly across uses of x-rays and imaging in the healing arts. New equipment has weakened the distinction between diagnostic, therapeutic and combined human uses of x-rays. Not included from ...
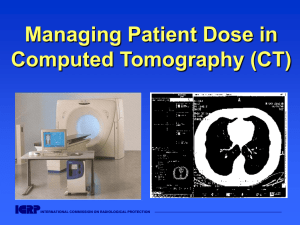
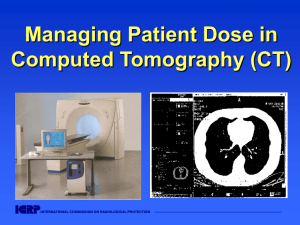
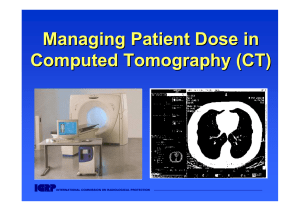
Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT)
... INTERNATIONAL COMMISSION ON RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION ...
... INTERNATIONAL COMMISSION ON RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION ...
image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT)
... structures. This is the case for tumors in the immediate vicinity of the spinal cord, brain stem, optic nerve, or parotid gland, especially if dose escalation is desired or particular attention has to be paid to organ sparing in the case of reirradiation. Moreover, IGRT is advantageous in the treatm ...
... structures. This is the case for tumors in the immediate vicinity of the spinal cord, brain stem, optic nerve, or parotid gland, especially if dose escalation is desired or particular attention has to be paid to organ sparing in the case of reirradiation. Moreover, IGRT is advantageous in the treatm ...
ACR Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Reference Levels in Medical
... an investigation level to identify unusually high radiation doses or exposure levels for common diagnostic medical X-ray imaging procedures [1-3]. Reference levels are based on actual patient doses for specific procedures measured at a number of representative clinical facilities. The levels are set ...
... an investigation level to identify unusually high radiation doses or exposure levels for common diagnostic medical X-ray imaging procedures [1-3]. Reference levels are based on actual patient doses for specific procedures measured at a number of representative clinical facilities. The levels are set ...
190047_190047 - espace@Curtin
... to assess CT utilisation and dosimetry in Australia was a survey in 1996 of all CT facilities conducted by the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA), formerly the Australian Radiation Laboratory10. This study found Australia had the second highest provision of CT scanne ...
... to assess CT utilisation and dosimetry in Australia was a survey in 1996 of all CT facilities conducted by the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA), formerly the Australian Radiation Laboratory10. This study found Australia had the second highest provision of CT scanne ...
Chest X-rays - American Heart Association
... film. An X-ray machine will be turned on for a fraction of a second. During this time, a small beam of X-rays passes through the chest and makes an image on special photographic film. Sometimes two pictures are taken — a front and side view. The X-ray film takes about 10 minutes to develop. Sometime ...
... film. An X-ray machine will be turned on for a fraction of a second. During this time, a small beam of X-rays passes through the chest and makes an image on special photographic film. Sometimes two pictures are taken — a front and side view. The X-ray film takes about 10 minutes to develop. Sometime ...
Understanding Radiation Units
... Radiation Quantities and Units Equivalent dose (Unit = sievert, Sv ) – Compares the biological effects for different types of radiation, X-rays, Ɣrays, electrons, neutrons, protons, αparticles etc. – For X-rays, Ɣ-rays, electrons : absorbed dose and equivalent dose have the ...
... Radiation Quantities and Units Equivalent dose (Unit = sievert, Sv ) – Compares the biological effects for different types of radiation, X-rays, Ɣrays, electrons, neutrons, protons, αparticles etc. – For X-rays, Ɣ-rays, electrons : absorbed dose and equivalent dose have the ...
Pause and Pulse: Ten Steps That Help Manage Radiation Dose
... guidelines continue to be updated and now include guidelines in the performance of fluoroscopic examinations, including the upper gastrointestinal tract, small-bowel series, contrast enema, and VCUG in pediatric patients. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education and the Radiology Rev ...
... guidelines continue to be updated and now include guidelines in the performance of fluoroscopic examinations, including the upper gastrointestinal tract, small-bowel series, contrast enema, and VCUG in pediatric patients. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education and the Radiology Rev ...
Full Text - Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology
... ver the past decade there has been an increase in scrutiny pertaining to radiation dose associated with medical procedures from both professional societies and the lay press. In 2006, a total of 4 million interventional procedures performed in the United States accounted for approximately 14% of the ...
... ver the past decade there has been an increase in scrutiny pertaining to radiation dose associated with medical procedures from both professional societies and the lay press. In 2006, a total of 4 million interventional procedures performed in the United States accounted for approximately 14% of the ...
Cardiovascular Computed Tomography: Current and Future
... scan, and only turning it on during diastasis, as triggered by the ECG, radiation exposure is dramatically reduced (Figure 2.7). GE first published results using this method [12] with good clinical results and radiation doses of 1–2 mSv, [13] and this approach is now offered by all manufacturers. Us ...
... scan, and only turning it on during diastasis, as triggered by the ECG, radiation exposure is dramatically reduced (Figure 2.7). GE first published results using this method [12] with good clinical results and radiation doses of 1–2 mSv, [13] and this approach is now offered by all manufacturers. Us ...
Between-dataset difference in climate variables Between
... Figure 3 shows overall comparison of two datasets. • The most pronounced differences are seen in the highest elevation band (e.g., Precipitation, humidity, SW radiation) • The variable that exhibit the most difference is SW (i.e., SW in NLDA is much lower than VIC SW radiation). ...
... Figure 3 shows overall comparison of two datasets. • The most pronounced differences are seen in the highest elevation band (e.g., Precipitation, humidity, SW radiation) • The variable that exhibit the most difference is SW (i.e., SW in NLDA is much lower than VIC SW radiation). ...
Radiation burn

A radiation burn is damage to the skin or other biological tissue caused by exposure to radiation. The radiation types of greatest concern are thermal radiation, radio frequency energy, ultraviolet light and ionizing radiation.The most common type of radiation burn is a sunburn caused by UV radiation. High exposure to X-rays during diagnostic medical imaging or radiotherapy can also result in radiation burns. As the ionizing radiation interacts with cells within the body—damaging them—the body responds to this damage, typically resulting in erythema—that is, redness around the damaged area. Radiation burns are often associated with radiation-induced cancer due to the ability of ionizing radiation to interact with and damage DNA, occasionally inducing a cell to become cancerous. Cavity magnetrons can be improperly used to create surface and internal burning. Depending on the photon energy, gamma radiation can cause very deep gamma burns, with 60Co internal burns are common. Beta burns tend to be shallow as beta particles are not able to penetrate deep into the person; these burns can be similar to sunburn.Radiation burns can also occur with high power radio transmitters at any frequency where the body absorbs radio frequency energy and converts it to heat. The U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) considers 50 watts to be the lowest power above which radio stations must evaluate emission safety. Frequencies considered especially dangerous occur where the human body can become resonant, at 35 MHz, 70 MHz, 80-100 MHz, 400 MHz, and 1 GHz. Exposure to microwaves of too high intensity can cause microwave burns.