Mutations Practice
... is single stranded (one half of the ladder). At the ribosome, another type of RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the growing amino acid chain at the ribosome. BUT, sometimes there are problems with the DNA molecule that result in a change ...
... is single stranded (one half of the ladder). At the ribosome, another type of RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the growing amino acid chain at the ribosome. BUT, sometimes there are problems with the DNA molecule that result in a change ...
pyruvate
... Protein → Ala + aa aa→ NH4+ + α keto acids α keto acids → Ala (“simplest” aa). ThereforeSources total Ala released > Ala derived from proteins of Alanine (from Muscle) (ii) Liver: Ala → NH4+ + α keto acids NH4+ → urea (iii) As well Glucose → Pyruvate (no N) → Ala (with N) Therefore Ala serves as a v ...
... Protein → Ala + aa aa→ NH4+ + α keto acids α keto acids → Ala (“simplest” aa). ThereforeSources total Ala released > Ala derived from proteins of Alanine (from Muscle) (ii) Liver: Ala → NH4+ + α keto acids NH4+ → urea (iii) As well Glucose → Pyruvate (no N) → Ala (with N) Therefore Ala serves as a v ...
amino acids properties
... compound abbreviated as DOPA (dihydroxy-phenylalanine) . It acts as a neurotransmitter, i.e., trasnmission of impulses in the nervous system, Tryptophan is the precursor of a vitamin named nicotinic acid (B3). 3-As Source of Sulphur. Derived from the sulfur containing amino acids. 4- Amino acids are ...
... compound abbreviated as DOPA (dihydroxy-phenylalanine) . It acts as a neurotransmitter, i.e., trasnmission of impulses in the nervous system, Tryptophan is the precursor of a vitamin named nicotinic acid (B3). 3-As Source of Sulphur. Derived from the sulfur containing amino acids. 4- Amino acids are ...
Ch7METABOLISM
... we eat or “refuel” to supply this energy. If we are starving or fasting, the body must use fuel reserves from its own tissues Glycogen is used first, along with some fat breakdown. Glycogen is exhausted within several hours. Low blood glucose serves as a signal to promote further fat breakdown ...
... we eat or “refuel” to supply this energy. If we are starving or fasting, the body must use fuel reserves from its own tissues Glycogen is used first, along with some fat breakdown. Glycogen is exhausted within several hours. Low blood glucose serves as a signal to promote further fat breakdown ...
長榮管理學院九十學年度二年制技術學系招生考試
... 9. Which of the following most accurately describes the charge state of DNA under physiological conditions? a. Roughly uniformly positively charged along its length b. Roughly uniformly negatively charged along its length c. Roughly uniformly uncharged along its length d. Heterogeneously charged, wi ...
... 9. Which of the following most accurately describes the charge state of DNA under physiological conditions? a. Roughly uniformly positively charged along its length b. Roughly uniformly negatively charged along its length c. Roughly uniformly uncharged along its length d. Heterogeneously charged, wi ...
Glycolysis - Centre College
... Why is ATP "high energy"? • Charge repulsion of phosphates • Increase in entropy (number of molecules increases) • Resonance stabilization of product ...
... Why is ATP "high energy"? • Charge repulsion of phosphates • Increase in entropy (number of molecules increases) • Resonance stabilization of product ...
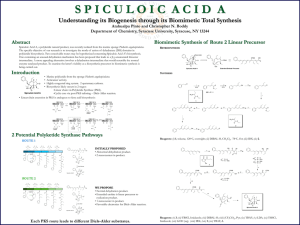
Total Synthesis of Spiculoic Acid A
... • Linear chain extension in PKS is analogous to fatty acid biosynthesis: ...
... • Linear chain extension in PKS is analogous to fatty acid biosynthesis: ...
УДК: 547
... Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno, Grodno State Medical University, Belarus To date, there are three main levels of exploitation of biochemical (metabolic) properties of amino acids and their derivatives in clinical practice: I. the use of amino acids or multi-component mixtures of amino acids ...
... Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno, Grodno State Medical University, Belarus To date, there are three main levels of exploitation of biochemical (metabolic) properties of amino acids and their derivatives in clinical practice: I. the use of amino acids or multi-component mixtures of amino acids ...
charged
... The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA and finally translated into the sequence of proteins. The genetic unit coding for one single amino acid is a codon. One gene codes for one proteins, one cistron for one polypeptide chain. As many proteins consist of only one polypeptide chain, m ...
... The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA and finally translated into the sequence of proteins. The genetic unit coding for one single amino acid is a codon. One gene codes for one proteins, one cistron for one polypeptide chain. As many proteins consist of only one polypeptide chain, m ...
Aromatic amino acid metabolism
... Biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids starts with a common pathway, the Shikimate pathway. The biosynthesis begins with Phosphoenolpyruvate and Erythrose-4- phosphate to form Shikimate. Shikimate then goes on to form the branch point intermediate Chorismate. Chorismate can be converted into a ...
... Biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids starts with a common pathway, the Shikimate pathway. The biosynthesis begins with Phosphoenolpyruvate and Erythrose-4- phosphate to form Shikimate. Shikimate then goes on to form the branch point intermediate Chorismate. Chorismate can be converted into a ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II State whether the following statements are True or False ...
... II State whether the following statements are True or False ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... the cytoplasm • Ribosome binds to mRNA and tRNA brings in amino acids which bond together to form a protein. • Codon and anticodon must be complementary ...
... the cytoplasm • Ribosome binds to mRNA and tRNA brings in amino acids which bond together to form a protein. • Codon and anticodon must be complementary ...
Study Guide for Understanding the Concept of Protein Synthesis
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a "taxi" by which the "escort" ribosomes take the amino acids and position them into place as Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Step #5: Ribosomes: From the rRNA, the amino acids continue their journey within the cytoplasm, resting on "floating" ribosomes or on the Rough ER. These ri ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a "taxi" by which the "escort" ribosomes take the amino acids and position them into place as Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Step #5: Ribosomes: From the rRNA, the amino acids continue their journey within the cytoplasm, resting on "floating" ribosomes or on the Rough ER. These ri ...
Bio Chap 2 Biomolecules
... The levels of protein structure • Primary – chains of amino acids • Secondary – folds • Tertiary – compacting • Quaternary – two or more chains ...
... The levels of protein structure • Primary – chains of amino acids • Secondary – folds • Tertiary – compacting • Quaternary – two or more chains ...
Chapter 3 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... Monosaccharides – single sugar that is simple, containing as few as three carbon atoms, but when they play a central role in energy storage, they contain six carbons C6H12O6 is not only the chemical formula for glucose, but for both structural isomers and stereoisomers Disaccharides (two linked mono ...
... Monosaccharides – single sugar that is simple, containing as few as three carbon atoms, but when they play a central role in energy storage, they contain six carbons C6H12O6 is not only the chemical formula for glucose, but for both structural isomers and stereoisomers Disaccharides (two linked mono ...
Proteins - Chavis Biology
... b. There are _______commonly occurring amino acids that are found in proteins c. ____________________________________________ are those that must be ingested in the diet. 3. __________________________join amino acids a. It’s a condensation reaction (meaning that _____________________________________ ...
... b. There are _______commonly occurring amino acids that are found in proteins c. ____________________________________________ are those that must be ingested in the diet. 3. __________________________join amino acids a. It’s a condensation reaction (meaning that _____________________________________ ...