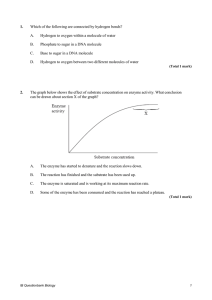
Fundamentals of Biochemistry
... energy changes associated with various glycolytic steps are largely concerned with G! - Of the 10 steps of glycolysis, only three (Steps 1/3/10) operate far from equilibrium ( G << 0)—implying that they COULD be largely responsible for flux control! ...
... energy changes associated with various glycolytic steps are largely concerned with G! - Of the 10 steps of glycolysis, only three (Steps 1/3/10) operate far from equilibrium ( G << 0)—implying that they COULD be largely responsible for flux control! ...
Regulation of Acetyl-Coenzyme A Carboxylase and
... Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase, A cetyl-CoA Synthetase, Light D ependence o f Fatty Acid Synthesis in Chloroplasts In analogy to chloroplast fatty acid synthesis from acetate the key enzym es o f acetate fixation, acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in rapidly Triton X-100 lysed spinach chloro ...
... Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase, A cetyl-CoA Synthetase, Light D ependence o f Fatty Acid Synthesis in Chloroplasts In analogy to chloroplast fatty acid synthesis from acetate the key enzym es o f acetate fixation, acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in rapidly Triton X-100 lysed spinach chloro ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY - Illinois State University
... • The brain relies almost solely on glucose for energy needs • The liver participates in the interconversions of all types of metabolic fuels: carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids • Products of digestion pass immediately to the liver for metabolism or redistribution • The liver regulates distr ...
... • The brain relies almost solely on glucose for energy needs • The liver participates in the interconversions of all types of metabolic fuels: carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids • Products of digestion pass immediately to the liver for metabolism or redistribution • The liver regulates distr ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Glycogen
... • A reducing sugar has an anomeric C that has NOT formed a glycosidic bond, such that it can reduce oxidizing agents. Recall what an anomeric C is! ...
... • A reducing sugar has an anomeric C that has NOT formed a glycosidic bond, such that it can reduce oxidizing agents. Recall what an anomeric C is! ...
Electron transfer from aromatic amino acids to guanine and adenine
... of the hole due to its chemical reaction with water, oxygen and other species is relatively slow,11,12 the hole migrates within DNA using G and A nucleobases as stepping stones.38 In protein–DNA complexes, an amino acid residues X that has a lower oxidation potential than G and A, can act as electro ...
... of the hole due to its chemical reaction with water, oxygen and other species is relatively slow,11,12 the hole migrates within DNA using G and A nucleobases as stepping stones.38 In protein–DNA complexes, an amino acid residues X that has a lower oxidation potential than G and A, can act as electro ...
Cholesterol
... LYSOLECITHIN + CHOLESTEROL ESTER • LCAT is activated by apo-A1 and deficiency in LCAT means that HDL can’t take ...
... LYSOLECITHIN + CHOLESTEROL ESTER • LCAT is activated by apo-A1 and deficiency in LCAT means that HDL can’t take ...
Comparative genomic analysis of carbon and nitrogen assimilation
... Results: In this study, we probed that both Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans incorporate CO2 via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle; however, the former bacterium has two copies of the Rubisco type I gene whereas the latter has only one copy. In contrast, we demonstrated ...
... Results: In this study, we probed that both Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans incorporate CO2 via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle; however, the former bacterium has two copies of the Rubisco type I gene whereas the latter has only one copy. In contrast, we demonstrated ...
The Use of Botanical Extracts as Topical Skin
... species, such as bearberry. The mode of action appears to be by inhibition of melanosomal tyrosinase and DHICA (5,6dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid) polymerase activities at noncytotoxic concentrations rather than by suppression of the synthesis and expression of this enzyme (Maeda and Fukuda, 1996 ...
... species, such as bearberry. The mode of action appears to be by inhibition of melanosomal tyrosinase and DHICA (5,6dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid) polymerase activities at noncytotoxic concentrations rather than by suppression of the synthesis and expression of this enzyme (Maeda and Fukuda, 1996 ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein Multiple-Choice Questions
... 7) Using RNA as a template for protein synthesis instead of translating proteins directly from the DNA is advantageous for the cell because A) RNA is much more stable than DNA. B) RNA acts as an expendable copy of the genetic material. C) only one mRNA molecule can be transcribed from a single gene, ...
... 7) Using RNA as a template for protein synthesis instead of translating proteins directly from the DNA is advantageous for the cell because A) RNA is much more stable than DNA. B) RNA acts as an expendable copy of the genetic material. C) only one mRNA molecule can be transcribed from a single gene, ...
Biomarkery a mechanismy toxicity
... organics) = nonpolar narcotic toxicity (membrane toxicity) (effects at relatively high concentrations, depends on Kow) 2) Besides the nonpolar narcosis, more polar compounds may affect also „nonspecifically“ affect membrane proteins (polar narcosis) (effects at lower concentrations than expected fro ...
... organics) = nonpolar narcotic toxicity (membrane toxicity) (effects at relatively high concentrations, depends on Kow) 2) Besides the nonpolar narcosis, more polar compounds may affect also „nonspecifically“ affect membrane proteins (polar narcosis) (effects at lower concentrations than expected fro ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... ACP condensing enzyme. The decarboxylation of malonyl ACP generates an enolate anion which is a good nucleophile that attacks the carbonyl of thioester of acetyl-S-KSase to form acetoacetyl ACP. The exergonic decarboxylation reaction drives the condensation reaction. The CO2 group added to acetyl Co ...
... ACP condensing enzyme. The decarboxylation of malonyl ACP generates an enolate anion which is a good nucleophile that attacks the carbonyl of thioester of acetyl-S-KSase to form acetoacetyl ACP. The exergonic decarboxylation reaction drives the condensation reaction. The CO2 group added to acetyl Co ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... therefore, these enzymes account for about 30% of the world’s enzyme production [7]. The major three classes of amylase have been identified in many microorganisms, namely a- amylase, β- amylases and glucoamylases [17]. All these enzymes are belongs to Glycosides hydrolases, although some a amylase ...
... therefore, these enzymes account for about 30% of the world’s enzyme production [7]. The major three classes of amylase have been identified in many microorganisms, namely a- amylase, β- amylases and glucoamylases [17]. All these enzymes are belongs to Glycosides hydrolases, although some a amylase ...
Patterns of prokaryotic lateral gene transfers affecting
... ’TMDs ≥ 4’ or ‘TMDs 1-3’ refers to the number of TMDs predicted on protein sequences. Transporters typically have at least four TMDs (TMDs ≥ 4). Proteins with one to three TMDs represent putative membrane proteins. d EC numbers were annotated for each entry based on a significant sequence similarity ...
... ’TMDs ≥ 4’ or ‘TMDs 1-3’ refers to the number of TMDs predicted on protein sequences. Transporters typically have at least four TMDs (TMDs ≥ 4). Proteins with one to three TMDs represent putative membrane proteins. d EC numbers were annotated for each entry based on a significant sequence similarity ...
magamtol talalt cikkek
... The sequences of two Drosophila and one rabbit protein phosphatase (PP) 1 catalytic subunits were determined from their cDNA. The sequence of Drosophila PP1 alpha 1 was deduced from a 2.2-kb cDNA purified from an embryonic cDNA library, while that for Drosophila PP1 beta was obtained from overlappin ...
... The sequences of two Drosophila and one rabbit protein phosphatase (PP) 1 catalytic subunits were determined from their cDNA. The sequence of Drosophila PP1 alpha 1 was deduced from a 2.2-kb cDNA purified from an embryonic cDNA library, while that for Drosophila PP1 beta was obtained from overlappin ...
Proteolytic Degradation of Hemoglobin in the Intestine of the Human
... cooperative cascades. We investigated the roles played by 3 distinct proteases from adults of the human hookworm Necator americanus. The aspartic protease Na-APR-1 and the cysteine protease Na-CP-3 were expressed in catalytically active form in yeast, and the metalloprotease Na-MEP-1 was expressed i ...
... cooperative cascades. We investigated the roles played by 3 distinct proteases from adults of the human hookworm Necator americanus. The aspartic protease Na-APR-1 and the cysteine protease Na-CP-3 were expressed in catalytically active form in yeast, and the metalloprotease Na-MEP-1 was expressed i ...
Molecular and Structural Characterization of
... (Niemeyer, 1988). These compounds are thought to be stored in intact plants as glucosides within a different subcellular compartment from the glucosidase. Although the wheat and rye glucosidases hydrolyze DIBOA-Glc and DIMBOA-Glc, the preferred natural substrate for each enzyme is consistent with th ...
... (Niemeyer, 1988). These compounds are thought to be stored in intact plants as glucosides within a different subcellular compartment from the glucosidase. Although the wheat and rye glucosidases hydrolyze DIBOA-Glc and DIMBOA-Glc, the preferred natural substrate for each enzyme is consistent with th ...
Identification and characterization of the ergochrome gene cluster in
... The yellow ergochromes are dimers of tetrahydroxanthone units [7]. Four different xanthone derivatives were described as ergochrome units in C. purpurea and all possible combinations of two of these units occur in nature [8]. Their concentration in the sclerotia is considerably higher (5 g/kg) than ...
... The yellow ergochromes are dimers of tetrahydroxanthone units [7]. Four different xanthone derivatives were described as ergochrome units in C. purpurea and all possible combinations of two of these units occur in nature [8]. Their concentration in the sclerotia is considerably higher (5 g/kg) than ...
Invariant amino acids essential for decoding function of polypeptide
... one aromatic amino acid is exchanged with another one. Here, the decrease of the RF activity is highly selective: no change in response to UAA and UGA but a 3-fold loss of function toward UAG. Clearly, this selective inactivation is not due to damage of binding to the ribosome: two other activities ...
... one aromatic amino acid is exchanged with another one. Here, the decrease of the RF activity is highly selective: no change in response to UAA and UGA but a 3-fold loss of function toward UAG. Clearly, this selective inactivation is not due to damage of binding to the ribosome: two other activities ...
and Functions of y-Aminobutyric Acid
... GABA is a four-C, nonprotein amino acid found in virtually all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms as a significant component of the free amino acid pool. In higher plants GABA is synthesized primarily through the H+consuming a-decarboxylation of L-glutamate (L-Glu) in a reaction (L-Glu + H + -+ GA ...
... GABA is a four-C, nonprotein amino acid found in virtually all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms as a significant component of the free amino acid pool. In higher plants GABA is synthesized primarily through the H+consuming a-decarboxylation of L-glutamate (L-Glu) in a reaction (L-Glu + H + -+ GA ...
PDF - Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
... even sophisticated computer programs cannot reliably predict the impact of mutations (Potapov et al. 2009). Methods have been developed to infer site-specific selection from naturally occurring sequences (Rodrigue et al. 2010; Tamuri et al. 2012, 2014). Because the number of possible mutations is la ...
... even sophisticated computer programs cannot reliably predict the impact of mutations (Potapov et al. 2009). Methods have been developed to infer site-specific selection from naturally occurring sequences (Rodrigue et al. 2010; Tamuri et al. 2012, 2014). Because the number of possible mutations is la ...